Manoj Penmetcha
A Predictive Application Offloading Algorithm Using Small Datasets for Cloud Robotics
Aug 28, 2021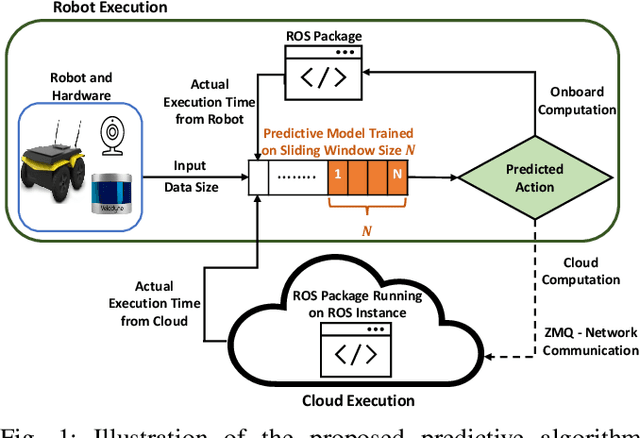
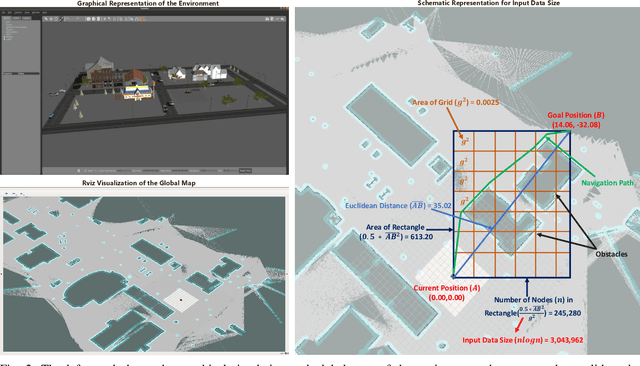
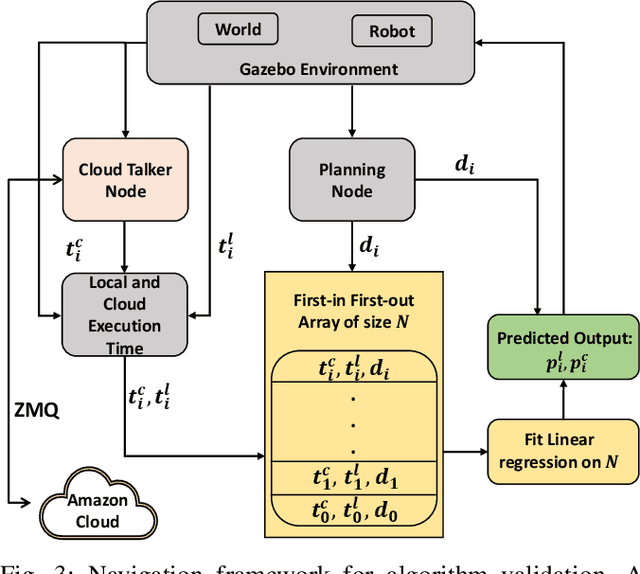
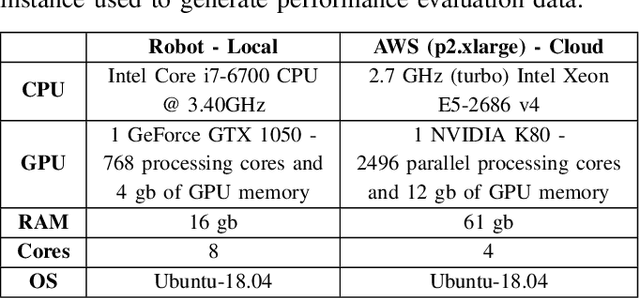
Abstract:Many robotic applications that are critical for robot performance require immediate feedback, hence execution time is a critical concern. Furthermore, it is common that robots come with a fixed quantity of hardware resources; if an application requires more computational resources than the robot can accommodate, its onboard execution might be extended to a degree that degrades the robot performance. Cloud computing, on the other hand, features on-demand computational resources; by enabling robots to leverage those resources, application execution time can be reduced. The key to enabling robot use of cloud computing is designing an efficient offloading algorithm that makes optimum use of the robot onboard capabilities and also forms a quick consensus on when to offload without any prior knowledge or information about the application. In this paper, we propose a predictive algorithm to anticipate the time needed to execute an application for a given application data input size with the help of a small number of previous observations. To validate the algorithm, we train it on the previous N observations, which include independent (input data size) and dependent (execution time) variables. To understand how algorithm performance varies in terms of prediction accuracy and error, we tested various N values using linear regression and a mobile robot path planning application. From our experiments and analysis, we determined the algorithm to have acceptable error and prediction accuracy when N>40.
Smart Cloud: Scalable Cloud Robotic Architecture for Web-powered Multi-Robot Applications
Dec 09, 2019



Abstract:Robots have inherently limited onboard processing, storage, and power capabilities. Cloud computing resources have the potential to provide significant advantages for robots in many applications. However, to make use of these resources, frameworks must be developed that facilitate robot interactions with cloud services. In this paper, we propose a cloud-based architecture called Smart Cloud that intends to overcome the physical limitations of single- or multi-robot systems through massively parallel computation, provided on demand by cloud services. Smart Cloud is implemented on Amazon Web Services (AWS) and available for robots running on the Robot Operating System (ROS) and on non-ROS systems. Smart Cloud features a first-of-its-kind architecture that incorporates JavaScript-based libraries to run various robotic applications related to machine learning and other methods. This paper presents the architecture and its performance in terms of CPU power usage, latency, and security, and finally validates it for navigation and machine learning applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge