Maximilian Samsinger
Pruning in the Face of Adversaries
Aug 19, 2021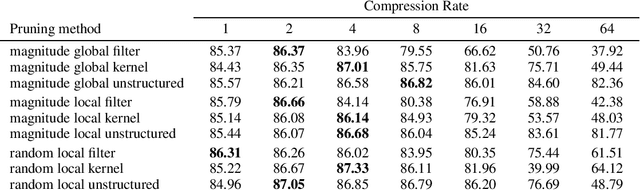
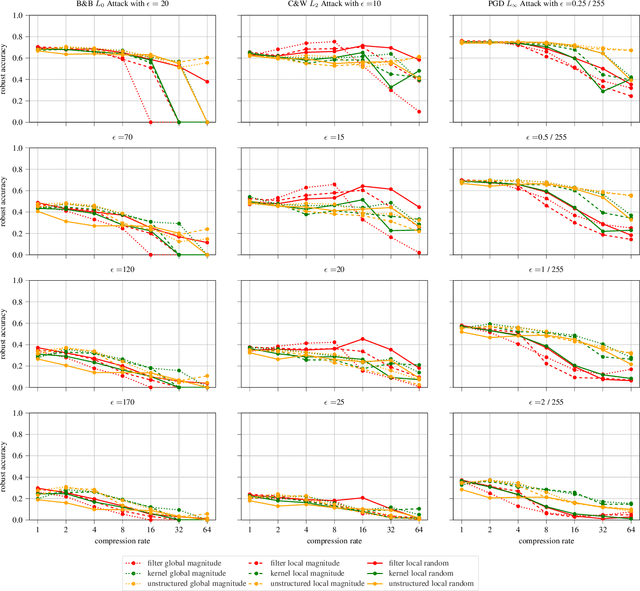
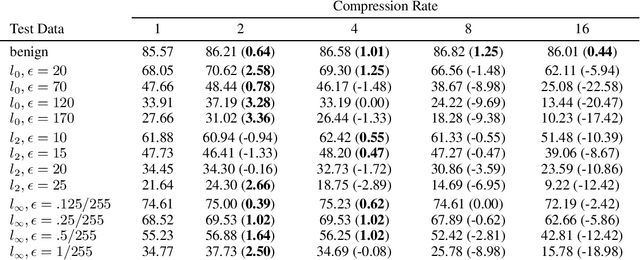
Abstract:The vulnerability of deep neural networks against adversarial examples - inputs with small imperceptible perturbations - has gained a lot of attention in the research community recently. Simultaneously, the number of parameters of state-of-the-art deep learning models has been growing massively, with implications on the memory and computational resources required to train and deploy such models. One approach to control the size of neural networks is retrospectively reducing the number of parameters, so-called neural network pruning. Available research on the impact of neural network pruning on the adversarial robustness is fragmentary and often does not adhere to established principles of robustness evaluation. We close this gap by evaluating the robustness of pruned models against L-0, L-2 and L-infinity attacks for a wide range of attack strengths, several architectures, data sets, pruning methods, and compression rates. Our results confirm that neural network pruning and adversarial robustness are not mutually exclusive. Instead, sweet spots can be found that are favorable in terms of model size and adversarial robustness. Furthermore, we extend our analysis to situations that incorporate additional assumptions on the adversarial scenario and show that depending on the situation, different strategies are optimal.
When Should You Defend Your Classifier -- A Game-theoretical Analysis of Countermeasures against Adversarial Examples
Aug 17, 2021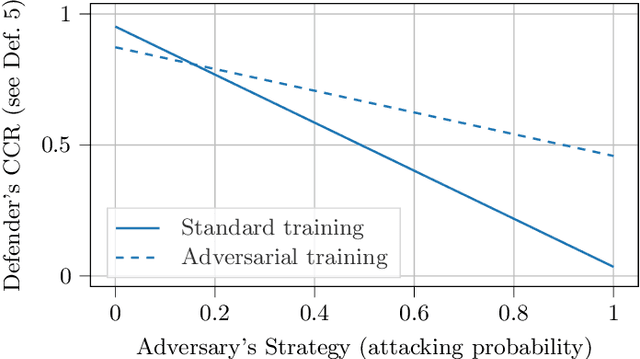
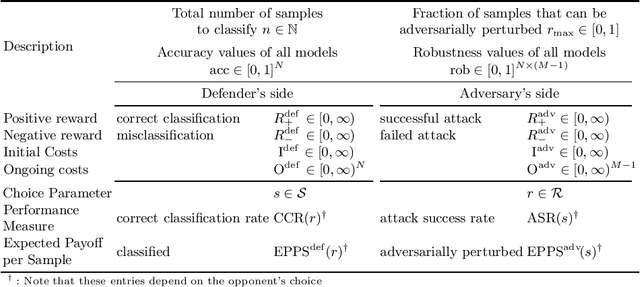
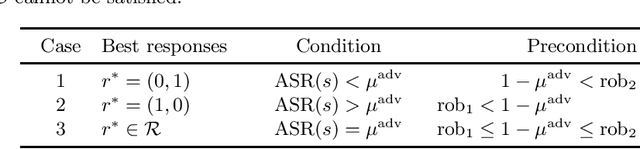
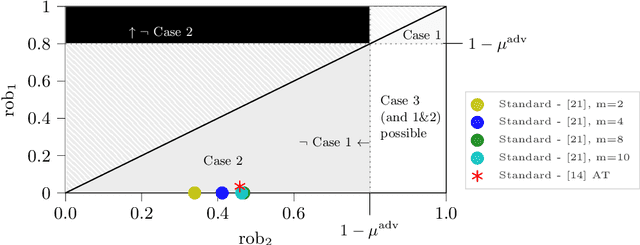
Abstract:Adversarial machine learning, i.e., increasing the robustness of machine learning algorithms against so-called adversarial examples, is now an established field. Yet, newly proposed methods are evaluated and compared under unrealistic scenarios where costs for adversary and defender are not considered and either all samples are attacked or no sample is attacked. We scrutinize these assumptions and propose the advanced adversarial classification game, which incorporates all relevant parameters of an adversary and a defender in adversarial classification. Especially, we take into account economic factors on both sides and the fact that all so far proposed countermeasures against adversarial examples reduce accuracy on benign samples. Analyzing the scenario in detail, where both players have two pure strategies, we identify all best responses and conclude that in practical settings, the most influential factor might be the maximum amount of adversarial examples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge