Marius Aasan
SPoT: Subpixel Placement of Tokens in Vision Transformers
Jul 02, 2025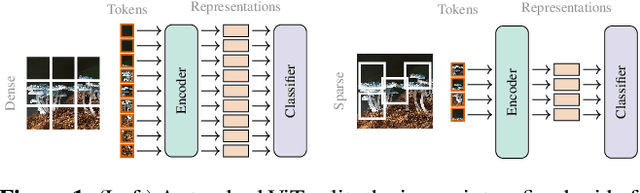
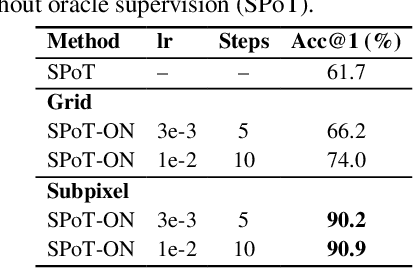
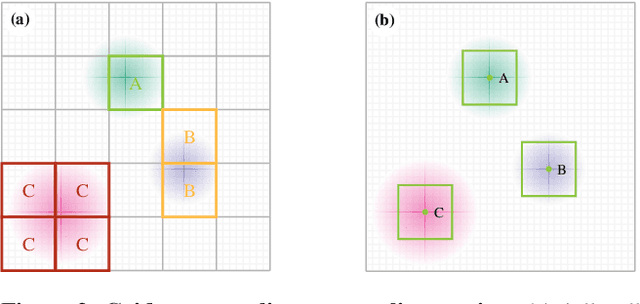
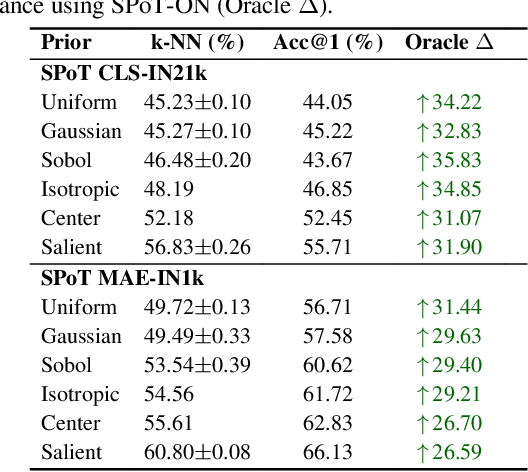
Abstract:Vision Transformers naturally accommodate sparsity, yet standard tokenization methods confine features to discrete patch grids. This constraint prevents models from fully exploiting sparse regimes, forcing awkward compromises. We propose Subpixel Placement of Tokens (SPoT), a novel tokenization strategy that positions tokens continuously within images, effectively sidestepping grid-based limitations. With our proposed oracle-guided search, we uncover substantial performance gains achievable with ideal subpixel token positioning, drastically reducing the number of tokens necessary for accurate predictions during inference. SPoT provides a new direction for flexible, efficient, and interpretable ViT architectures, redefining sparsity as a strategic advantage rather than an imposed limitation.
A Spitting Image: Modular Superpixel Tokenization in Vision Transformers
Aug 15, 2024Abstract:Vision Transformer (ViT) architectures traditionally employ a grid-based approach to tokenization independent of the semantic content of an image. We propose a modular superpixel tokenization strategy which decouples tokenization and feature extraction; a shift from contemporary approaches where these are treated as an undifferentiated whole. Using on-line content-aware tokenization and scale- and shape-invariant positional embeddings, we perform experiments and ablations that contrast our approach with patch-based tokenization and randomized partitions as baselines. We show that our method significantly improves the faithfulness of attributions, gives pixel-level granularity on zero-shot unsupervised dense prediction tasks, while maintaining predictive performance in classification tasks. Our approach provides a modular tokenization framework commensurable with standard architectures, extending the space of ViTs to a larger class of semantically-rich models.
SelfGraphVQA: A Self-Supervised Graph Neural Network for Scene-based Question Answering
Oct 03, 2023



Abstract:The intersection of vision and language is of major interest due to the increased focus on seamless integration between recognition and reasoning. Scene graphs (SGs) have emerged as a useful tool for multimodal image analysis, showing impressive performance in tasks such as Visual Question Answering (VQA). In this work, we demonstrate that despite the effectiveness of scene graphs in VQA tasks, current methods that utilize idealized annotated scene graphs struggle to generalize when using predicted scene graphs extracted from images. To address this issue, we introduce the SelfGraphVQA framework. Our approach extracts a scene graph from an input image using a pre-trained scene graph generator and employs semantically-preserving augmentation with self-supervised techniques. This method improves the utilization of graph representations in VQA tasks by circumventing the need for costly and potentially biased annotated data. By creating alternative views of the extracted graphs through image augmentations, we can learn joint embeddings by optimizing the informational content in their representations using an un-normalized contrastive approach. As we work with SGs, we experiment with three distinct maximization strategies: node-wise, graph-wise, and permutation-equivariant regularization. We empirically showcase the effectiveness of the extracted scene graph for VQA and demonstrate that these approaches enhance overall performance by highlighting the significance of visual information. This offers a more practical solution for VQA tasks that rely on SGs for complex reasoning questions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge