Mark Selden
BotNet: A Simulator for Studying the Effects of Accurate Communication Models on Multi-agent and Swarm Control
Aug 31, 2021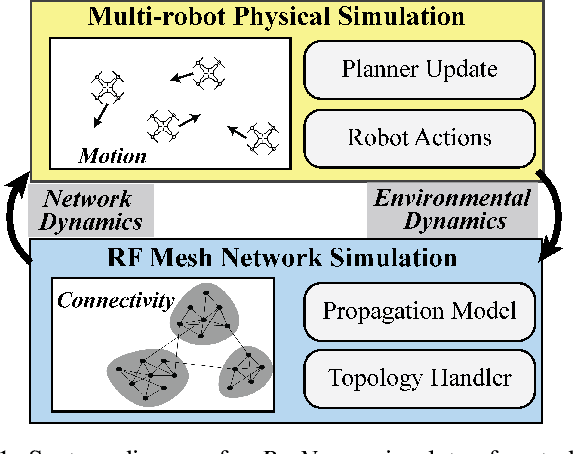
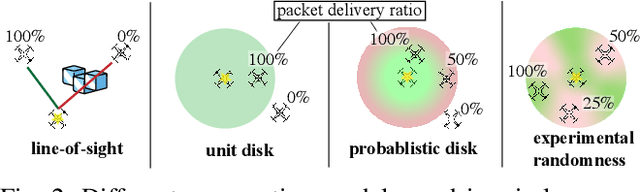
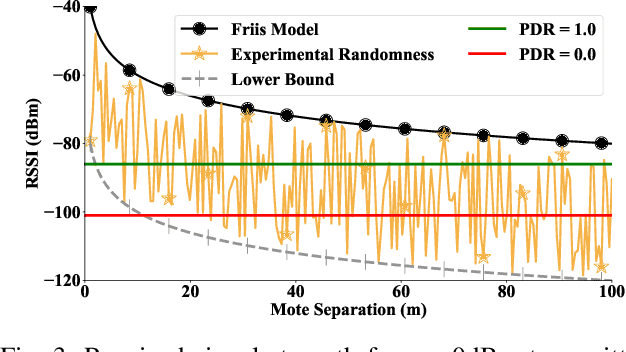
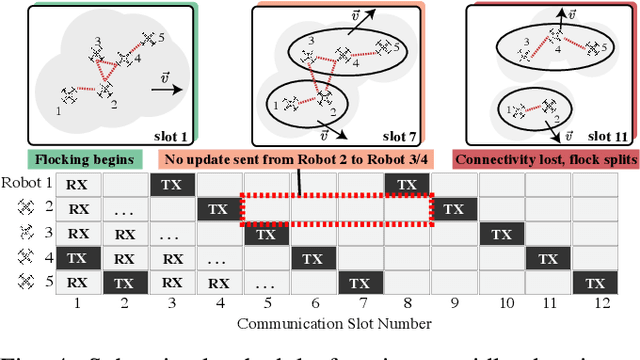
Abstract:Decentralized control in multi-robot systems is dependent on accurate and reliable communication between agents. Important communication factors, such as latency and packet delivery ratio, are strong functions of the number of agents in the network. Findings from studies of mobile and high node-count radio-frequency (RF) mesh networks have only been transferred to the domain of multi-robot systems to a limited extent, and typical multi-agent robotic simulators often depend on simple propagation models that do not reflect the behavior of realistic RF networks. In this paper, we present a new open source swarm robotics simulator, BotNet, with an embedded standards-compliant time-synchronized channel hopping (6TiSCH) RF mesh network simulator. Using this simulator we show how more accurate communications models can limit even simple multi-robot control tasks such as flocking and formation control, with agent counts ranging from 10 up to 2500 agents. The experimental results are used to motivate changes to the inter-robot communication propagation models and other networking components currently used in practice in order to bridge the sim-to-real gap.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge