Man-Sheng Chen
Dual Information Enhanced Multi-view Attributed Graph Clustering
Nov 28, 2022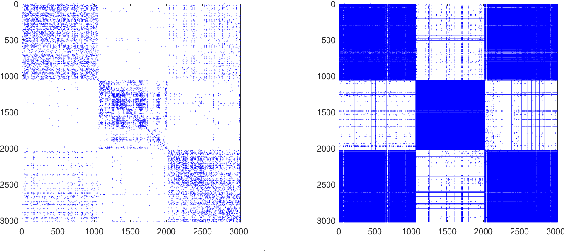
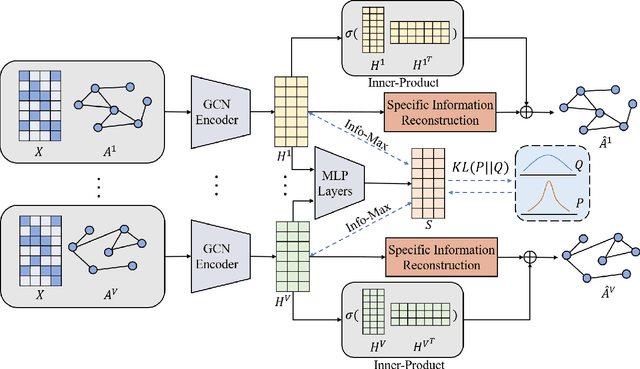
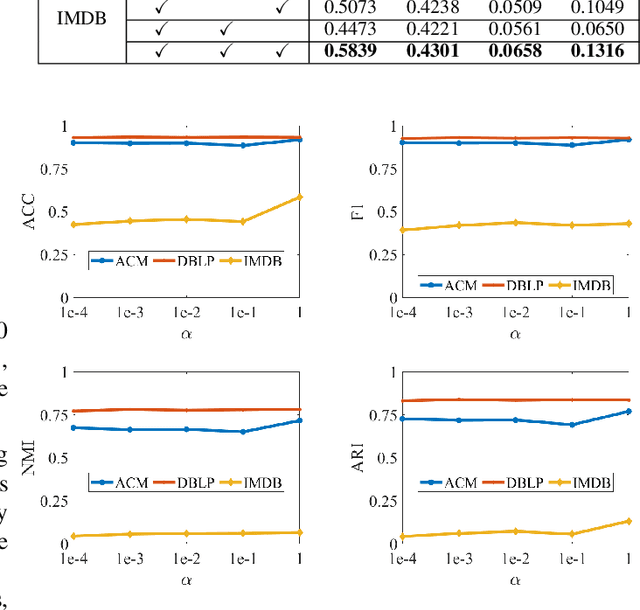
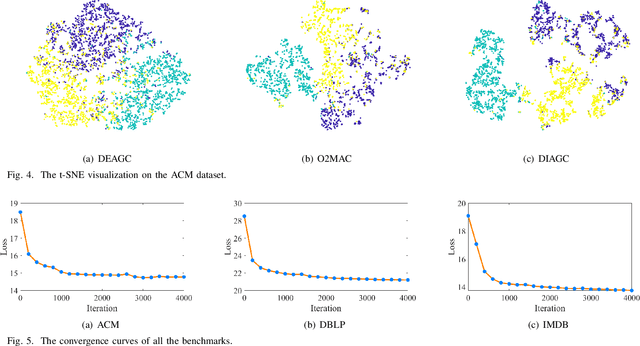
Abstract:Multi-view attributed graph clustering is an important approach to partition multi-view data based on the attribute feature and adjacent matrices from different views. Some attempts have been made in utilizing Graph Neural Network (GNN), which have achieved promising clustering performance. Despite this, few of them pay attention to the inherent specific information embedded in multiple views. Meanwhile, they are incapable of recovering the latent high-level representation from the low-level ones, greatly limiting the downstream clustering performance. To fill these gaps, a novel Dual Information enhanced multi-view Attributed Graph Clustering (DIAGC) method is proposed in this paper. Specifically, the proposed method introduces the Specific Information Reconstruction (SIR) module to disentangle the explorations of the consensus and specific information from multiple views, which enables GCN to capture the more essential low-level representations. Besides, the Mutual Information Maximization (MIM) module maximizes the agreement between the latent high-level representation and low-level ones, and enables the high-level representation to satisfy the desired clustering structure with the help of the Self-supervised Clustering (SC) module. Extensive experiments on several real-world benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DIAGC method compared with the state-of-the-art baselines.
Adaptively-weighted Integral Space for Fast Multiview Clustering
Aug 25, 2022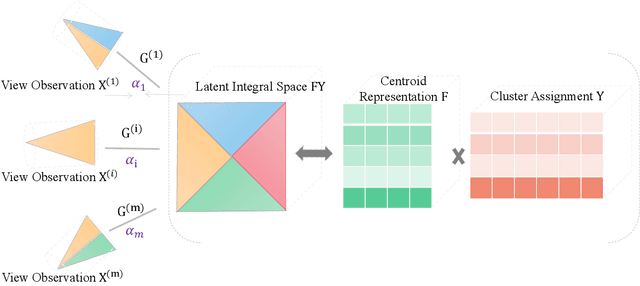
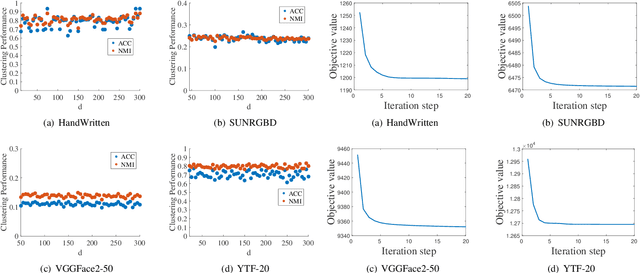
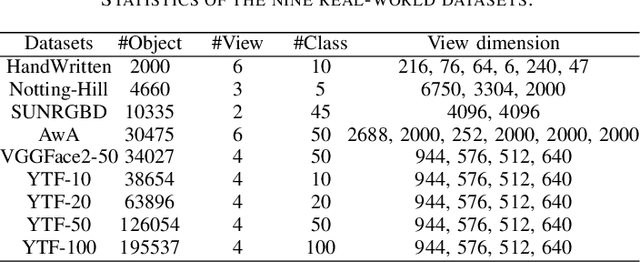
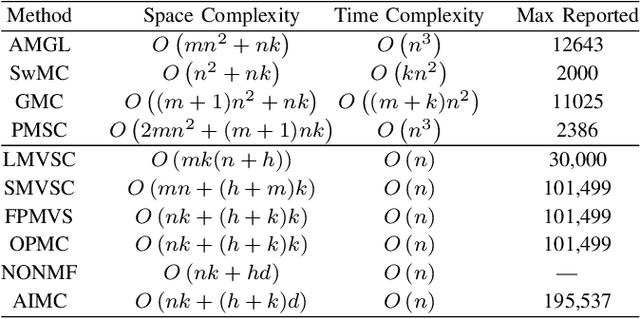
Abstract:Multiview clustering has been extensively studied to take advantage of multi-source information to improve the clustering performance. In general, most of the existing works typically compute an n * n affinity graph by some similarity/distance metrics (e.g. the Euclidean distance) or learned representations, and explore the pairwise correlations across views. But unfortunately, a quadratic or even cubic complexity is often needed, bringing about difficulty in clustering largescale datasets. Some efforts have been made recently to capture data distribution in multiple views by selecting view-wise anchor representations with k-means, or by direct matrix factorization on the original observations. Despite the significant success, few of them have considered the view-insufficiency issue, implicitly holding the assumption that each individual view is sufficient to recover the cluster structure. Moreover, the latent integral space as well as the shared cluster structure from multiple insufficient views is not able to be simultaneously discovered. In view of this, we propose an Adaptively-weighted Integral Space for Fast Multiview Clustering (AIMC) with nearly linear complexity. Specifically, view generation models are designed to reconstruct the view observations from the latent integral space with diverse adaptive contributions. Meanwhile, a centroid representation with orthogonality constraint and cluster partition are seamlessly constructed to approximate the latent integral space. An alternate minimizing algorithm is developed to solve the optimization problem, which is proved to have linear time complexity w.r.t. the sample size. Extensive experiments conducted on several realworld datasets confirm the superiority of the proposed AIMC method compared with the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge