Marcelo M Mattar
Visual scoping operations for physical assembly
Jun 10, 2021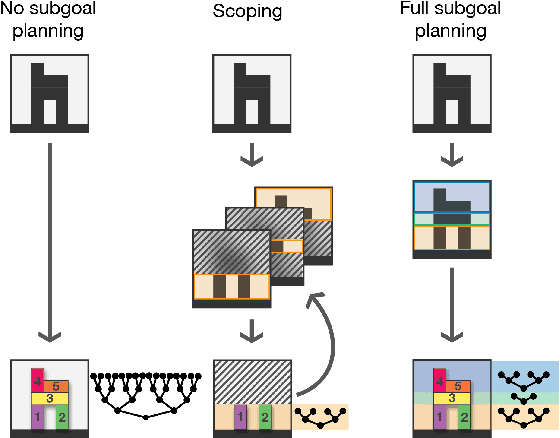
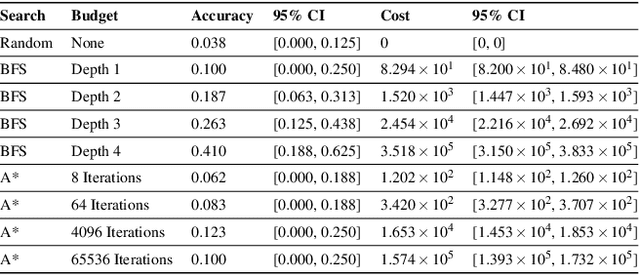
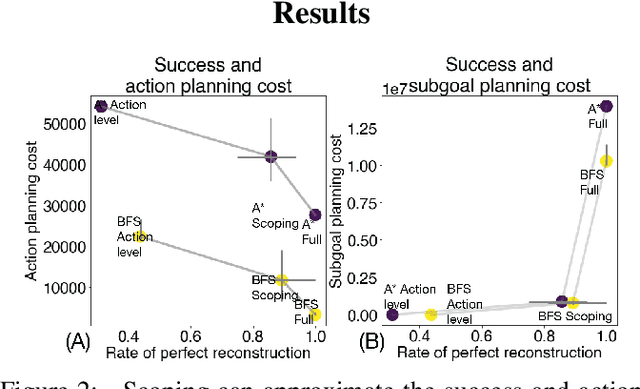
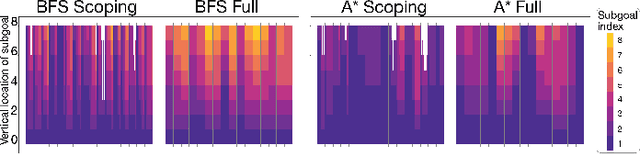
Abstract:Planning is hard. The use of subgoals can make planning more tractable, but selecting these subgoals is computationally costly. What algorithms might enable us to reap the benefits of planning using subgoals while minimizing the computational overhead of selecting them? We propose visual scoping, a strategy that interleaves planning and acting by alternately defining a spatial region as the next subgoal and selecting actions to achieve it. We evaluated our visual scoping algorithm on a variety of physical assembly problems against two baselines: planning all subgoals in advance and planning without subgoals. We found that visual scoping achieves comparable task performance to the subgoal planner while requiring only a fraction of the total computational cost. Together, these results contribute to our understanding of how humans might make efficient use of cognitive resources to solve complex planning problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge