Manita Pote
Coordinated Reply Attacks in Influence Operations: Characterization and Detection
Oct 25, 2024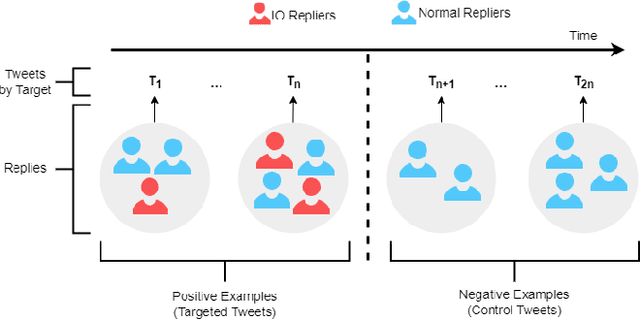
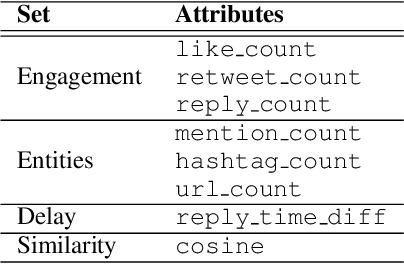
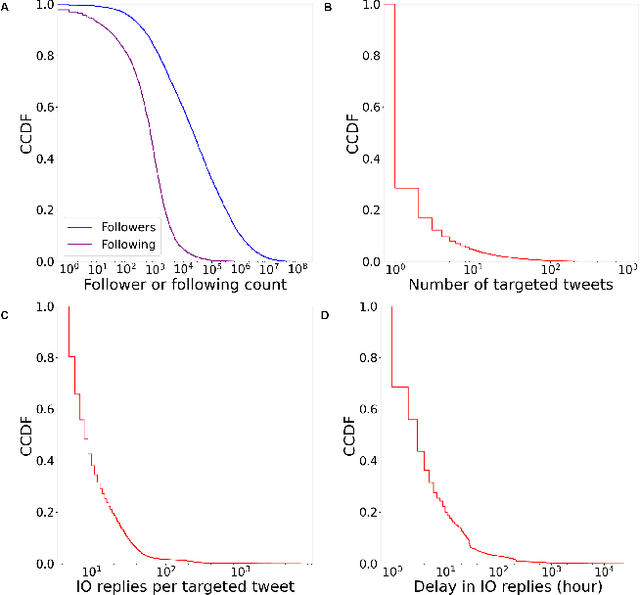
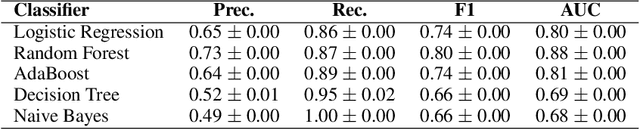
Abstract:Coordinated reply attacks are a tactic observed in online influence operations and other coordinated campaigns to support or harass targeted individuals, or influence them or their followers. Despite its potential to influence the public, past studies have yet to analyze or provide a methodology to detect this tactic. In this study, we characterize coordinated reply attacks in the context of influence operations on Twitter. Our analysis reveals that the primary targets of these attacks are influential people such as journalists, news media, state officials, and politicians. We propose two supervised machine-learning models, one to classify tweets to determine whether they are targeted by a reply attack, and one to classify accounts that reply to a targeted tweet to determine whether they are part of a coordinated attack. The classifiers achieve AUC scores of 0.88 and 0.97, respectively. These results indicate that accounts involved in reply attacks can be detected, and the targeted accounts themselves can serve as sensors for influence operation detection.
Survey on Embedding Models for Knowledge Graph and its Applications
Apr 14, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge Graph (KG) is a graph based data structure to represent facts of the world where nodes represent real world entities or abstract concept and edges represent relation between the entities. Graph as representation for knowledge has several drawbacks like data sparsity, computational complexity and manual feature engineering. Knowledge Graph embedding tackles the drawback by representing entities and relation in low dimensional vector space by capturing the semantic relation between them. There are different KG embedding models. Here, we discuss translation based and neural network based embedding models which differ based on semantic property, scoring function and architecture they use. Further, we discuss application of KG in some domains that use deep learning models and leverage social media data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge