Masahiro Mitsuhara
ST-ABN: Visual Explanation Taking into Account Spatio-temporal Information for Video Recognition
Oct 29, 2021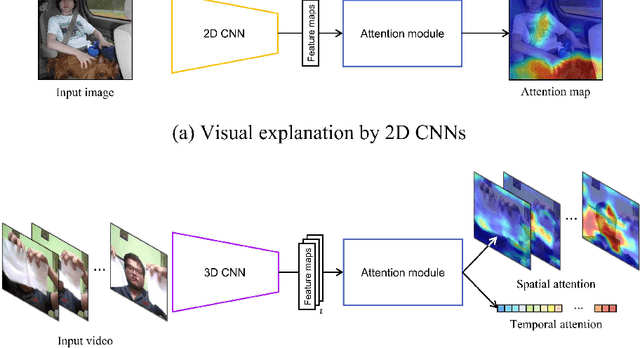
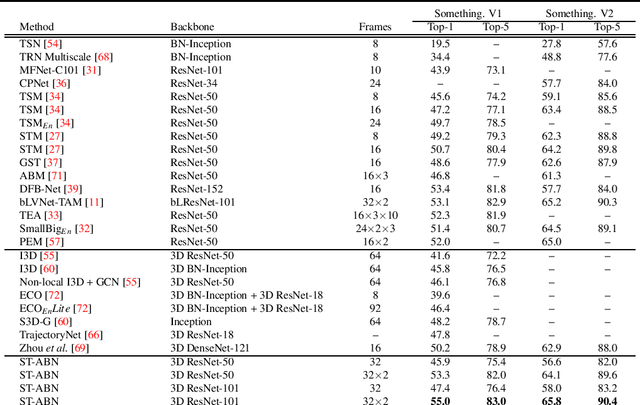
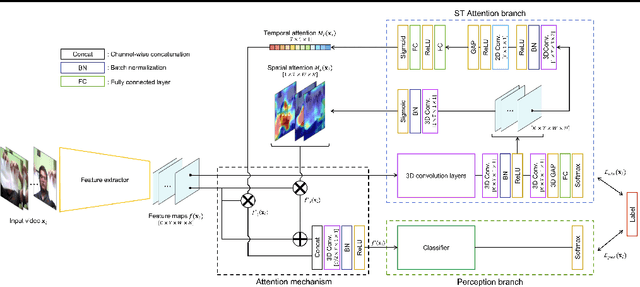

Abstract:It is difficult for people to interpret the decision-making in the inference process of deep neural networks. Visual explanation is one method for interpreting the decision-making of deep learning. It analyzes the decision-making of 2D CNNs by visualizing an attention map that highlights discriminative regions. Visual explanation for interpreting the decision-making process in video recognition is more difficult because it is necessary to consider not only spatial but also temporal information, which is different from the case of still images. In this paper, we propose a visual explanation method called spatio-temporal attention branch network (ST-ABN) for video recognition. It enables visual explanation for both spatial and temporal information. ST-ABN acquires the importance of spatial and temporal information during network inference and applies it to recognition processing to improve recognition performance and visual explainability. Experimental results with Something-Something datasets V1 \& V2 demonstrated that ST-ABN enables visual explanation that takes into account spatial and temporal information simultaneously and improves recognition performance.
Embedding Human Knowledge in Deep Neural Network via Attention Map
May 09, 2019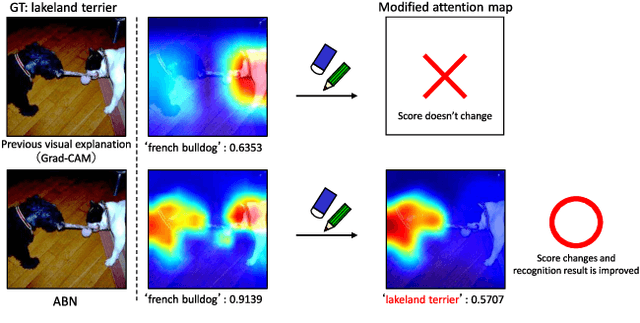
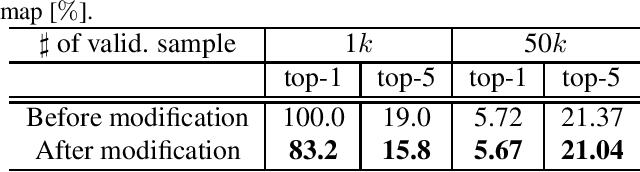
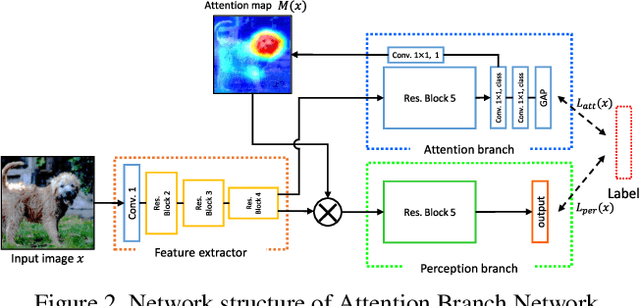
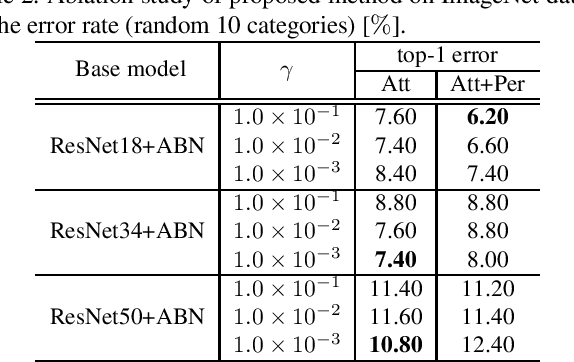
Abstract:Human-in-the-loop (HITL), which introduces human knowledge to machine learning, has been used in fine-grained recognition to estimate categories from the difference of local features. The conventional HITL approach has been successfully applied in non-deep machine learning, but it is difficult to use it with deep learning due to the enormous number of model parameters. To tackle this problem, in this paper, we propose using the Attention Branch Network (ABN) which is a visual explanation model. ABN applies an attention map for visual explanation to an attention mechanism. First, we manually modify the attention map obtained from ABN on the basis of human knowledge. Then, we use the modified attention map to an attention mechanism that enables ABN to adjust the recognition score. Second, for applying HITL to deep learning, we propose a fine-tuning approach that uses the modified attention map. Our fine-tuning updates the attention and perception branches of the ABN by using the training loss calculated from the attention map output from the ABN along with the modified attention map. This fine-tuning enables the ABN to output an attention map corresponding to human knowledge. Additionally, we use the updated attention map with its embedded human knowledge as an attention mechanism and inference at the perception branch, which improves the performance of ABN. Experimental results with the ImageNet dataset, CUB-200-2010 dataset, and IDRiD demonstrate that our approach clarifies the attention map in terms of visual explanation and improves the classification performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge