Matthias Cetto
Discourse-Aware Text Simplification: From Complex Sentences to Linked Propositions
Aug 01, 2023Abstract:Sentences that present a complex syntax act as a major stumbling block for downstream Natural Language Processing applications whose predictive quality deteriorates with sentence length and complexity. The task of Text Simplification (TS) may remedy this situation. It aims to modify sentences in order to make them easier to process, using a set of rewriting operations, such as reordering, deletion, or splitting. State-of-the-art syntactic TS approaches suffer from two major drawbacks: first, they follow a very conservative approach in that they tend to retain the input rather than transforming it, and second, they ignore the cohesive nature of texts, where context spread across clauses or sentences is needed to infer the true meaning of a statement. To address these problems, we present a discourse-aware TS approach that splits and rephrases complex English sentences within the semantic context in which they occur. Based on a linguistically grounded transformation stage that uses clausal and phrasal disembedding mechanisms, complex sentences are transformed into shorter utterances with a simple canonical structure that can be easily analyzed by downstream applications. With sentence splitting, we thus address a TS task that has hardly been explored so far. Moreover, we introduce the notion of minimality in this context, as we aim to decompose source sentences into a set of self-contained minimal semantic units. To avoid breaking down the input into a disjointed sequence of statements that is difficult to interpret because important contextual information is missing, we incorporate the semantic context between the split propositions in the form of hierarchical structures and semantic relationships. In that way, we generate a semantic hierarchy of minimal propositions that leads to a novel representation of complex assertions that puts a semantic layer on top of the simplified sentences.
Context-Preserving Text Simplification
May 24, 2021


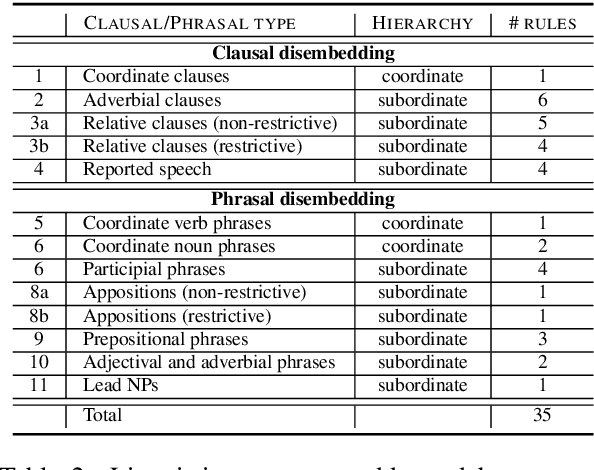
Abstract:We present a context-preserving text simplification (TS) approach that recursively splits and rephrases complex English sentences into a semantic hierarchy of simplified sentences. Using a set of linguistically principled transformation patterns, input sentences are converted into a hierarchical representation in the form of core sentences and accompanying contexts that are linked via rhetorical relations. Hence, as opposed to previously proposed sentence splitting approaches, which commonly do not take into account discourse-level aspects, our TS approach preserves the semantic relationship of the decomposed constituents in the output. A comparative analysis with the annotations contained in the RST-DT shows that we are able to capture the contextual hierarchy between the split sentences with a precision of 89% and reach an average precision of 69% for the classification of the rhetorical relations that hold between them.
DisSim: A Discourse-Aware Syntactic Text Simplification Frameworkfor English and German
Sep 26, 2019

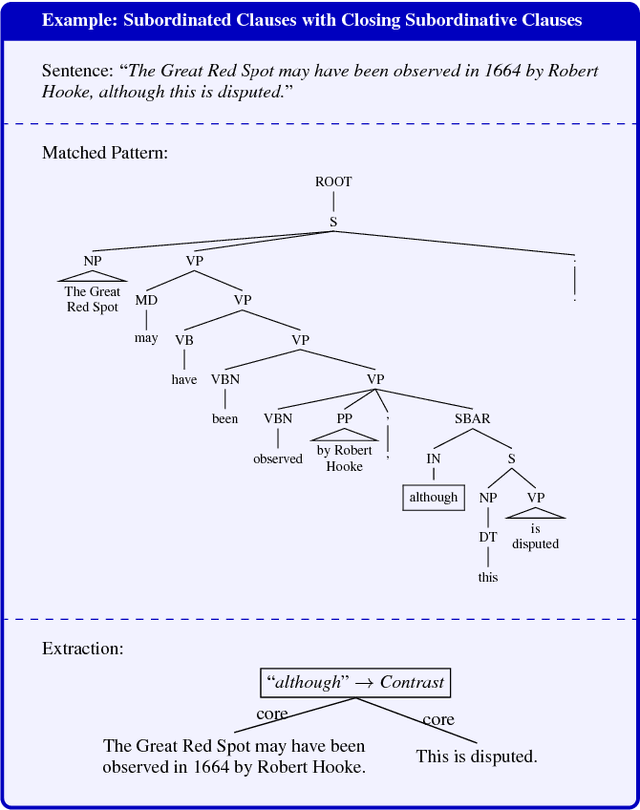
Abstract:We introduce DisSim, a discourse-aware sentence splitting framework for English and German whose goal is to transform syntactically complex sentences into an intermediate representation that presents a simple and more regular structure which is easier to process for downstream semantic applications. For this purpose, we turn input sentences into a two-layered semantic hierarchy in the form of core facts and accompanying contexts, while identifying the rhetorical relations that hold between them. In that way, we preserve the coherence structure of the input and, hence, its interpretability for downstream tasks.
Transforming Complex Sentences into a Semantic Hierarchy
Jun 03, 2019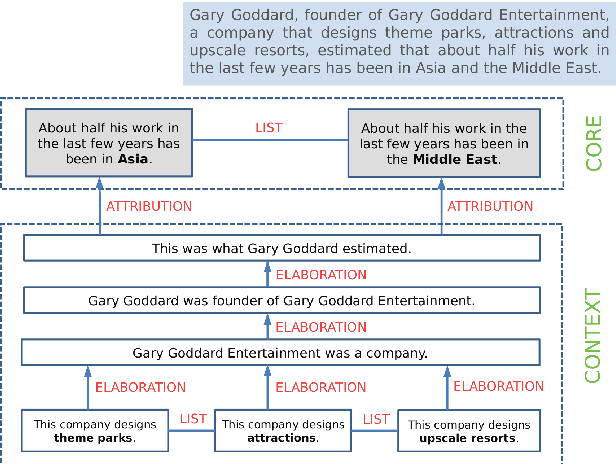
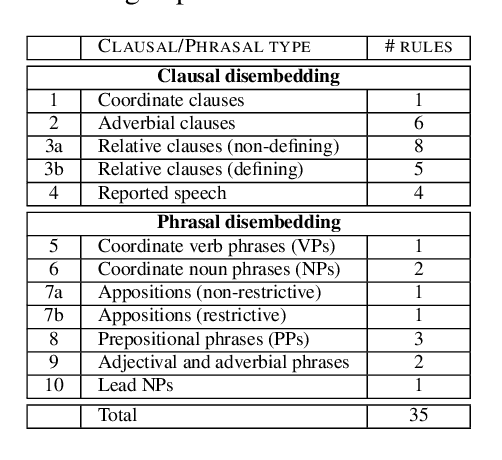

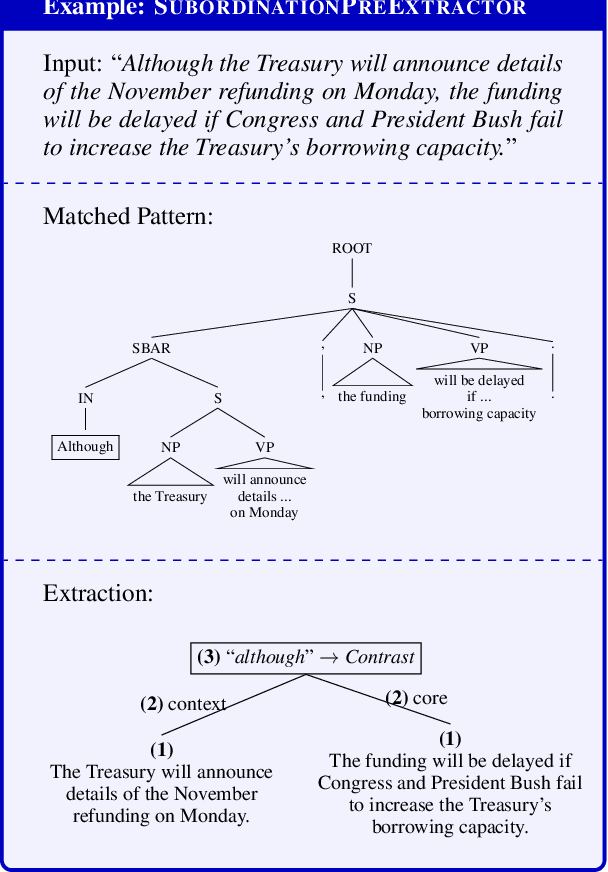
Abstract:We present an approach for recursively splitting and rephrasing complex English sentences into a novel semantic hierarchy of simplified sentences, with each of them presenting a more regular structure that may facilitate a wide variety of artificial intelligence tasks, such as machine translation (MT) or information extraction (IE). Using a set of hand-crafted transformation rules, input sentences are recursively transformed into a two-layered hierarchical representation in the form of core sentences and accompanying contexts that are linked via rhetorical relations. In this way, the semantic relationship of the decomposed constituents is preserved in the output, maintaining its interpretability for downstream applications. Both a thorough manual analysis and automatic evaluation across three datasets from two different domains demonstrate that the proposed syntactic simplification approach outperforms the state of the art in structural text simplification. Moreover, an extrinsic evaluation shows that when applying our framework as a preprocessing step the performance of state-of-the-art Open IE systems can be improved by up to 346% in precision and 52% in recall. To enable reproducible research, all code is provided online.
Graphene: A Context-Preserving Open Information Extraction System
Aug 28, 2018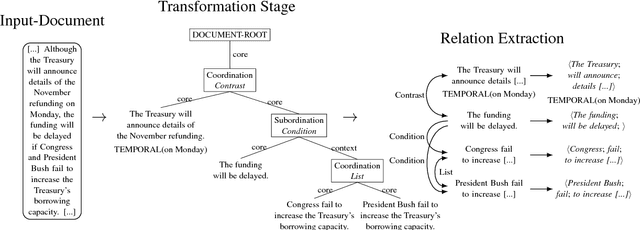

Abstract:We introduce Graphene, an Open IE system whose goal is to generate accurate, meaningful and complete propositions that may facilitate a variety of downstream semantic applications. For this purpose, we transform syntactically complex input sentences into clean, compact structures in the form of core facts and accompanying contexts, while identifying the rhetorical relations that hold between them in order to maintain their semantic relationship. In that way, we preserve the context of the relational tuples extracted from a source sentence, generating a novel lightweight semantic representation for Open IE that enhances the expressiveness of the extracted propositions.
Graphene: Semantically-Linked Propositions in Open Information Extraction
Jul 30, 2018


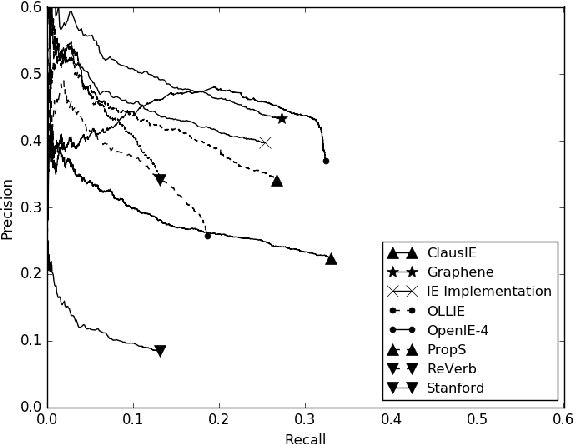
Abstract:We present an Open Information Extraction (IE) approach that uses a two-layered transformation stage consisting of a clausal disembedding layer and a phrasal disembedding layer, together with rhetorical relation identification. In that way, we convert sentences that present a complex linguistic structure into simplified, syntactically sound sentences, from which we can extract propositions that are represented in a two-layered hierarchy in the form of core relational tuples and accompanying contextual information which are semantically linked via rhetorical relations. In a comparative evaluation, we demonstrate that our reference implementation Graphene outperforms state-of-the-art Open IE systems in the construction of correct n-ary predicate-argument structures. Moreover, we show that existing Open IE approaches can benefit from the transformation process of our framework.
A Survey on Open Information Extraction
Jun 14, 2018

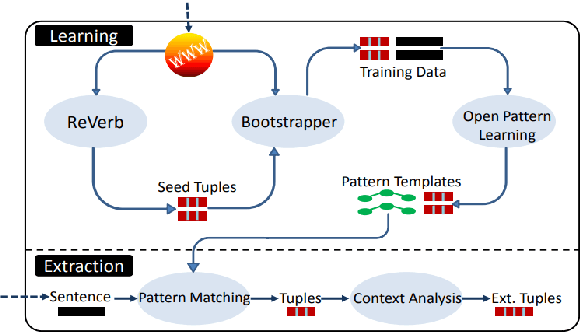

Abstract:We provide a detailed overview of the various approaches that were proposed to date to solve the task of Open Information Extraction. We present the major challenges that such systems face, show the evolution of the suggested approaches over time and depict the specific issues they address. In addition, we provide a critique of the commonly applied evaluation procedures for assessing the performance of Open IE systems and highlight some directions for future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge