Manuele Bicego
On the Probabilistic Learnability of Compact Neural Network Preimage Bounds
Nov 10, 2025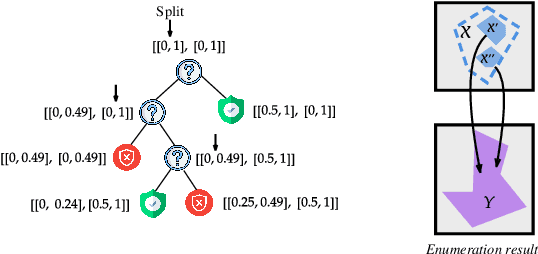
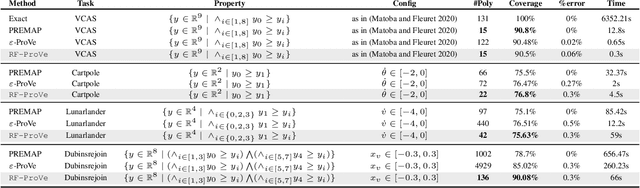
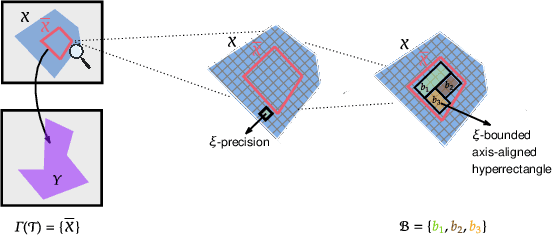
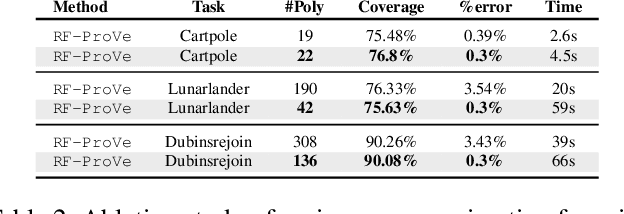
Abstract:Although recent provable methods have been developed to compute preimage bounds for neural networks, their scalability is fundamentally limited by the #P-hardness of the problem. In this work, we adopt a novel probabilistic perspective, aiming to deliver solutions with high-confidence guarantees and bounded error. To this end, we investigate the potential of bootstrap-based and randomized approaches that are capable of capturing complex patterns in high-dimensional spaces, including input regions where a given output property holds. In detail, we introduce $\textbf{R}$andom $\textbf{F}$orest $\textbf{Pro}$perty $\textbf{Ve}$rifier ($\texttt{RF-ProVe}$), a method that exploits an ensemble of randomized decision trees to generate candidate input regions satisfying a desired output property and refines them through active resampling. Our theoretical derivations offer formal statistical guarantees on region purity and global coverage, providing a practical, scalable solution for computing compact preimage approximations in cases where exact solvers fail to scale.
Null/No Information Rate : a statistical test to assess if a classification accuracy is significant for a given problem
Jun 09, 2023Abstract:In many research contexts, especially in the biomedical field, after studying and developing a classification system a natural question arises: "Is this accuracy enough high?", or better, "Can we say, with a statistically significant confidence, that our classification system is able to solve the problem"? To answer to this question, we can use the statistical test described in this paper, which is referred in some cases as NIR (No Information Rate or Null Information Rate).
Feature Level Fusion of Face and Fingerprint Biometrics
Feb 12, 2010
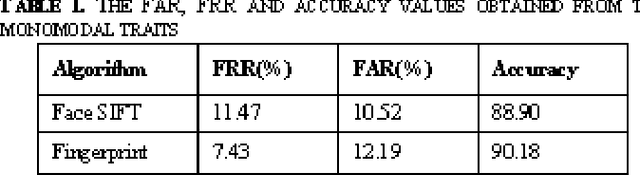

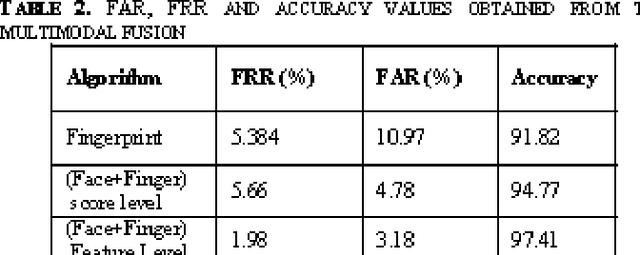
Abstract:The aim of this paper is to study the fusion at feature extraction level for face and fingerprint biometrics. The proposed approach is based on the fusion of the two traits by extracting independent feature pointsets from the two modalities, and making the two pointsets compatible for concatenation. Moreover, to handle the problem of curse of dimensionality, the feature pointsets are properly reduced in dimension. Different feature reduction techniques are implemented, prior and after the feature pointsets fusion, and the results are duly recorded. The fused feature pointset for the database and the query face and fingerprint images are matched using techniques based on either the point pattern matching, or the Delaunay triangulation. Comparative experiments are conducted on chimeric and real databases, to assess the actual advantage of the fusion performed at the feature extraction level, in comparison to the matching score level.
* 6 pages, 7 figures, conference
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge