Mason Poggemann
TRACE: A Differentiable Approach to Line-level Stroke Recovery for Offline Handwritten Text
May 24, 2021



Abstract:Stroke order and velocity are helpful features in the fields of signature verification, handwriting recognition, and handwriting synthesis. Recovering these features from offline handwritten text is a challenging and well-studied problem. We propose a new model called TRACE (Trajectory Recovery by an Adaptively-trained Convolutional Encoder). TRACE is a differentiable approach that uses a convolutional recurrent neural network (CRNN) to infer temporal stroke information from long lines of offline handwritten text with many characters and dynamic time warping (DTW) to align predictions and ground truth points. TRACE is perhaps the first system to be trained end-to-end on entire lines of text of arbitrary width and does not require the use of dynamic exemplars. Moreover, the system does not require images to undergo any pre-processing, nor do the predictions require any post-processing. Consequently, the recovered trajectory is differentiable and can be used as a loss function for other tasks, including synthesizing offline handwritten text. We demonstrate that temporal stroke information recovered by TRACE from offline data can be used for handwriting synthesis and establish the first benchmarks for a stroke trajectory recovery system trained on the IAM online handwriting dataset.
Preprocessor Selection for Machine Learning Pipelines
Oct 23, 2018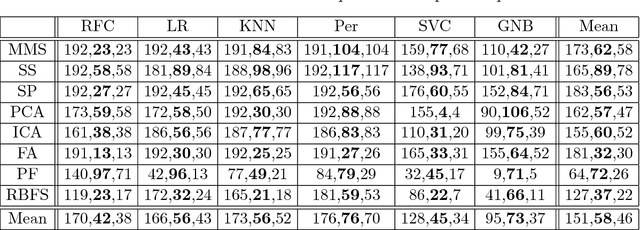



Abstract:Much of the work in metalearning has focused on classifier selection, combined more recently with hyperparameter optimization, with little concern for data preprocessing. Yet, it is generally well accepted that machine learning applications require not only model building, but also data preprocessing. In other words, practical solutions consist of pipelines of machine learning operators rather than single algorithms. Interestingly, our experiments suggest that, on average, data preprocessing hinders accuracy, while the best performing pipelines do actually make use of preprocessors. Here, we conduct an extensive empirical study over a wide range of learning algorithms and preprocessors, and use metalearning to determine when one should make use of preprocessors in ML pipeline design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge