Matthew R. DeVerna
A Marketplace for AI-Generated Adult Content and Deepfakes
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Generative AI systems increasingly enable the production of highly realistic synthetic media. Civitai, a popular community-driven platform for AI-generated content, operates a monetized feature called Bounties, which allows users to commission the generation of content in exchange for payment. To examine how this mechanism is used and what content it incentivizes, we conduct a longitudinal analysis of all publicly available bounty requests collected over a 14-month period following the platform's launch. We find that the bounty marketplace is dominated by tools that let users steer AI models toward content they were not trained to generate. At the same time, requests for content that is "Not Safe For Work" are widespread and have increased steadily over time, now comprising a majority of all bounties. Participation in bounty creation is uneven, with 20% of requesters accounting for roughly half of requests. Requests for "deepfake" - media depicting identifiable real individuals - exhibit a higher concentration than other types of bounties. A nontrivial subset of these requests involves explicit deepfakes despite platform policies prohibiting such content. These bounties disproportionately target female celebrities, revealing a pronounced gender asymmetry in social harm. Together, these findings show how monetized, community-driven generative AI platforms can produce gendered harms, raising questions about consent, governance, and enforcement.
Artificial intelligence is ineffective and potentially harmful for fact checking
Sep 01, 2023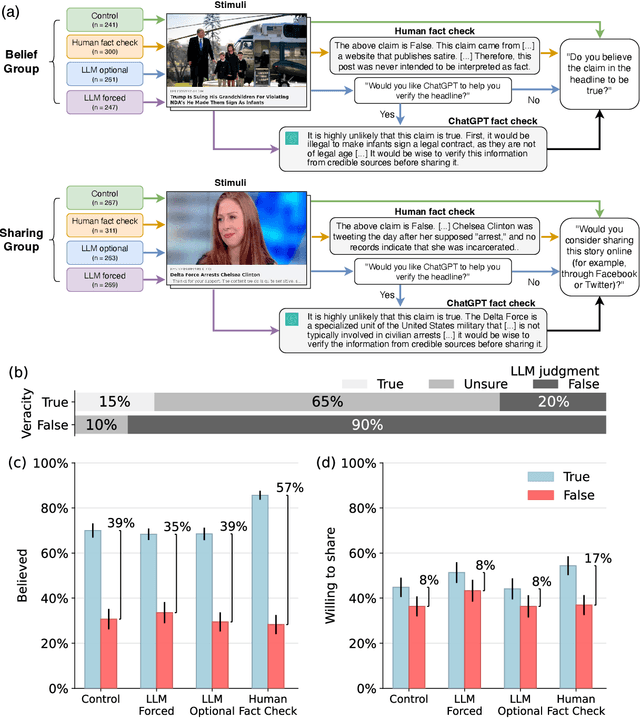
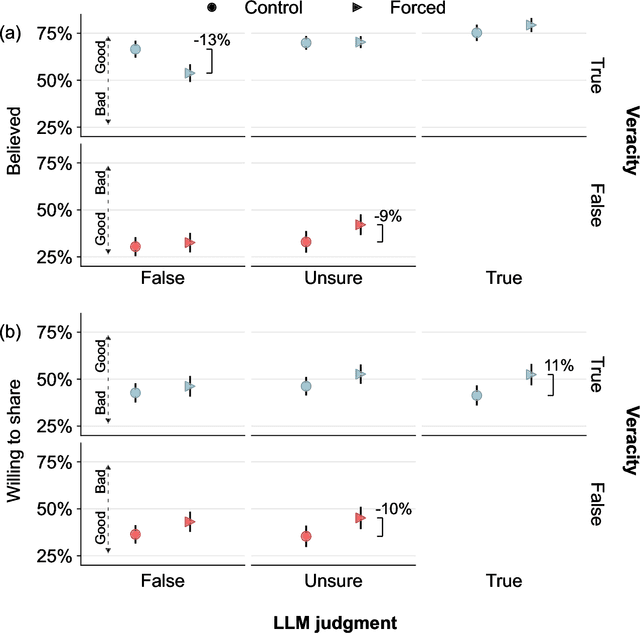
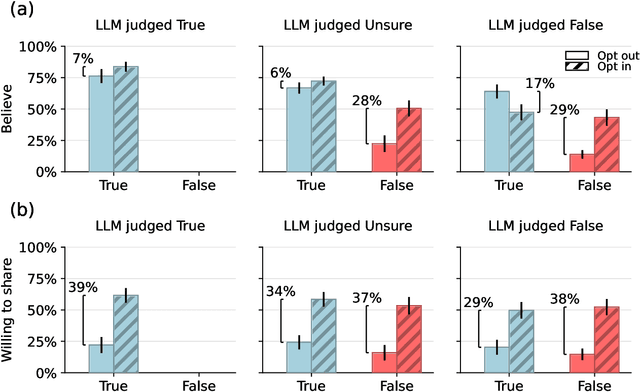
Abstract:Fact checking can be an effective strategy against misinformation, but its implementation at scale is impeded by the overwhelming volume of information online. Recent artificial intelligence (AI) language models have shown impressive ability in fact-checking tasks, but how humans interact with fact-checking information provided by these models is unclear. Here we investigate the impact of fact checks generated by a popular AI model on belief in, and sharing intent of, political news in a preregistered randomized control experiment. Although the AI performs reasonably well in debunking false headlines, we find that it does not significantly affect participants' ability to discern headline accuracy or share accurate news. However, the AI fact-checker is harmful in specific cases: it decreases beliefs in true headlines that it mislabels as false and increases beliefs for false headlines that it is unsure about. On the positive side, the AI increases sharing intents for correctly labeled true headlines. When participants are given the option to view AI fact checks and choose to do so, they are significantly more likely to share both true and false news but only more likely to believe false news. Our findings highlight an important source of potential harm stemming from AI applications and underscore the critical need for policies to prevent or mitigate such unintended consequences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge