Mamadou Keita
RAVID: Retrieval-Augmented Visual Detection: A Knowledge-Driven Approach for AI-Generated Image Identification
Aug 05, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we introduce RAVID, the first framework for AI-generated image detection that leverages visual retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). While RAG methods have shown promise in mitigating factual inaccuracies in foundation models, they have primarily focused on text, leaving visual knowledge underexplored. Meanwhile, existing detection methods, which struggle with generalization and robustness, often rely on low-level artifacts and model-specific features, limiting their adaptability. To address this, RAVID dynamically retrieves relevant images to enhance detection. Our approach utilizes a fine-tuned CLIP image encoder, RAVID CLIP, enhanced with category-related prompts to improve representation learning. We further integrate a vision-language model (VLM) to fuse retrieved images with the query, enriching the input and improving accuracy. Given a query image, RAVID generates an embedding using RAVID CLIP, retrieves the most relevant images from a database, and combines these with the query image to form an enriched input for a VLM (e.g., Qwen-VL or Openflamingo). Experiments on the UniversalFakeDetect benchmark, which covers 19 generative models, show that RAVID achieves state-of-the-art performance with an average accuracy of 93.85%. RAVID also outperforms traditional methods in terms of robustness, maintaining high accuracy even under image degradations such as Gaussian blur and JPEG compression. Specifically, RAVID achieves an average accuracy of 80.27% under degradation conditions, compared to 63.44% for the state-of-the-art model C2P-CLIP, demonstrating consistent improvements in both Gaussian blur and JPEG compression scenarios. The code will be publicly available upon acceptance.
DeeCLIP: A Robust and Generalizable Transformer-Based Framework for Detecting AI-Generated Images
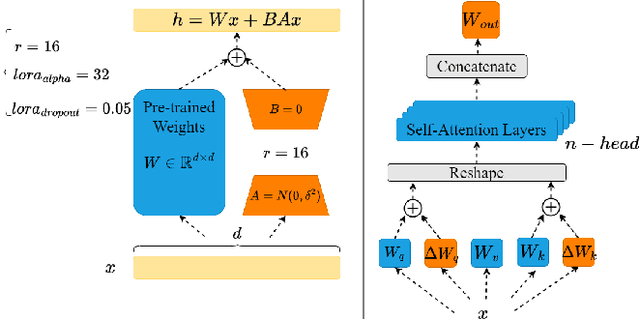
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces DeeCLIP, a novel framework for detecting AI-generated images using CLIP-ViT and fusion learning. Despite significant advancements in generative models capable of creating highly photorealistic images, existing detection methods often struggle to generalize across different models and are highly sensitive to minor perturbations. To address these challenges, DeeCLIP incorporates DeeFuser, a fusion module that combines high-level and low-level features, improving robustness against degradations such as compression and blurring. Additionally, we apply triplet loss to refine the embedding space, enhancing the model's ability to distinguish between real and synthetic content. To further enable lightweight adaptation while preserving pre-trained knowledge, we adopt parameter-efficient fine-tuning using low-rank adaptation (LoRA) within the CLIP-ViT backbone. This approach supports effective zero-shot learning without sacrificing generalization. Trained exclusively on 4-class ProGAN data, DeeCLIP achieves an average accuracy of 89.00% on 19 test subsets composed of generative adversarial network (GAN) and diffusion models. Despite having fewer trainable parameters, DeeCLIP outperforms existing methods, demonstrating superior robustness against various generative models and real-world distortions. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/Mamadou-Keita/DeeCLIP for research purposes.
Bi-LORA: A Vision-Language Approach for Synthetic Image Detection
Apr 07, 2024



Abstract:Advancements in deep image synthesis techniques, such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models (DMs), have ushered in an era of generating highly realistic images. While this technological progress has captured significant interest, it has also raised concerns about the potential difficulty in distinguishing real images from their synthetic counterparts. This paper takes inspiration from the potent convergence capabilities between vision and language, coupled with the zero-shot nature of vision-language models (VLMs). We introduce an innovative method called Bi-LORA that leverages VLMs, combined with low-rank adaptation (LORA) tuning techniques, to enhance the precision of synthetic image detection for unseen model-generated images. The pivotal conceptual shift in our methodology revolves around reframing binary classification as an image captioning task, leveraging the distinctive capabilities of cutting-edge VLM, notably bootstrapping language image pre-training (BLIP2). Rigorous and comprehensive experiments are conducted to validate the effectiveness of our proposed approach, particularly in detecting unseen diffusion-generated images from unknown diffusion-based generative models during training, showcasing robustness to noise, and demonstrating generalization capabilities to GANs. The obtained results showcase an impressive average accuracy of 93.41% in synthetic image detection on unseen generation models. The code and models associated with this research can be publicly accessed at https://github.com/Mamadou-Keita/VLM-DETECT.
Harnessing the Power of Large Vision Language Models for Synthetic Image Detection
Apr 03, 2024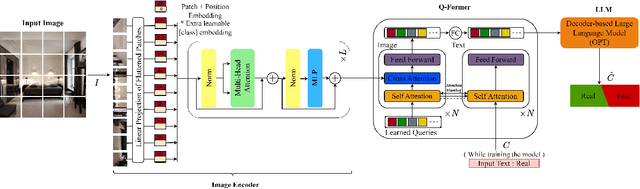
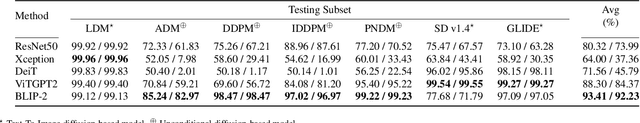

Abstract:In recent years, the emergence of models capable of generating images from text has attracted considerable interest, offering the possibility of creating realistic images from text descriptions. Yet these advances have also raised concerns about the potential misuse of these images, including the creation of misleading content such as fake news and propaganda. This study investigates the effectiveness of using advanced vision-language models (VLMs) for synthetic image identification. Specifically, the focus is on tuning state-of-the-art image captioning models for synthetic image detection. By harnessing the robust understanding capabilities of large VLMs, the aim is to distinguish authentic images from synthetic images produced by diffusion-based models. This study contributes to the advancement of synthetic image detection by exploiting the capabilities of visual language models such as BLIP-2 and ViTGPT2. By tailoring image captioning models, we address the challenges associated with the potential misuse of synthetic images in real-world applications. Results described in this paper highlight the promising role of VLMs in the field of synthetic image detection, outperforming conventional image-based detection techniques. Code and models can be found at https://github.com/Mamadou-Keita/VLM-DETECT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge