Maxim Makatchev
Expressing Ethnicity through Behaviors of a Robot Character
Mar 14, 2013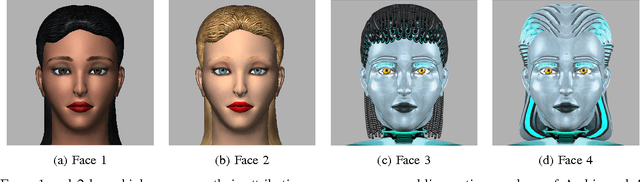
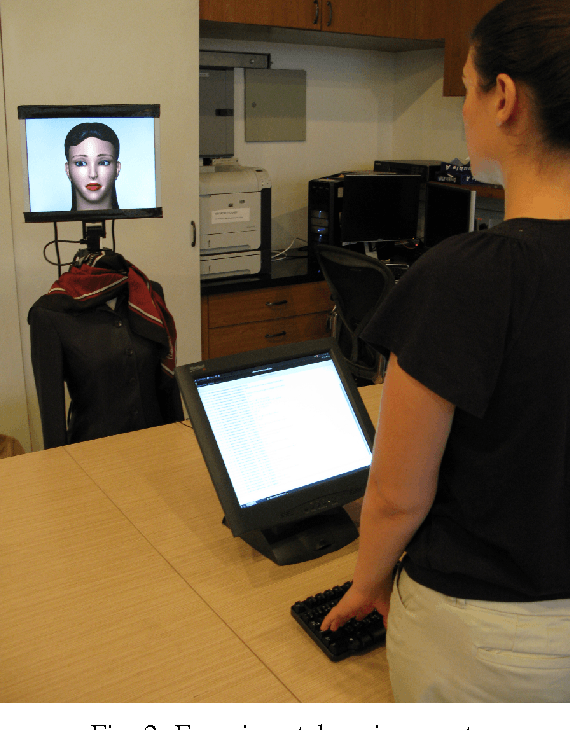

Abstract:Achieving homophily, or association based on similarity, between a human user and a robot holds a promise of improved perception and task performance. However, no previous studies that address homophily via ethnic similarity with robots exist. In this paper, we discuss the difficulties of evoking ethnic cues in a robot, as opposed to a virtual agent, and an approach to overcome those difficulties based on using ethnically salient behaviors. We outline our methodology for selecting and evaluating such behaviors, and culminate with a study that evaluates our hypotheses of the possibility of ethnic attribution of a robot character through verbal and nonverbal behaviors and of achieving the homophily effect.
* 10 pages, 4 figures
A Cross-cultural Corpus of Annotated Verbal and Nonverbal Behaviors in Receptionist Encounters
Mar 11, 2012



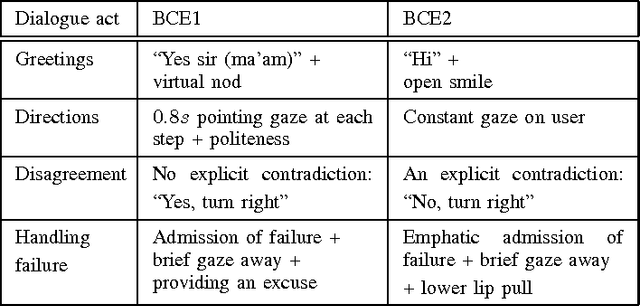
Abstract:We present the first annotated corpus of nonverbal behaviors in receptionist interactions, and the first nonverbal corpus (excluding the original video and audio data) of service encounters freely available online. Native speakers of American English and Arabic participated in a naturalistic role play at reception desks of university buildings in Doha, Qatar and Pittsburgh, USA. Their manually annotated nonverbal behaviors include gaze direction, hand and head gestures, torso positions, and facial expressions. We discuss possible uses of the corpus and envision it to become a useful tool for the human-robot interaction community.
Perception of Personality and Naturalness through Dialogues by Native Speakers of American English and Arabic
May 23, 2011


Abstract:Linguistic markers of personality traits have been studied extensively, but few cross-cultural studies exist. In this paper, we evaluate how native speakers of American English and Arabic perceive personality traits and naturalness of English utterances that vary along the dimensions of verbosity, hedging, lexical and syntactic alignment, and formality. The utterances are the turns within dialogue fragments that are presented as text transcripts to the workers of Amazon's Mechanical Turk. The results of the study suggest that all four dimensions can be used as linguistic markers of all personality traits by both language communities. A further comparative analysis shows cross-cultural differences for some combinations of measures of personality traits and naturalness, the dimensions of linguistic variability and dialogue acts.
On the Cell-based Complexity of Recognition of Bounded Configurations by Finite Dynamic Cellular Automata
Oct 11, 2002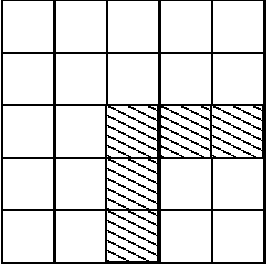
Abstract:This paper studies complexity of recognition of classes of bounded configurations by a generalization of conventional cellular automata (CA) -- finite dynamic cellular automata (FDCA). Inspired by the CA-based models of biological and computer vision, this study attempts to derive the properties of a complexity measure and of the classes of input configurations that make it beneficial to realize the recognition via a two-layered automaton as compared to a one-layered automaton. A formalized model of an image pattern recognition task is utilized to demonstrate that the derived conditions can be satisfied for a non-empty set of practical problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge