Marek Z. Reformat
Negated Complementary Commonsense using Large Language Models
Jul 13, 2023Abstract:Larger language models, such as GPT-3, have shown to be excellent in many tasks. However, we demonstrate that out-of-ordinary questions can throw the model off guard. This work focuses on finding answers to negated complementary questions in commonsense scenarios. We illustrate how such questions adversely affect the model responses. We propose a model-agnostic methodology to improve the performance in negated complementary scenarios. Our method outperforms few-shot generation from GPT-3 (by more than 11 points) and, more importantly, highlights the significance of studying the response of large language models in negated complementary questions. The code, data, and experiments are available under: https://github.com/navidre/negated_complementary_commonsense.
Reinforcement Learning for Topic Models
May 08, 2023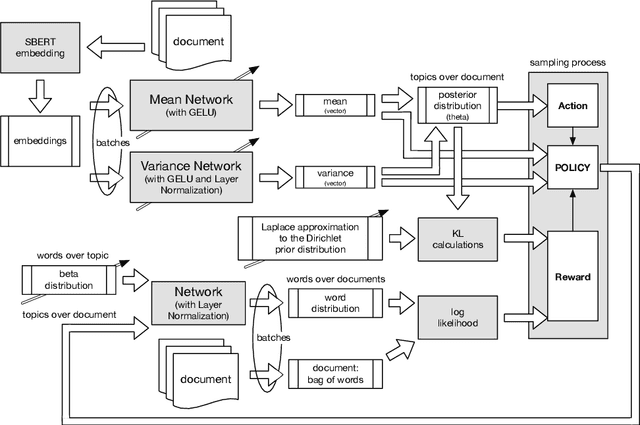
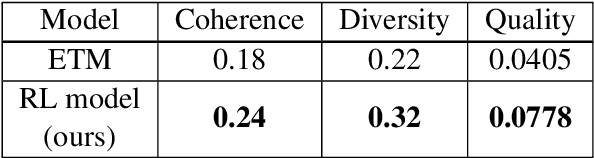
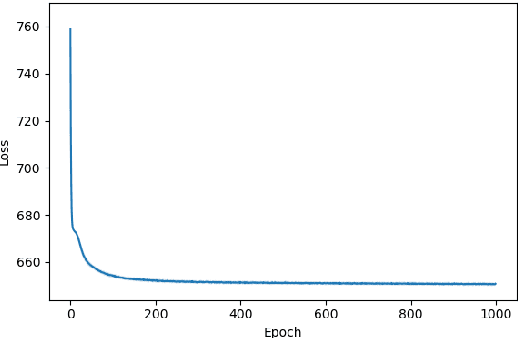
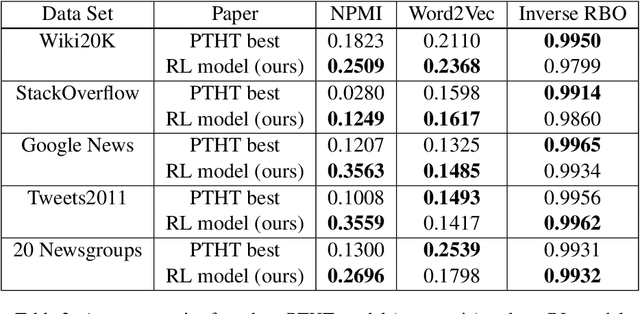
Abstract:We apply reinforcement learning techniques to topic modeling by replacing the variational autoencoder in ProdLDA with a continuous action space reinforcement learning policy. We train the system with a policy gradient algorithm REINFORCE. Additionally, we introduced several modifications: modernize the neural network architecture, weight the ELBO loss, use contextual embeddings, and monitor the learning process via computing topic diversity and coherence for each training step. Experiments are performed on 11 data sets. Our unsupervised model outperforms all other unsupervised models and performs on par with or better than most models using supervised labeling. Our model is outperformed on certain data sets by a model using supervised labeling and contrastive learning. We have also conducted an ablation study to provide empirical evidence of performance improvements from changes we made to ProdLDA and found that the reinforcement learning formulation boosts performance.
Super-Prompting: Utilizing Model-Independent Contextual Data to Reduce Data Annotation Required in Visual Commonsense Tasks
Apr 25, 2022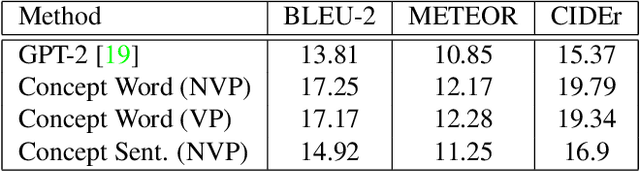

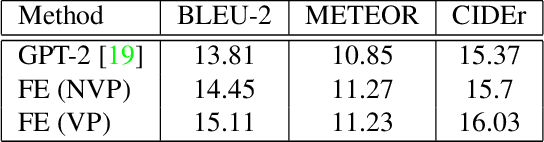
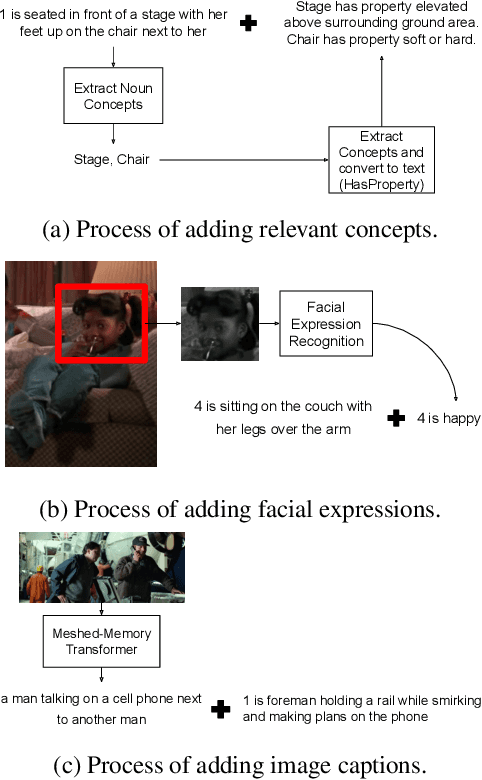
Abstract:Pre-trained language models have shown excellent results in few-shot learning scenarios using in-context learning. Although it is impressive, the size of language models can be prohibitive to make them usable in on-device applications, such as sensors or smartphones. With smaller language models, task-specific data annotation is needed to fine-tune the language model for a specific purpose. However, data annotation can have a substantial financial and time burden for small research groups, startups, and even companies. In this paper, we analyze different prompt-based fine-tuning techniques to improve results on both language and multimodal causal transformer models. To evaluate our results, we use a dataset focusing on visual commonsense reasoning in time. Our results show that by simple model-agnostic prompt-based fine-tuning, comparable results can be reached by only using 35%-40% of the fine-tuning training dataset. The proposed approaches result in significant time and financial savings. As the proposed methods make minimal architectural assumptions, other researchers can use the results in their transformer models with minimal adaptations. We plan to release the source code freely to make it easier for the community to use and contribute to our work.
Analysis of Word Embeddings using Fuzzy Clustering
Jul 20, 2019
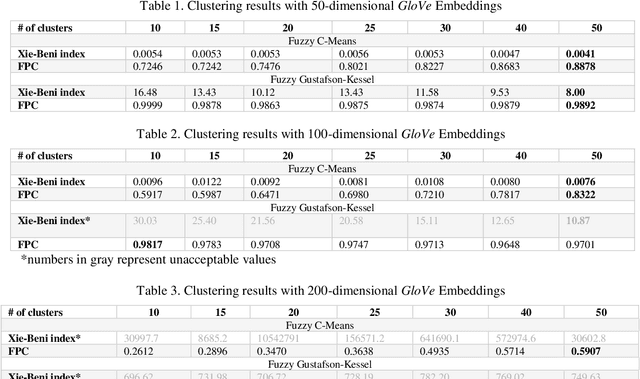
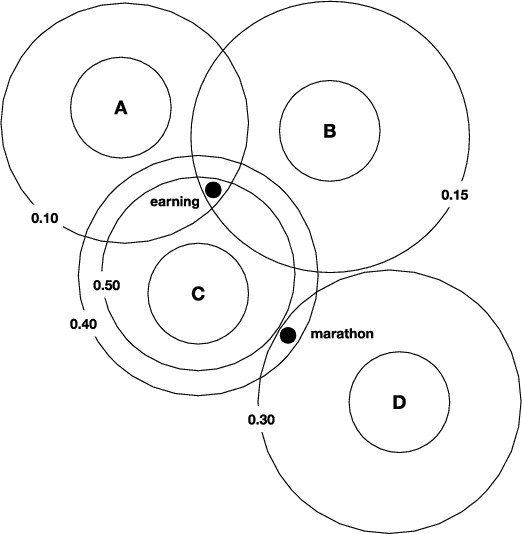
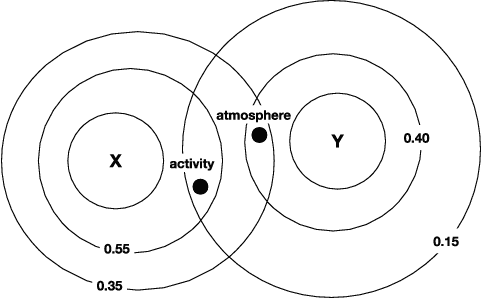
Abstract:In data dominated systems and applications, a concept of representing words in a numerical format has gained a lot of attention. There are a few approaches used to generate such a representation. An interesting issue that should be considered is the ability of such representations - called embeddings - to imitate human-based semantic similarity between words. In this study, we perform a fuzzy-based analysis of vector representations of words, i.e., word embeddings. We use two popular fuzzy clustering algorithms on count-based word embeddings, known as GloVe, of different dimensionality. Words from WordSim-353, called the gold standard, are represented as vectors and clustered. The results indicate that fuzzy clustering algorithms are very sensitive to high-dimensional data, and parameter tuning can dramatically change their performance. We show that by adjusting the value of the fuzzifier parameter, fuzzy clustering can be successfully applied to vectors of high - up to one hundred - dimensions. Additionally, we illustrate that fuzzy clustering allows to provide interesting results regarding membership of words to different clusters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge