Mai Thanh Thai
Smart Textile-Driven Soft Spine Exosuit for Lifting Tasks in Industrial Applications
Feb 04, 2024Abstract:Work related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs) are often caused by repetitive lifting, making them a significant concern in occupational health. Although wearable assist devices have become the norm for mitigating the risk of back pain, most spinal assist devices still possess a partially rigid structure that impacts the user comfort and flexibility. This paper addresses this issue by presenting a smart textile actuated spine assistance robotic exosuit (SARE), which can conform to the back seamlessly without impeding the user movement and is incredibly lightweight. The SARE can assist the human erector spinae to complete any action with virtually infinite degrees of freedom. To detect the strain on the spine and to control the smart textile automatically, a soft knitting sensor which utilizes fluid pressure as sensing element is used. The new device is validated experimentally with human subjects where it reduces peak electromyography (EMG) signals of lumbar erector spinae by around 32 percent in loaded and around 22 percent in unloaded conditions. Moreover, the integrated EMG decreased by around 24.2 percent under loaded condition and around 23.6 percent under unloaded condition. In summary, the artificial muscle wearable device represents an anatomical solution to reduce the risk of muscle strain, metabolic energy cost and back pain associated with repetitive lifting tasks.
Advanced Intelligent Systems for Surgical Robotics
Jan 02, 2020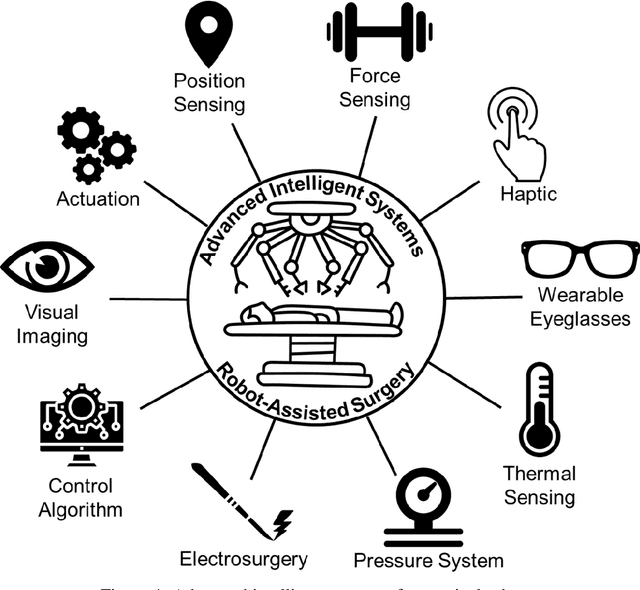
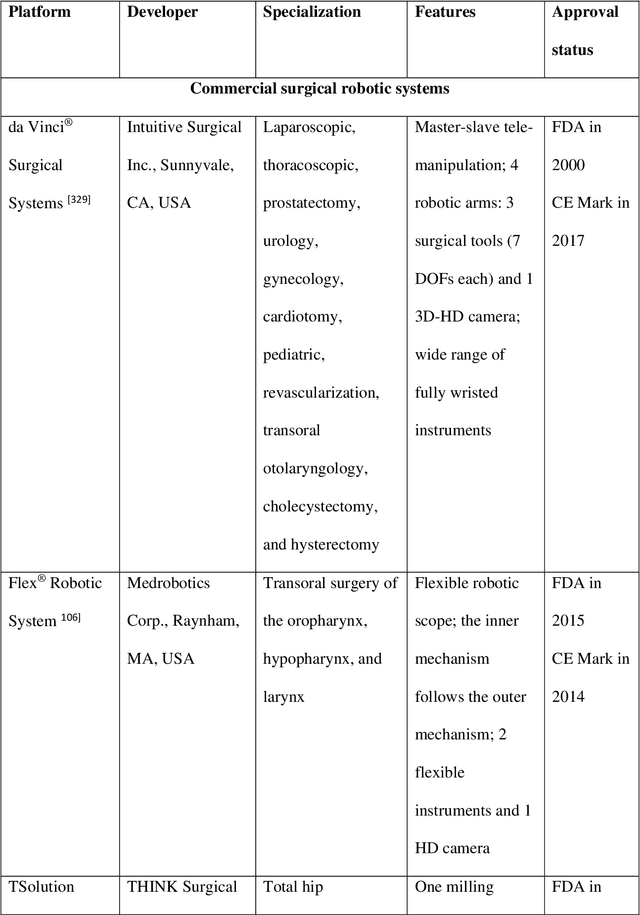
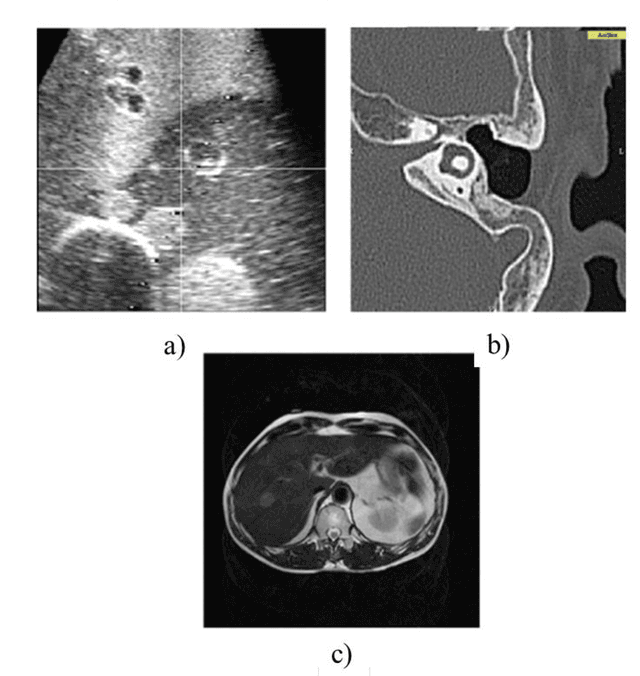
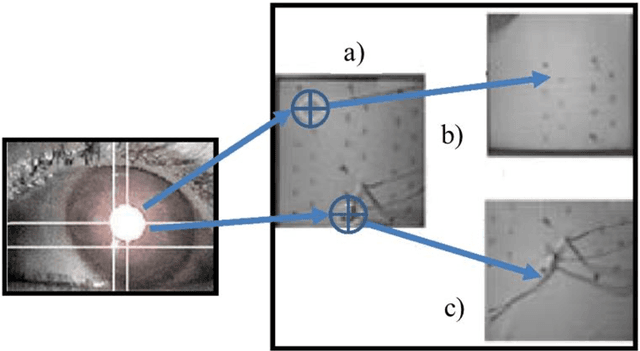
Abstract:Surgical robots have had clinical use since the mid 1990s. Robot-assisted surgeries offer many benefits over the conventional approach including lower risk of infection and blood loss, shorter recovery, and an overall safer procedure for patients. The past few decades have shown many emerging surgical robotic platforms that can work in complex and confined channels of the internal human organs and improve the cognitive and physical skills of the surgeons during the operation. Advanced technologies for sensing, actuation, and intelligent control have enabled multiple surgical devices to simultaneously operate within the human body at low cost and with more efficiency. Despite advances, current surgical intervention systems are not able to execute autonomous tasks and make cognitive decisions that are analogous to that of humans. This paper will overview a historical development of surgery from conventional open to robotic-assisted approaches with discussion on the capabilities of advanced intelligent systems and devices that are currently implemented in existing surgical robotic systems. It will also revisit available autonomous surgical platforms with comments on the essential technologies, existing challenges, and suggestions for the future development of intelligent robotic-assisted surgical systems towards the achievement of fully autonomous operation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge