Marc Spigai
TAS
A Cycle GAN Approach for Heterogeneous Domain Adaptation in Land Use Classification
Apr 22, 2020
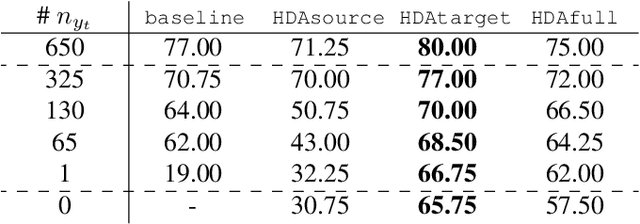


Abstract:In the field of remote sensing and more specifically in Earth Observation, new data are available every day, coming from different sensors. Leveraging on those data in classification tasks comes at the price of intense labelling tasks that are not realistic in operational settings. While domain adaptation could be useful to counterbalance this problem, most of the usual methods assume that the data to adapt are comparable (they belong to the same metric space), which is not the case when multiple sensors are at stake. Heterogeneous domain adaptation methods are a particular solution to this problem. We present a novel method to deal with such cases, based on a modified cycleGAN version that incorporates classification losses and a metric space alignment term. We demonstrate its power on a land use classification tasks, with images from both Google Earth and Sentinel-2.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge