Matteo Rinaldi
Ku-Band AlScn-On-Diamond SAW Resonators with Phase Velocity above 8600 m/s
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:In this work, an Aluminum Scandium Nitride (AlScN) on Diamond Sezawa-mode surface acoustic wave (SAW) platform for RF filtering at Ku-band (12-18 GHz) is demonstrated. Thanks to the high acoustic velocity and low-loss diamond substrate, the prototype resonator at 12.9 GHz achieves a high phase velocity ($v_p$) of 8671 m/s, a maximum Bode-$Q$ of 408, and coupling coefficient ($k_{\mathrm{eff}}^2$) of 2.1%, outperforming high-velocity substrates such as SiC and sapphire by more than 20% in velocity. Resonators spanning 8-18 GHz are presented. The platform's high power handling above 12.5 dBm is also experimentally validated.
Millimeter Wave Thin-Film Bulk Acoustic Resonator in Sputtered Scandium Aluminum Nitride Using Platinum Electrodes
Nov 22, 2023



Abstract:This work describes sputtered scandium aluminum nitride (ScAlN) thin-film bulk acoustic resonators (FBAR) at millimeter wave (mmWave) with high quality factor (Q) using platinum (Pt) electrodes. FBARs with combinations of Pt and aluminum (Al) electrodes, i.e., Al top Al bottom, Pt top Al bottom, Al top Pt bottom, and Pt top Pt bottom, are built to study the impact of electrodes on mmWave FBARs. The demonstrated FBAR with Pt top and bottom electrodes achieve electromechanical coupling (k2) of 4.0% and Q of 116 for the first-order symmetric (S1) mode at 13.7 GHz, and k2 of 1.8% and Q of 94 for third-order symmetric (S3) mode at 61.6 GHz. Through these results, we confirmed that even in the frequency band of approximately 60 GHz, ScAlN FBAR can achieve a Q factor approaching 100 with optimized fabrication and acoustic/EM design. Further development calls for stacks with better quality in piezoelectric and metallic layers.
Automatic Music Playlist Generation via Simulation-based Reinforcement Learning
Oct 13, 2023



Abstract:Personalization of playlists is a common feature in music streaming services, but conventional techniques, such as collaborative filtering, rely on explicit assumptions regarding content quality to learn how to make recommendations. Such assumptions often result in misalignment between offline model objectives and online user satisfaction metrics. In this paper, we present a reinforcement learning framework that solves for such limitations by directly optimizing for user satisfaction metrics via the use of a simulated playlist-generation environment. Using this simulator we develop and train a modified Deep Q-Network, the action head DQN (AH-DQN), in a manner that addresses the challenges imposed by the large state and action space of our RL formulation. The resulting policy is capable of making recommendations from large and dynamic sets of candidate items with the expectation of maximizing consumption metrics. We analyze and evaluate agents offline via simulations that use environment models trained on both public and proprietary streaming datasets. We show how these agents lead to better user-satisfaction metrics compared to baseline methods during online A/B tests. Finally, we demonstrate that performance assessments produced from our simulator are strongly correlated with observed online metric results.
Millimeter Wave Thin-Film Bulk Acoustic Resonator in Sputtered Scandium Aluminum Nitride
Sep 06, 2023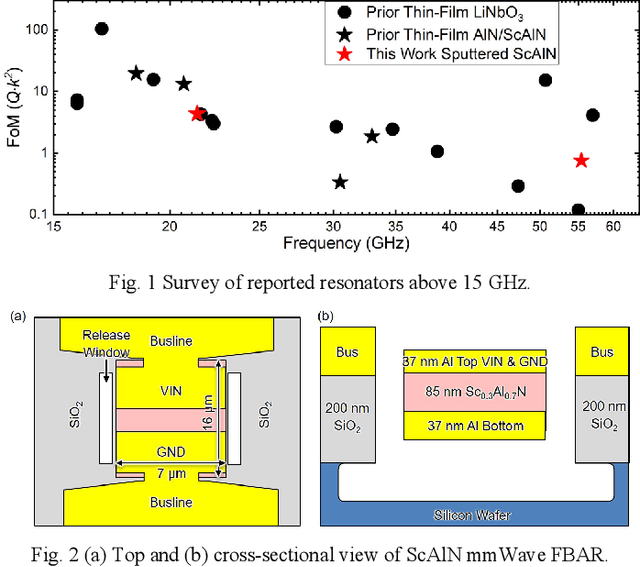
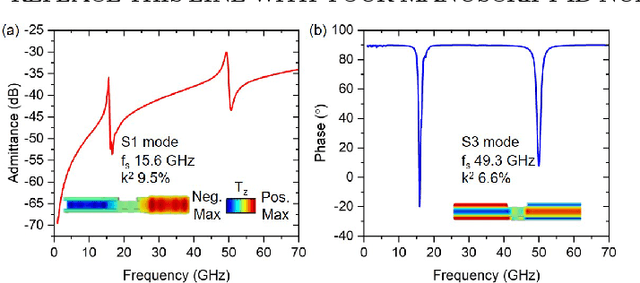
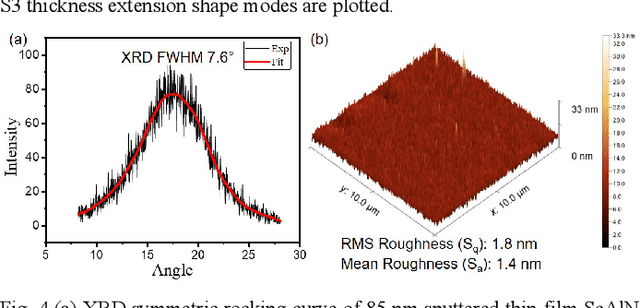
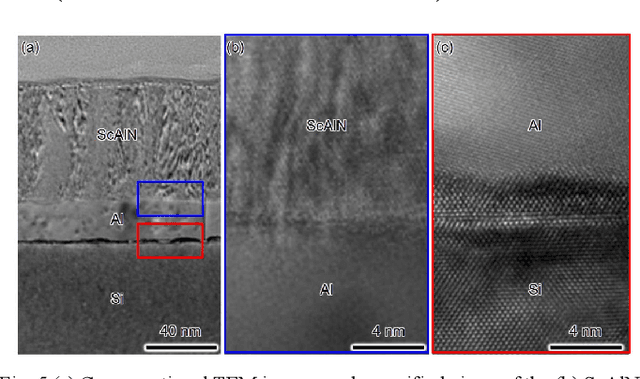
Abstract:This work reports a millimeter wave (mmWave) thin-film bulk acoustic resonator (FBAR) in sputtered scandium aluminum nitride (ScAlN). This paper identifies challenges of frequency scaling sputtered ScAlN into mmWave and proposes a stack and new fabrication procedure with a sputtered Sc0.3Al0.7N on Al on Si carrier wafer. The resonator achieves electromechanical coupling (k2) of 7.0% and quality factor (Q) of 62 for the first-order symmetric (S1) mode at 21.4 GHz, along with k2 of 4.0% and Q of 19 for the third-order symmetric (S3) mode at 55.4 GHz, showing higher figures of merit (FoM, k2xQ) than reported AlN/ScAlN-based mmWave acoustic resonators. The ScAlN quality is identified by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD), identifying the bottlenecks in the existing piezoelectric-metal stack. Further improvement of ScAlN/AlN-based mmWave acoustic resonators calls for better crystalline quality from improved thin-film deposition methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge