Masoud Yari
Skip-WaveNet: A Wavelet based Multi-scale Architecture to Trace Firn Layers in Radar Echograms
Oct 30, 2023Abstract:Echograms created from airborne radar sensors capture the profile of firn layers present on top of an ice sheet. Accurate tracking of these layers is essential to calculate the snow accumulation rates, which are required to investigate the contribution of polar ice cap melt to sea level rise. However, automatically processing the radar echograms to detect the underlying firn layers is a challenging problem. In our work, we develop wavelet-based multi-scale deep learning architectures for these radar echograms to improve firn layer detection. We show that wavelet based architectures improve the optimal dataset scale (ODS) and optimal image scale (OIS) F-scores by 3.99% and 3.7%, respectively, over the non-wavelet architecture. Further, our proposed Skip-WaveNet architecture generates new wavelets in each iteration, achieves higher generalizability as compared to state-of-the-art firn layer detection networks, and estimates layer depths with a mean absolute error of 3.31 pixels and 94.3% average precision. Such a network can be used by scientists to trace firn layers, calculate the annual snow accumulation rates, estimate the resulting surface mass balance of the ice sheet, and help project global sea level rise.
Physics Informed Recurrent Neural Networks for Seismic Response Evaluation of Nonlinear Systems
Aug 16, 2023Abstract:Dynamic response evaluation in structural engineering is the process of determining the response of a structure, such as member forces, node displacements, etc when subjected to dynamic loads such as earthquakes, wind, or impact. This is an important aspect of structural analysis, as it enables engineers to assess structural performance under extreme loading conditions and make informed decisions about the design and safety of the structure. Conventional methods for dynamic response evaluation involve numerical simulations using finite element analysis (FEA), where the structure is modeled using finite elements, and the equations of motion are solved numerically. Although effective, this approach can be computationally intensive and may not be suitable for real-time applications. To address these limitations, recent advancements in machine learning, specifically artificial neural networks, have been applied to dynamic response evaluation in structural engineering. These techniques leverage large data sets and sophisticated algorithms to learn the complex relationship between inputs and outputs, making them ideal for such problems. In this paper, a novel approach is proposed for evaluating the dynamic response of multi-degree-of-freedom (MDOF) systems using physics-informed recurrent neural networks. The focus of this paper is to evaluate the seismic (earthquake) response of nonlinear structures. The predicted response will be compared to state-of-the-art methods such as FEA to assess the efficacy of the physics-informed RNN model.
Regression Networks For Calculating Englacial Layer Thickness
Apr 10, 2021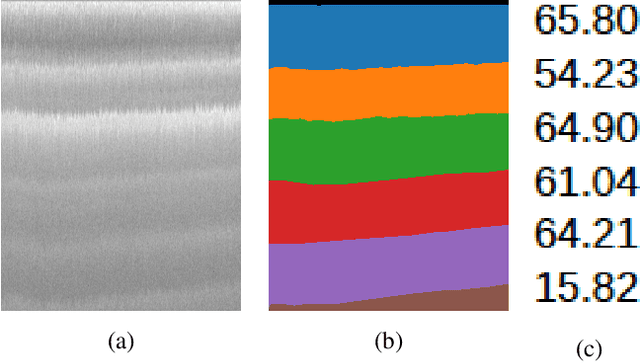

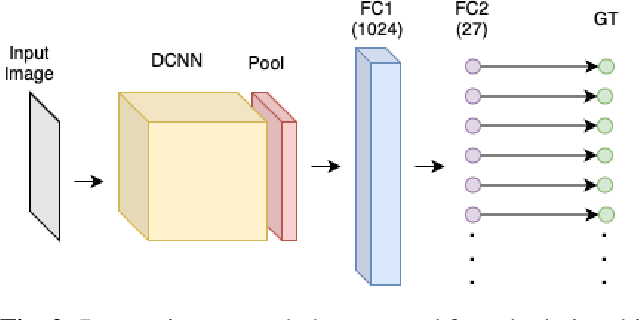
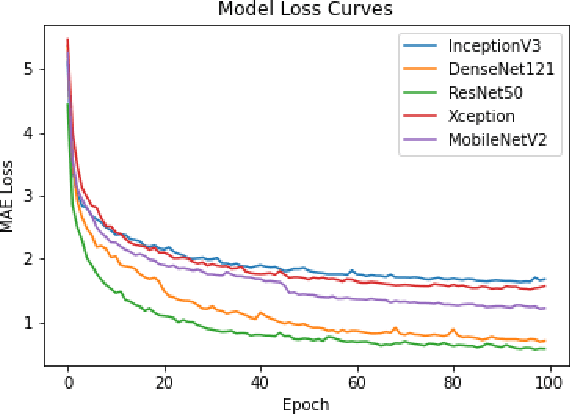
Abstract:Ice thickness estimation is an important aspect of ice sheet studies. In this work, we use convolutional neural networks with multiple output nodes to regress and learn the thickness of internal ice layers in Snow Radar images collected in northwest Greenland. We experiment with some state-of-the-art networks and find that with the residual connections of ResNet50, we could achieve a mean absolute error of 1.251 pixels over the test set. Such regression-based networks can further be improved by embedding domain knowledge and radar information in the neural network in order to reduce the requirement of manual annotations.
FloodNet: A High Resolution Aerial Imagery Dataset for Post Flood Scene Understanding
Dec 05, 2020



Abstract:Visual scene understanding is the core task in making any crucial decision in any computer vision system. Although popular computer vision datasets like Cityscapes, MS-COCO, PASCAL provide good benchmarks for several tasks (e.g. image classification, segmentation, object detection), these datasets are hardly suitable for post disaster damage assessments. On the other hand, existing natural disaster datasets include mainly satellite imagery which have low spatial resolution and a high revisit period. Therefore, they do not have a scope to provide quick and efficient damage assessment tasks. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle(UAV) can effortlessly access difficult places during any disaster and collect high resolution imagery that is required for aforementioned tasks of computer vision. To address these issues we present a high resolution UAV imagery, FloodNet, captured after the hurricane Harvey. This dataset demonstrates the post flooded damages of the affected areas. The images are labeled pixel-wise for semantic segmentation task and questions are produced for the task of visual question answering. FloodNet poses several challenges including detection of flooded roads and buildings and distinguishing between natural water and flooded water. With the advancement of deep learning algorithms, we can analyze the impact of any disaster which can make a precise understanding of the affected areas. In this paper, we compare and contrast the performances of baseline methods for image classification, semantic segmentation, and visual question answering on our dataset.
Deep Ice Layer Tracking and Thickness Estimation using Fully Convolutional Networks
Sep 01, 2020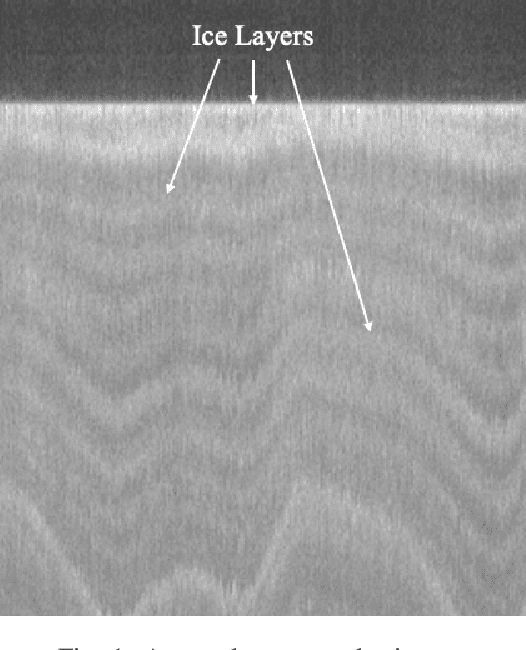
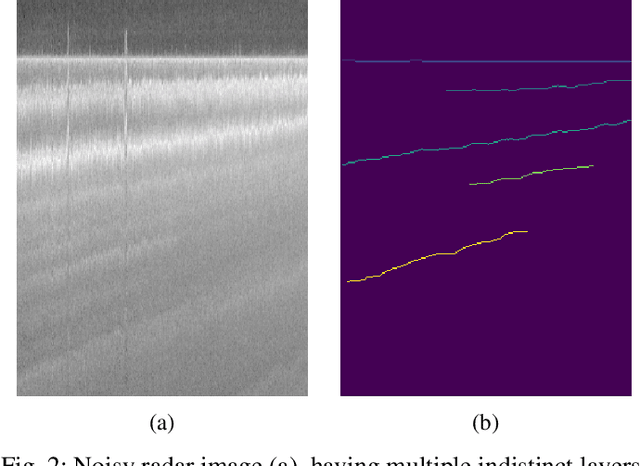
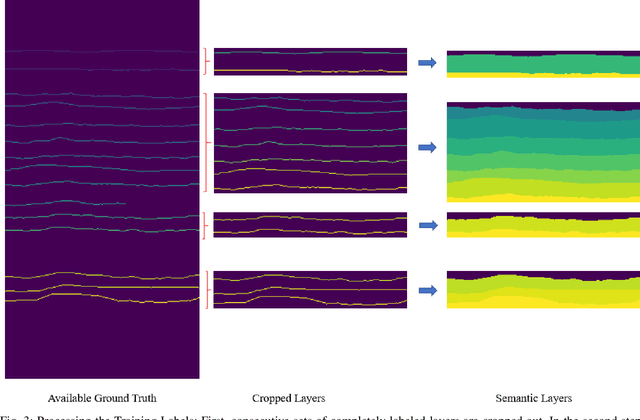
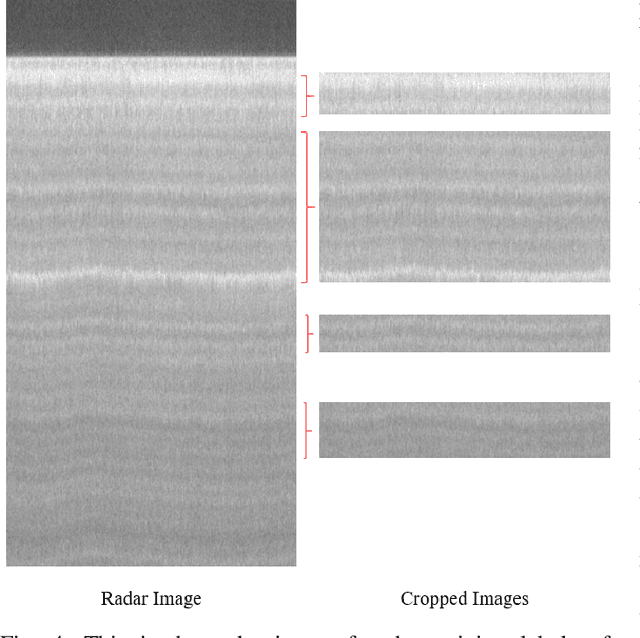
Abstract:Global warming is rapidly reducing glaciers and ice sheets across the world. Real time assessment of this reduction is required so as to monitor its global climatic impact. In this paper, we introduce a novel way of estimating the thickness of each internal ice layer using Snow Radar images and Fully Convolutional Networks. The estimated thickness can be analysed to understand snow accumulation each year. To understand the depth and structure of each internal ice layer, we carry out a set of image processing techniques and perform semantic segmentation on the radar images. After detecting each ice layer uniquely, we calculate its thickness and compare it with the available ground truth. Through this procedure we were able to estimate the ice layer thicknesses within a Mean Absolute Error of approximately 3.6 pixels. Such a Deep Learning based method can be used with ever-increasing datasets to make accurate assessments for cryospheric studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge