Matthias Rolf
Active exploration for body model learning through self-touch on a humanoid robot with artificial skin
Aug 31, 2020
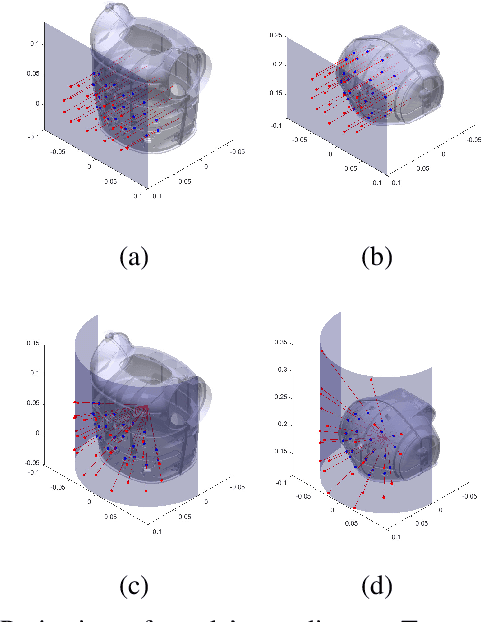
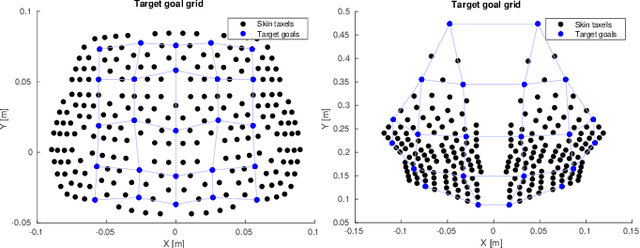
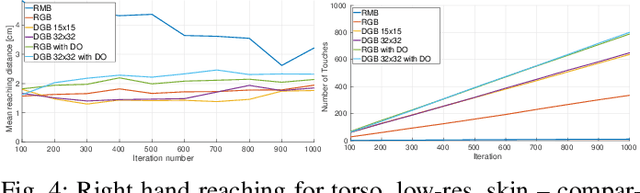
Abstract:The mechanisms of infant development are far from understood. Learning about one's own body is likely a foundation for subsequent development. Here we look specifically at the problem of how spontaneous touches to the body in early infancy may give rise to first body models and bootstrap further development such as reaching competence. Unlike visually elicited reaching, reaching to own body requires connections of the tactile and motor space only, bypassing vision. Still, the problems of high dimensionality and redundancy of the motor system persist. In this work, we present an embodied computational model on a simulated humanoid robot with artificial sensitive skin on large areas of its body. The robot should autonomously develop the capacity to reach for every tactile sensor on its body. To do this efficiently, we employ the computational framework of intrinsic motivations and variants of goal babbling, as opposed to motor babbling, that prove to make the exploration process faster and alleviate the ill-posedness of learning inverse kinematics. Based on our results, we discuss the next steps in relation to infant studies: what information will be necessary to further ground this computational model in behavioral data.
Where do goals come from? A Generic Approach to Autonomous Goal-System Development
Oct 21, 2014



Abstract:Goals express agents' intentions and allow them to organize their behavior based on low-dimensional abstractions of high-dimensional world states. How can agents develop such goals autonomously? This paper proposes a detailed conceptual and computational account to this longstanding problem. We argue to consider goals as high-level abstractions of lower-level intention mechanisms such as rewards and values, and point out that goals need to be considered alongside with a detection of the own actions' effects. We propose Latent Goal Analysis as a computational learning formulation thereof, and show constructively that any reward or value function can by explained by goals and such self-detection as latent mechanisms. We first show that learned goals provide a highly effective dimensionality reduction in a practical reinforcement learning problem. Then, we investigate a developmental scenario in which entirely task-unspecific rewards induced by visual saliency lead to self and goal representations that constitute goal-directed reaching.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge