Martin Günther
A Scene Graph Backed Approach to Open Set Semantic Mapping
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While Open Set Semantic Mapping and 3D Semantic Scene Graphs (3DSSGs) are established paradigms in robotic perception, deploying them effectively to support high-level reasoning in large-scale, real-world environments remains a significant challenge. Most existing approaches decouple perception from representation, treating the scene graph as a derivative layer generated post hoc. This limits both consistency and scalability. In contrast, we propose a mapping architecture where the 3DSSG serves as the foundational backend, acting as the primary knowledge representation for the entire mapping process. Our approach leverages prior work on incremental scene graph prediction to infer and update the graph structure in real-time as the environment is explored. This ensures that the map remains topologically consistent and computationally efficient, even during extended operations in large-scale settings. By maintaining an explicit, spatially grounded representation that supports both flat and hierarchical topologies, we bridge the gap between sub-symbolic raw sensor data and high-level symbolic reasoning. Consequently, this provides a stable, verifiable structure that knowledge-driven frameworks, ranging from knowledge graphs and ontologies to Large Language Models (LLMs), can directly exploit, enabling agents to operate with enhanced interpretability, trustworthiness, and alignment to human concepts.
LIEREx: Language-Image Embeddings for Robotic Exploration
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Semantic maps allow a robot to reason about its surroundings to fulfill tasks such as navigating known environments, finding specific objects, and exploring unmapped areas. Traditional mapping approaches provide accurate geometric representations but are often constrained by pre-designed symbolic vocabularies. The reliance on fixed object classes makes it impractical to handle out-of-distribution knowledge not defined at design time. Recent advances in Vision-Language Foundation Models, such as CLIP, enable open-set mapping, where objects are encoded as high-dimensional embeddings rather than fixed labels. In LIEREx, we integrate these VLFMs with established 3D Semantic Scene Graphs to enable target-directed exploration by an autonomous agent in partially unknown environments.
* This preprint has not undergone peer review or any post-submission improvements or corrections. The Version of Record of this article is published in KI - Künstliche Intelligenz, and is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s13218-026-00902-6
ExPrIS: Knowledge-Level Expectations as Priors for Object Interpretation from Sensor Data
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:While deep learning has significantly advanced robotic object recognition, purely data-driven approaches often lack semantic consistency and fail to leverage valuable, pre-existing knowledge about the environment. This report presents the ExPrIS project, which addresses this challenge by investigating how knowledge-level expectations can serve as to improve object interpretation from sensor data. Our approach is based on the incremental construction of a 3D Semantic Scene Graph (3DSSG). We integrate expectations from two sources: contextual priors from past observations and semantic knowledge from external graphs like ConceptNet. These are embedded into a heterogeneous Graph Neural Network (GNN) to create an expectation-biased inference process. This method moves beyond static, frame-by-frame analysis to enhance the robustness and consistency of scene understanding over time. The report details this architecture, its evaluation, and outlines its planned integration on a mobile robotic platform.
* This preprint has not undergone peer review or any post-submission improvements or corrections. The Version of Record of this article is published in KI - Künstliche Intelligenz, and is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s13218-026-00901-7
Uncertainty-Resilient Active Intention Recognition for Robotic Assistants
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Purposeful behavior in robotic assistants requires the integration of multiple components and technological advances. Often, the problem is reduced to recognizing explicit prompts, which limits autonomy, or is oversimplified through assumptions such as near-perfect information. We argue that a critical gap remains unaddressed -- specifically, the challenge of reasoning about the uncertain outcomes and perception errors inherent to human intention recognition. In response, we present a framework designed to be resilient to uncertainty and sensor noise, integrating real-time sensor data with a combination of planners. Centered around an intention-recognition POMDP, our approach addresses cooperative planning and acting under uncertainty. Our integrated framework has been successfully tested on a physical robot with promising results.
Online Knowledge Integration for 3D Semantic Mapping: A Survey
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:Semantic mapping is a key component of robots operating in and interacting with objects in structured environments. Traditionally, geometric and knowledge representations within a semantic map have only been loosely integrated. However, recent advances in deep learning now allow full integration of prior knowledge, represented as knowledge graphs or language concepts, into sensor data processing and semantic mapping pipelines. Semantic scene graphs and language models enable modern semantic mapping approaches to incorporate graph-based prior knowledge or to leverage the rich information in human language both during and after the mapping process. This has sparked substantial advances in semantic mapping, leading to previously impossible novel applications. This survey reviews these recent developments comprehensively, with a focus on online integration of knowledge into semantic mapping. We specifically focus on methods using semantic scene graphs for integrating symbolic prior knowledge and language models for respective capture of implicit common-sense knowledge and natural language concepts
YCB-M: A Multi-Camera RGB-D Dataset for Object Recognition and 6DoF Pose Estimation
Apr 24, 2020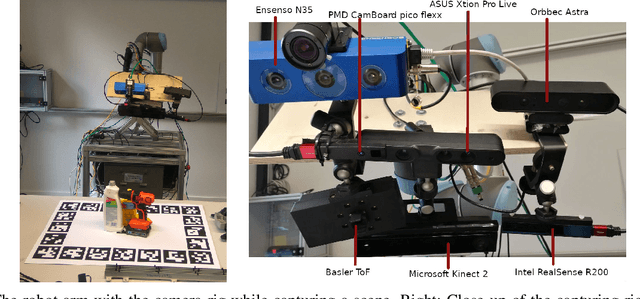


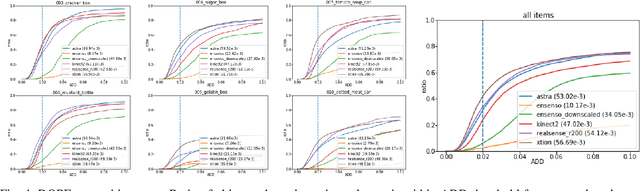
Abstract:While a great variety of 3D cameras have been introduced in recent years, most publicly available datasets for object recognition and pose estimation focus on one single camera. In this work, we present a dataset of 32 scenes that have been captured by 7 different 3D cameras, totaling 49,294 frames. This allows evaluating the sensitivity of pose estimation algorithms to the specifics of the used camera and the development of more robust algorithms that are more independent of the camera model. Vice versa, our dataset enables researchers to perform a quantitative comparison of the data from several different cameras and depth sensing technologies and evaluate their algorithms before selecting a camera for their specific task. The scenes in our dataset contain 20 different objects from the common benchmark YCB object and model set [1], [2]. We provide full ground truth 6DoF poses for each object, per-pixel segmentation, 2D and 3D bounding boxes and a measure of the amount of occlusion of each object. We have also performed an initial evaluation of the cameras using our dataset on a state-of-the-art object recognition and pose estimation system [3].
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge