Matteo Messa
StarcNet: Machine Learning for Star Cluster Identification
Dec 16, 2020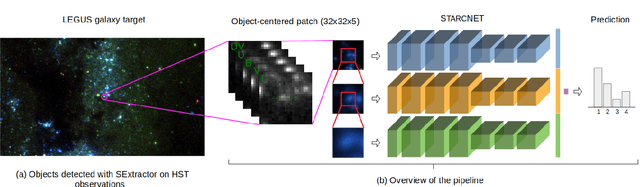
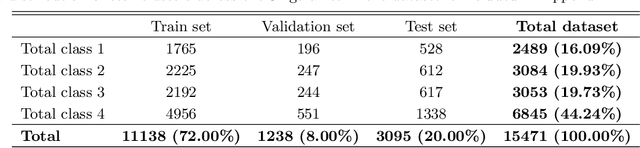
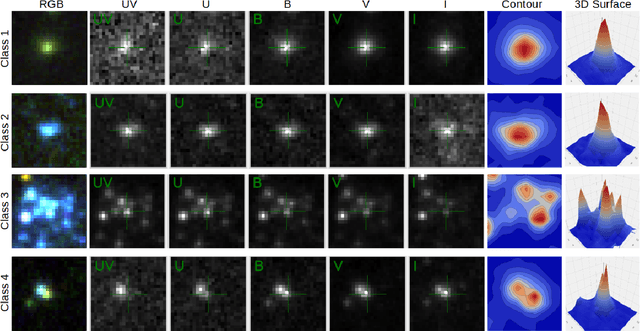
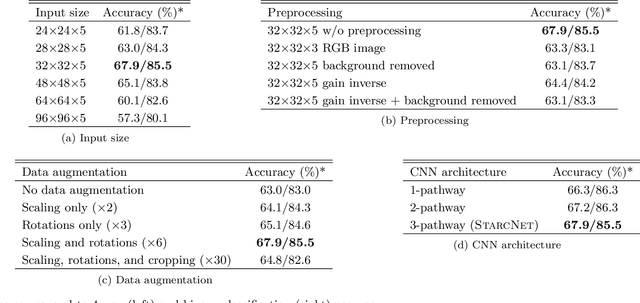
Abstract:We present a machine learning (ML) pipeline to identify star clusters in the multi{color images of nearby galaxies, from observations obtained with the Hubble Space Telescope as part of the Treasury Project LEGUS (Legacy ExtraGalactic Ultraviolet Survey). StarcNet (STAR Cluster classification NETwork) is a multi-scale convolutional neural network (CNN) which achieves an accuracy of 68.6% (4 classes)/86.0% (2 classes: cluster/non-cluster) for star cluster classification in the images of the LEGUS galaxies, nearly matching human expert performance. We test the performance of StarcNet by applying pre-trained CNN model to galaxies not included in the training set, finding accuracies similar to the reference one. We test the effect of StarcNet predictions on the inferred cluster properties by comparing multi-color luminosity functions and mass-age plots from catalogs produced by StarcNet and by human-labeling; distributions in luminosity, color, and physical characteristics of star clusters are similar for the human and ML classified samples. There are two advantages to the ML approach: (1) reproducibility of the classifications: the ML algorithm's biases are fixed and can be measured for subsequent analysis; and (2) speed of classification: the algorithm requires minutes for tasks that humans require weeks to months to perform. By achieving comparable accuracy to human classifiers, StarcNet will enable extending classifications to a larger number of candidate samples than currently available, thus increasing significantly the statistics for cluster studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge