Maud Tournoud
CBIO
Controlling Large Electric Vehicle Charging Stations via User Behavior Modeling and Stochastic Programming
Feb 21, 2024
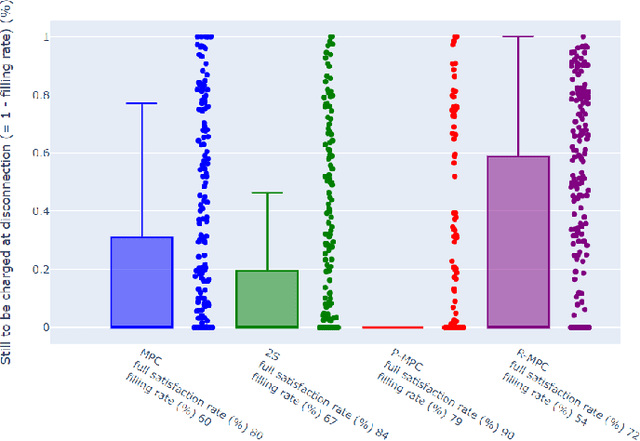
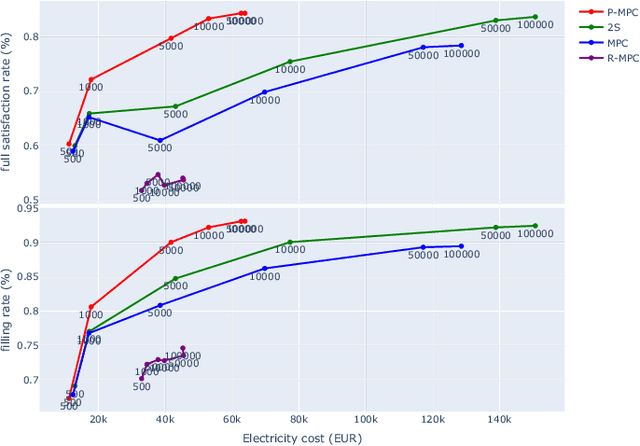
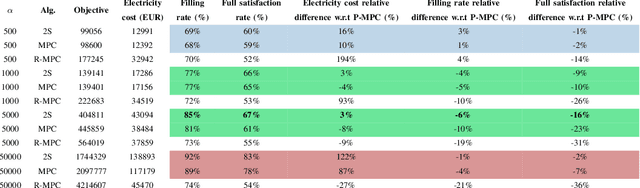
Abstract:This paper introduces an Electric Vehicle Charging Station (EVCS) model that incorporates real-world constraints, such as slot power limitations, contract threshold overruns penalties, or early disconnections of electric vehicles (EVs). We propose a formulation of the problem of EVCS control under uncertainty, and implement two Multi-Stage Stochastic Programming approaches that leverage user-provided information, namely, Model Predictive Control and Two-Stage Stochastic Programming. The model addresses uncertainties in charging session start and end times, as well as in energy demand. A user's behavior model based on a sojourn-time-dependent stochastic process enhances cost reduction while maintaining customer satisfaction. The benefits of the two proposed methods are showcased against two baselines over a 22-day simulation using a real-world dataset. The two-stage approach proves robust against early disconnections, considering a more significant number of uncertainty scenarios for optimization. The algorithm prioritizing user satisfaction over electricity cost achieves a 20% and 36% improvement in two user satisfaction metrics compared to an industry-standard baseline. Additionally, the algorithm striking the best balance between cost and user satisfaction exhibits a mere 3% relative cost increase compared to the theoretically optimal baseline - for which the nonanticipativity constraint is relaxed - while attaining 94% and 84% of the user satisfaction performance in the two used satisfaction metrics.
Large-scale Machine Learning for Metagenomics Sequence Classification
May 26, 2015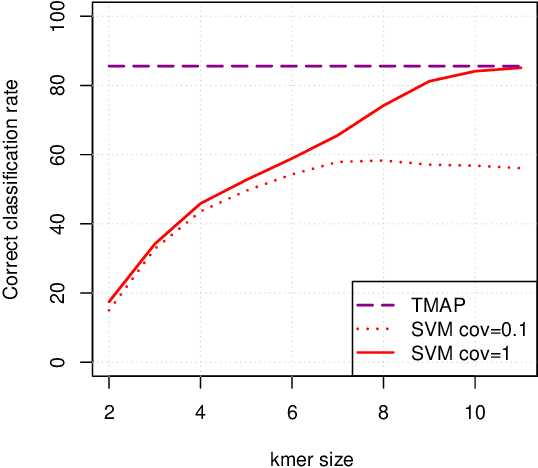
Abstract:Metagenomics characterizes the taxonomic diversity of microbial communities by sequencing DNA directly from an environmental sample. One of the main challenges in metagenomics data analysis is the binning step, where each sequenced read is assigned to a taxonomic clade. Due to the large volume of metagenomics datasets, binning methods need fast and accurate algorithms that can operate with reasonable computing requirements. While standard alignment-based methods provide state-of-the-art performance, compositional approaches that assign a taxonomic class to a DNA read based on the k-mers it contains have the potential to provide faster solutions. In this work, we investigate the potential of modern, large-scale machine learning implementations for taxonomic affectation of next-generation sequencing reads based on their k-mers profile. We show that machine learning-based compositional approaches benefit from increasing the number of fragments sampled from reference genome to tune their parameters, up to a coverage of about 10, and from increasing the k-mer size to about 12. Tuning these models involves training a machine learning model on about 10 8 samples in 10 7 dimensions, which is out of reach of standard soft-wares but can be done efficiently with modern implementations for large-scale machine learning. The resulting models are competitive in terms of accuracy with well-established alignment tools for problems involving a small to moderate number of candidate species, and for reasonable amounts of sequencing errors. We show, however, that compositional approaches are still limited in their ability to deal with problems involving a greater number of species, and more sensitive to sequencing errors. We finally confirm that compositional approach achieve faster prediction times, with a gain of 3 to 15 times with respect to the BWA-MEM short read mapper, depending on the number of candidate species and the level of sequencing noise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge