Marcos Tamargo-Arizmendi
Domain-Adaptive Neural Posterior Estimation for Strong Gravitational Lens Analysis
Oct 21, 2024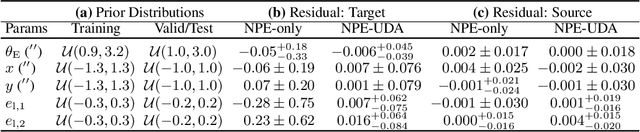
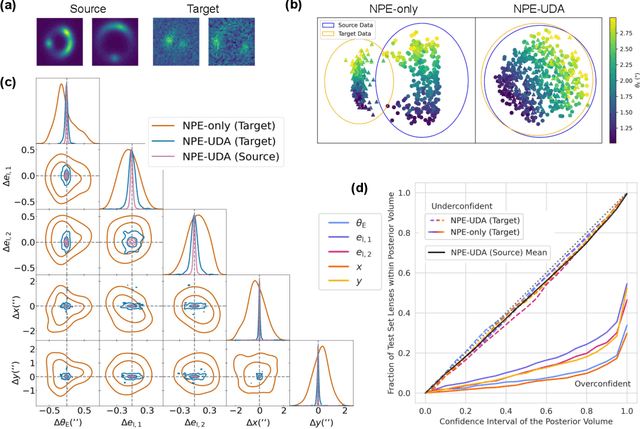
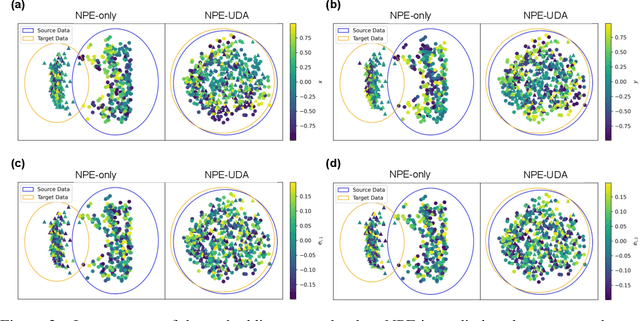
Abstract:Modeling strong gravitational lenses is prohibitively expensive for modern and next-generation cosmic survey data. Neural posterior estimation (NPE), a simulation-based inference (SBI) approach, has been studied as an avenue for efficient analysis of strong lensing data. However, NPE has not been demonstrated to perform well on out-of-domain target data -- e.g., when trained on simulated data and then applied to real, observational data. In this work, we perform the first study of the efficacy of NPE in combination with unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA). The source domain is noiseless, and the target domain has noise mimicking modern cosmology surveys. We find that combining UDA and NPE improves the accuracy of the inference by 1-2 orders of magnitude and significantly improves the posterior coverage over an NPE model without UDA. We anticipate that this combination of approaches will help enable future applications of NPE models to real observational data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge