Manav Kohli
Channel and Spectrum Consumption Models for Urban Outdoor-to-Outdoor 28 GHz Wireless
Mar 14, 2025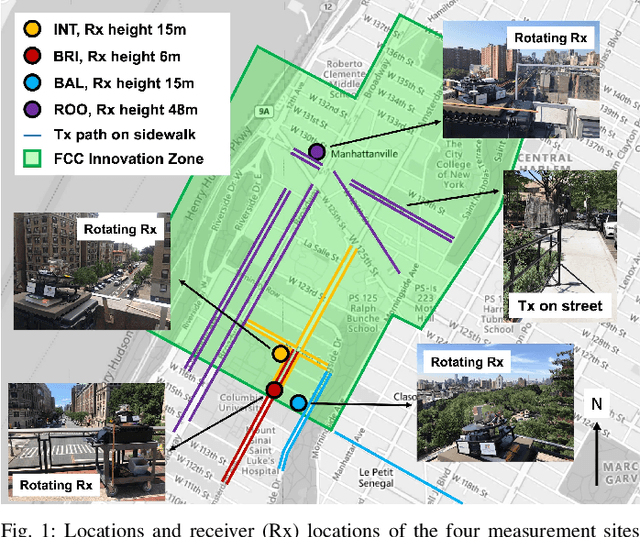
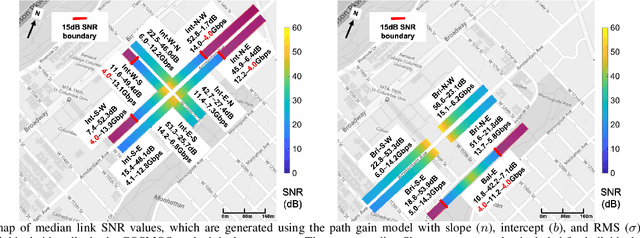
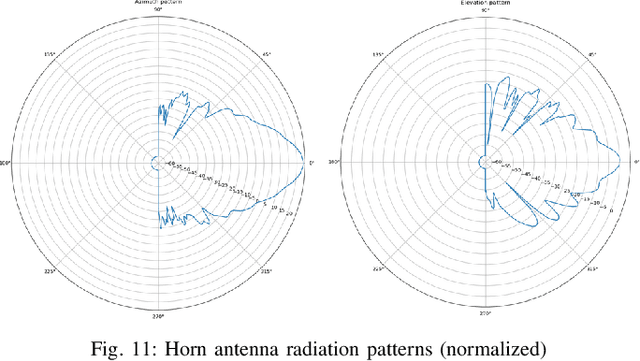
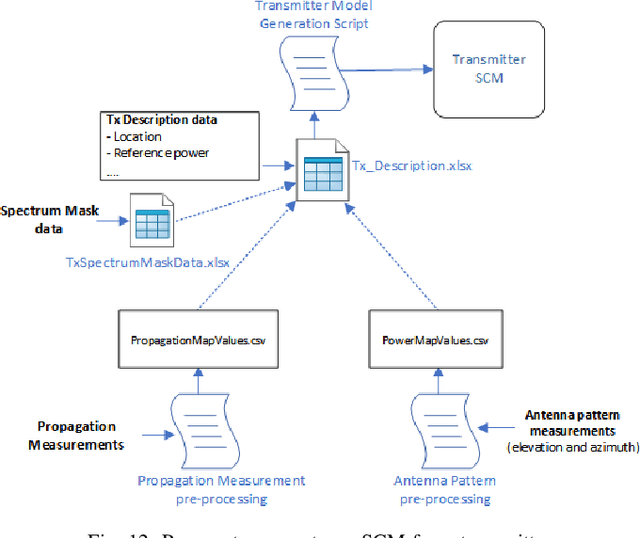
Abstract:Next generation wireless and mobile networks will utilize millimeter-wave (mmWave) communication to achieve significantly increased data rates. However, since mmWave radio signals experience high path loss, the operation of mmWave networks will require accurate channel models designed for specific deployment sites. In this paper, we focus on the deployment area of the PAWR COSMOS testbed in New York City and report extensive 28 GHz channel measurements. These include over 46 million power measurements collected from over 3,000 links on 24 sidewalks at 4 different sites and in different settings. Using these measurements, we study the effects of the setup and environments (e.g., transmitter height and seasonal effects). We then discuss the obtained path gain values and their fitted lines, and the resulting effective azimuth beamforming gain. Based on these results, we also study the link SNR values that can be supported on individual sidewalks and the corresponding theoretically achievable data rates. Finally, we develop a process to transform the measurements and generate Spectrum Consumption Models (SCMs) based on the IEEE 1900.5.2 standard. The generated SCMs facilitate the evaluation of spectrum sharing and interference management scenarios since they capture all the directional propagation effects reflected in the measurements and provide a way to easily share the main propagation characterization results derived from the measurements. We believe that the results can inform the COSMOS testbed deployment process and provide a benchmark for other deployment efforts in dense urban areas.
Design and Testbed Deployment of Frequency-Domain Equalization Full Duplex Radios
Jan 31, 2024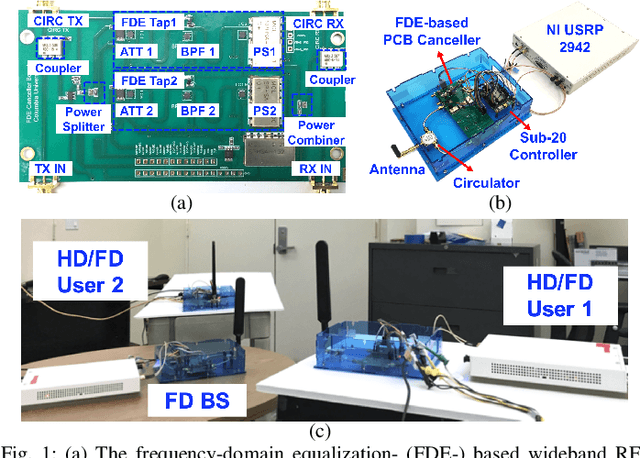
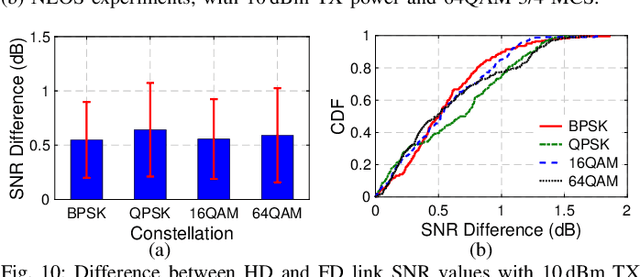
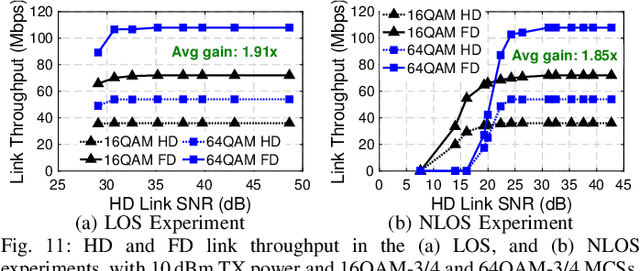
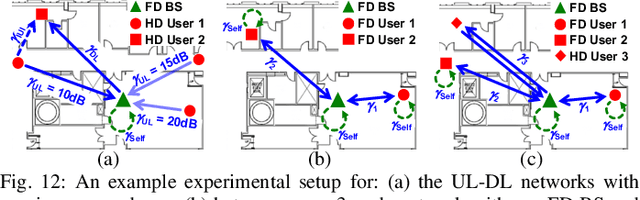
Abstract:Full-duplex (FD) wireless can significantly enhance spectrum efficiency but requires effective self-interference (SI) cancellers. RF SI cancellation (SIC) via frequency-domain equalization (FDE), where bandpass filters channelize the SI, is suited for integrated circuits (ICs). In this paper, we explore the limits and higher layer challenges associated with using such cancellers. We evaluate the performance of a custom FDE-based canceller using two testbeds; one with mobile FD radios and the other with upgraded, static FD radios in the PAWR COSMOS testbed. The latter is a lasting artifact for the research community, alongside a dataset containing baseband waveforms captured on the COSMOS FD radios, facilitating FD-related experimentation at the higher networking layers. We evaluate the performance of the FDE-based FD radios in both testbeds, with experiments showing 95 dB overall achieved SIC (52 dB from RF SIC) across 20 MHz bandwidth, and an average link-level FD rate gain of 1.87x. We also conduct experiments in (i) uplink-downlink networks with inter-user interference, and (ii) heterogeneous networks with half-duplex and FD users. The experimental FD gains in the two types of networks depend on the users' SNR values and the number of FD users, and are 1.14x-1.25x and 1.25x-1.73x, respectively, confirming previous analytical results.
Outdoor-to-Indoor 28 GHz Wireless Measurements in Manhattan: Path Loss, Environmental Effects, and 90% Coverage
May 19, 2022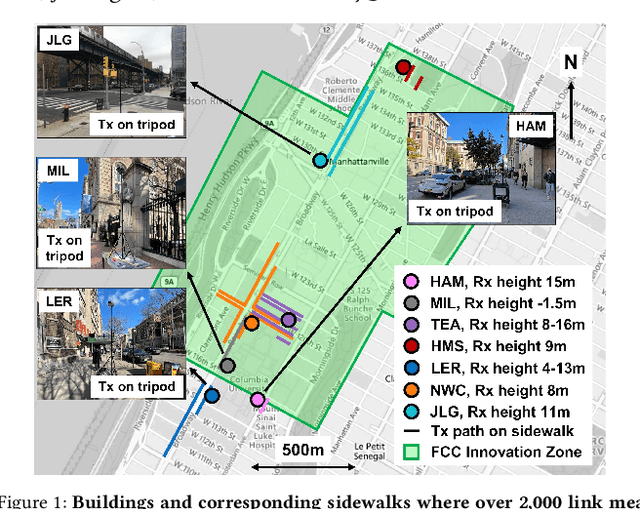
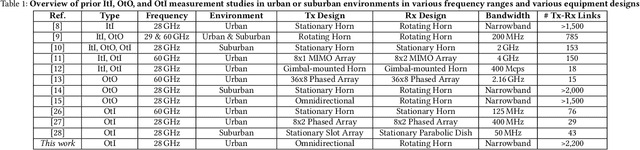
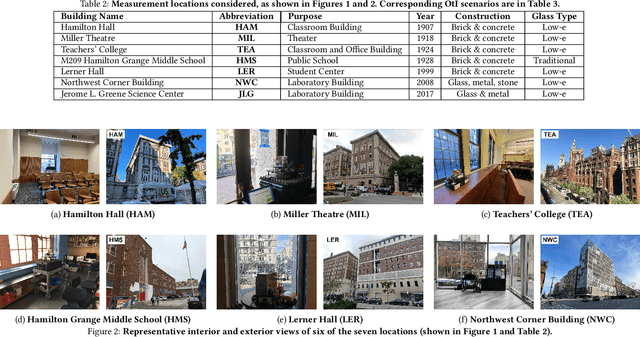
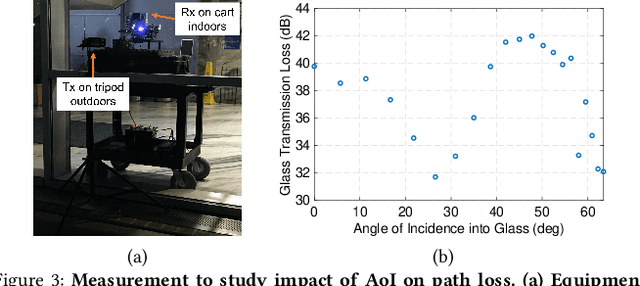
Abstract:Outdoor-to-indoor (OtI) signal propagation further challenges the already tight link budgets at millimeter-wave (mmWave). To gain insight into OtI mmWave scenarios at 28 GHz, we conducted an extensive measurement campaign consisting of over 2,200 link measurements. In total, 43 OtI scenarios were measured in West Harlem, New York City, covering seven highly diverse buildings. The measured OtI path gain can vary by up to 40 dB for a given link distance, and the empirical path gain model for all data shows an average of 30 dB excess loss over free space at distances beyond 50 m, with an RMS fitting error of 11.7 dB. The type of glass is found to be the single dominant feature for OtI loss, with 20 dB observed difference between empirical path gain models for scenarios with low-loss and high-loss glass. The presence of scaffolding, tree foliage, or elevated subway tracks, as well as difference in floor height are each found to have an impact between 5-10 dB. We show that for urban buildings with high-loss glass, OtI coverage can support 500 Mbps for 90% of indoor user equipment (UEs) with a base station (BS) antenna placed up to 49 m away. For buildings with low-loss glass, such as our case study covering multiple classrooms of a public school, data rates over 2.5/1.2 Gbps are possible from a BS 68/175 m away from the school building, when a line-of-sight path is available. We expect these results to be useful for the deployment of mmWave networks in dense urban environments as well as the development of relevant scheduling and beam management algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge