Manisha
Robust Prediction Model for Multidimensional and Unbalanced Datasets
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:Data Mining is a promising field and is applied in multiple domains for its predictive capabilities. Data in the real world cannot be readily used for data mining as it suffers from the problems of multidimensionality, unbalance and missing values. It is difficult to use its predictive capabilities by novice users. It is difficult for a beginner to find the relevant set of attributes from a large pool of data available. The paper presents a Robust Prediction Model that finds a relevant set of attributes; resolves the problems of unbalanced and multidimensional real-life datasets and helps in finding patterns for informed decision making. Model is tested upon five different datasets in the domain of Health Sector, Education, Business and Fraud Detection. The results showcase the robust behaviour of the model and its applicability in various domains.
CBRW: A Novel Approach for Cancelable Biometric Template Generation based on
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:Cancelable Biometric is a challenging research field in which security of an original biometric image is ensured by transforming the original biometric into another irreversible domain. Several approaches have been suggested in literature for generating cancelable biometric templates. In this paper, two novel and simple cancelable biometric template generation methods based on Random Walk (CBRW) have been proposed. By employing random walk and other steps given in the proposed two algorithms viz. CBRW-BitXOR and CBRW-BitCMP, the original biometric is transformed into a cancellable template. The performance of the proposed methods is compared with other state-of-the-art methods. Experiments have been performed on eight publicly available gray and color datasets i.e. CP (ear) (gray and color), UTIRIS (iris) (gray and color), ORL (face) (gray), IIT Delhi (iris) (gray and color), and AR (face) (color). Performance of the generated templates is measured in terms of Correlation Coefficient (Cr), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR), Structural Similarity (SSIM), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Number of Pixel Change Rate (NPCR), and Unified Average Changing Intensity (UACI). By experimental results, it has been proved that proposed methods are superior than other state-of-the-art methods in qualitative as well as quantitative analysis. Furthermore, CBRW performs better on both gray as well as color images.
On Generating Cancelable Biometric Template using Reverse of Boolean XOR
Apr 23, 2024



Abstract:Cancelable Biometric is repetitive distortion embedded in original Biometric image for keeping it secure from unauthorized access. In this paper, we have generated Cancelable Biometric templates with Reverse Boolean XOR technique. Three different methods have been proposed for generation of Cancelable Biometric templates based on Visual Secret Sharing scheme. In each method, one Secret image and n-1 Cover images are used as: (M1) One original Biometric image (Secret) with n- 1 randomly chosen Gray Cover images (M2) One original Secret image with n-1 Cover images, which are Randomly Permuted version of the original Secret image (M3) One Secret image with n-1 Cover images, both Secret image and Cover images are Randomly Permuted version of original Biometric image. Experiment works have performed on publicly available ORL Face database and IIT Delhi Iris database. The performance of the proposed methods is compared in terms of Co-relation Coefficient (Cr), Mean Square Error (MSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Structural Similarity (SSIM), Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR), Number of Pixel Change Rate (NPCR), and Unified Average Changing Intensity (UACI). It is found that among the three proposed method, M3 generates good quality Cancelable templates and gives best performance in terms of quality. M3 is also better in quantitative terms on ORL dataset while M2 and M3 are comparable on IIT Delhi Iris dataset.
Randomness assisted in-line holography with deep learning
Mar 30, 2023Abstract:We propose and demonstrate a holographic imaging scheme exploiting random illuminations for recording hologram and then applying numerical reconstruction and twin removal. We use an in-line holographic geometry to record the hologram in terms of the second-order correlation and apply the numerical approach to reconstruct the recorded hologram. The twin image issue of the in-line holographic scheme is resolved by an unsupervised deep learning(DL) based method using an auto-encoder scheme. This strategy helps to reconstruct high-quality quantitative images in comparison to the conventional holography where the hologram is recorded in the intensity rather than the second-order intensity correlation. Experimental results are presented for two objects, and a comparison of the reconstruction quality is given between the conventional inline holography and the one obtained with the proposed technique.
Reconstructing complex field through opaque scattering layer with structured light illumination
May 19, 2022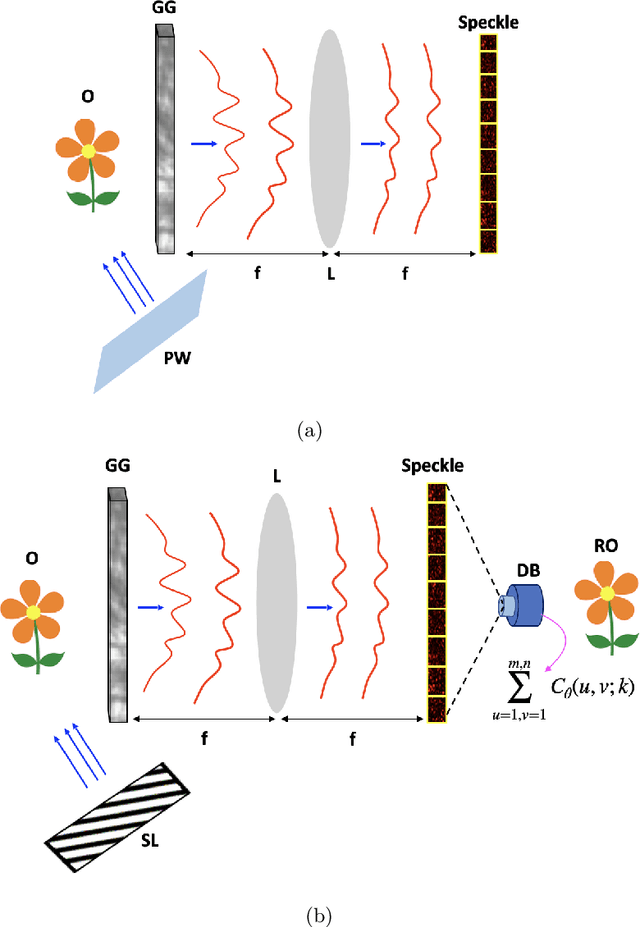
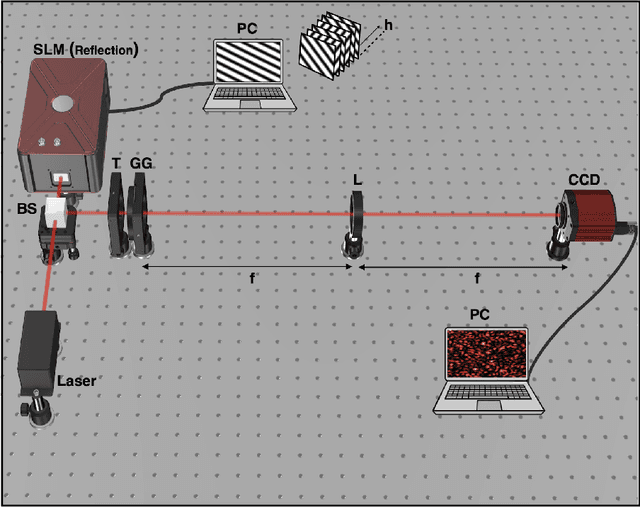
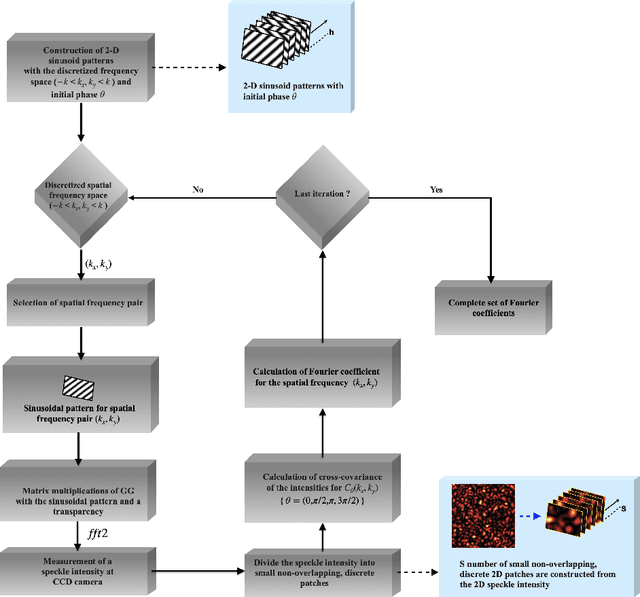
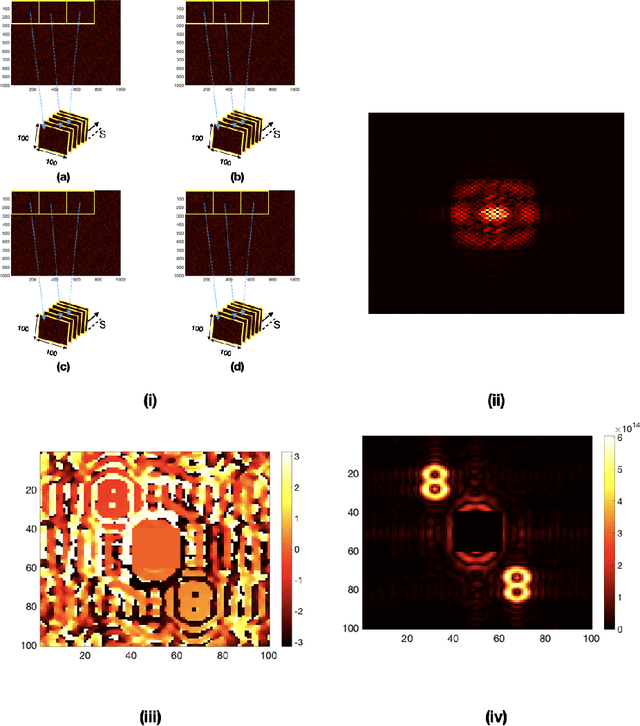
Abstract:The wavefront is scrambled when coherent light propagates through a random scattering medium and which makes direct use of the conventional optical methods ineffective. In this paper, we propose and demonstrate a structured light illumination for imaging through an opaque scattering layer. Proposed technique is reference free and capable to recover the complex field from intensities of the speckle patterns. This is realized by making use of the phase-shifting in the structured light illumination and applying spatial averaging of the speckle pattern in the intensity correlation measurement. An experimental design is presented and simulated results based on the experimental design are shown to demonstrate imaging of different complex-valued objects through scattering layer.
Beyond PRNU: Learning Robust Device-Specific Fingerprint for Source Camera Identification
Nov 03, 2021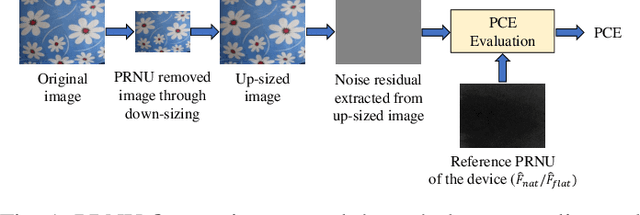
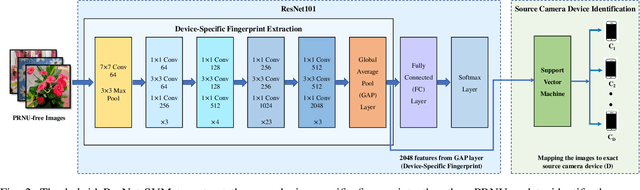
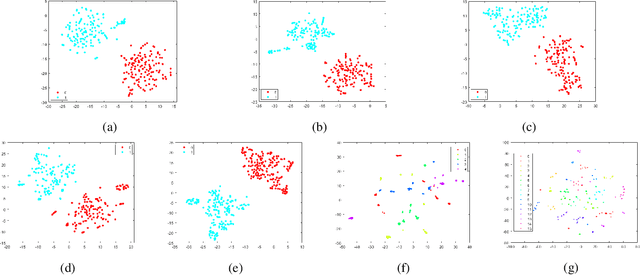
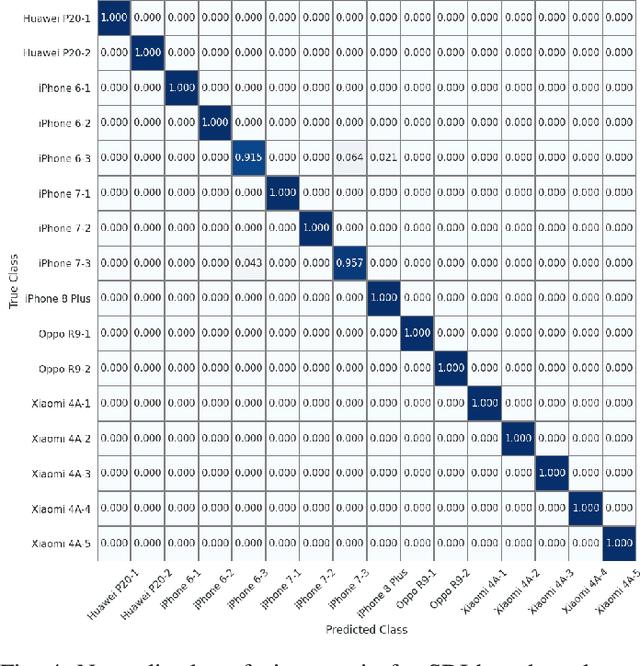
Abstract:Source camera identification tools assist image forensic investigators to associate an image in question with a suspect camera. Various techniques have been developed based on the analysis of the subtle traces left in the images during the acquisition. The Photo Response Non Uniformity (PRNU) noise pattern caused by sensor imperfections has been proven to be an effective way to identify the source camera. The existing literature suggests that the PRNU is the only fingerprint that is device-specific and capable of identifying the exact source device. However, the PRNU is susceptible to camera settings, image content, image processing operations, and counter-forensic attacks. A forensic investigator unaware of counter-forensic attacks or incidental image manipulations is at the risk of getting misled. The spatial synchronization requirement during the matching of two PRNUs also represents a major limitation of the PRNU. In recent years, deep learning based approaches have been successful in identifying source camera models. However, the identification of individual cameras of the same model through these data-driven approaches remains unsatisfactory. In this paper, we bring to light the existence of a new robust data-driven device-specific fingerprint in digital images which is capable of identifying the individual cameras of the same model. It is discovered that the new device fingerprint is location-independent, stochastic, and globally available, which resolve the spatial synchronization issue. Unlike the PRNU, which resides in the high-frequency band, the new device fingerprint is extracted from the low and mid-frequency bands, which resolves the fragility issue that the PRNU is unable to contend with. Our experiments on various datasets demonstrate that the new fingerprint is highly resilient to image manipulations such as rotation, gamma correction, and aggressive JPEG compression.
Role of Secondary Attributes to Boost the Prediction Accuracy of Students Employability Via Data Mining
Aug 09, 2017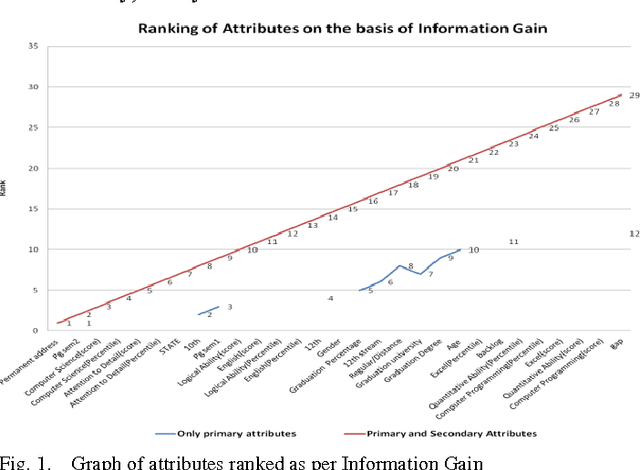
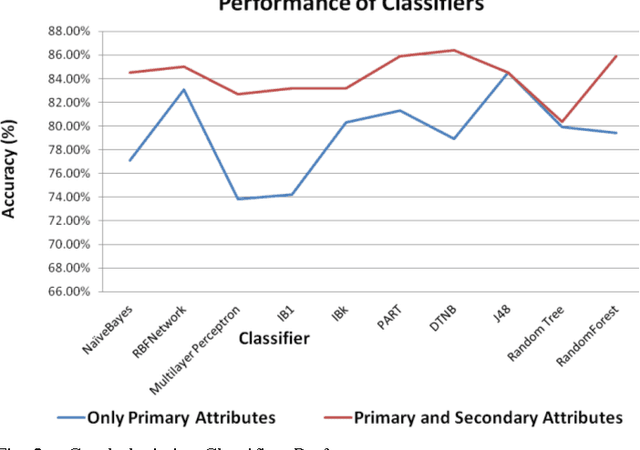
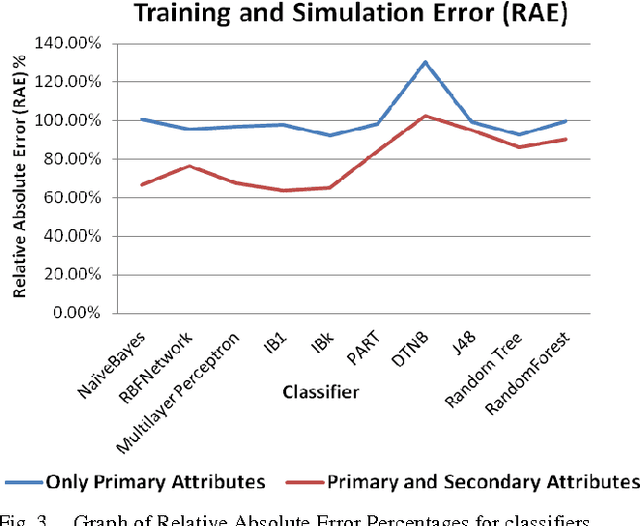
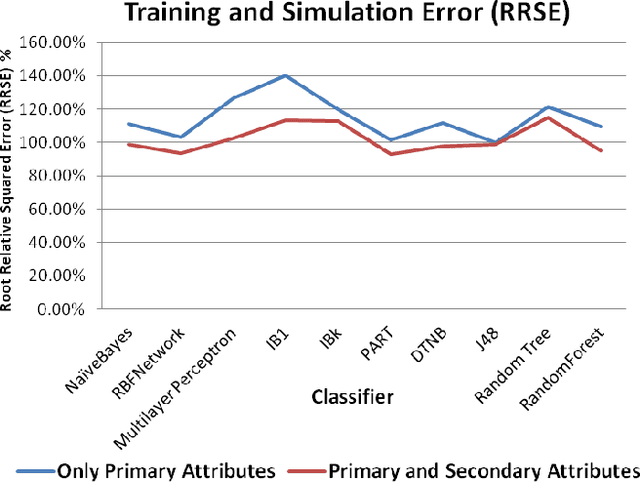
Abstract:Data Mining is best-known for its analytical and prediction capabilities. It is used in several areas such as fraud detection, predicting client behavior, money market behavior, bankruptcy prediction. It can also help in establishing an educational ecosystem, which discovers useful knowledge, and assist educators to take proactive decisions to boost student performance and employability. This paper presents an empirical study that compares varied classification algorithms on two datasets of MCA (Masters in Computer Applications) students collected from various affiliated colleges of a reputed state university in India. One dataset includes only primary attributes, whereas other dataset is feeded with secondary psychometric attributes in it. The results showcase that solely primary academic attributes do not lead to smart prediction accuracy of students employability, once they square measure within the initial year of their education. The study analyzes and stresses the role of secondary psychometric attributes for better prediction accuracy and analysis of students performance. Timely prediction and analysis of students performance can help Management, Teachers and Students to work on their gray areas for better results and employment opportunities.
* 7 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge