Mahrokh G. Shayesteh
Demodulation of Sparse PPM Signals with Low Samples Using Trained RIP Matrix
Sep 01, 2013



Abstract:Compressed sensing (CS) theory considers the restricted isometry property (RIP) as a sufficient condition for measurement matrix which guarantees the recovery of any sparse signal from its compressed measurements. The RIP condition also preserves enough information for classification of sparse symbols, even with fewer measurements. In this work, we utilize RIP bound as the cost function for training a simple neural network in order to exploit the near optimal measurements or equivalently near optimal features for classification of a known set of sparse symbols. As an example, we consider demodulation of pulse position modulation (PPM) signals. The results indicate that the proposed method has much better performance than the random measurements and requires less samples than the optimum matched filter demodulator, at the expense of some performance loss. Further, the proposed approach does not need equalizer for multipath channels in contrast to the conventional receiver.
Robust Head Pose Estimation Using Contourlet Transform
May 12, 2012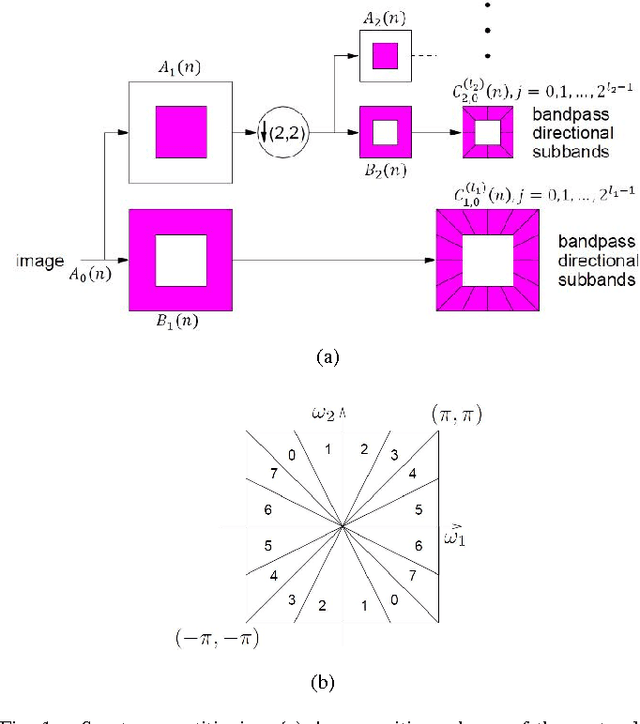

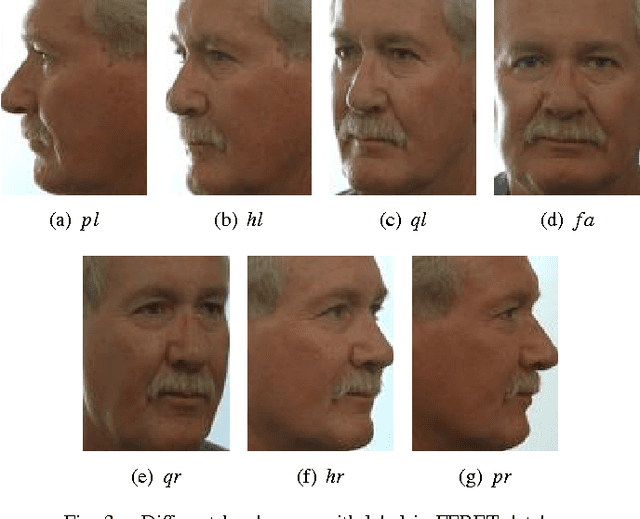
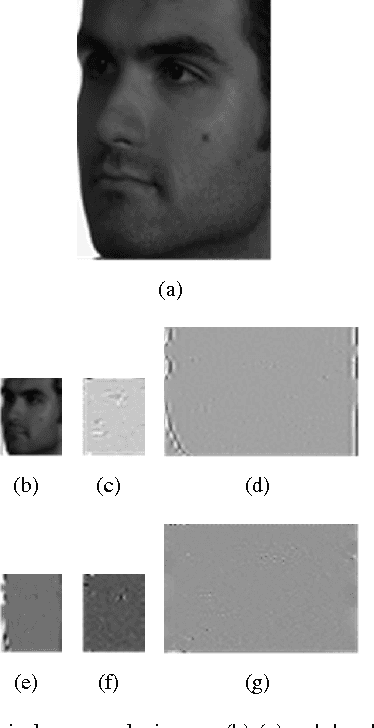
Abstract:Estimating pose of the head is an important preprocessing step in many pattern recognition and computer vision systems such as face recognition. Since the performance of the face recognition systems is greatly affected by the poses of the face, how to estimate the accurate pose of the face in human face image is still a challenging problem. In this paper, we represent a novel method for head pose estimation. To enhance the efficiency of the estimation we use contourlet transform for feature extraction. Contourlet transform is multi-resolution, multi-direction transform. In order to reduce the feature space dimension and obtain appropriate features we use LDA (Linear Discriminant Analysis) and PCA (Principal Component Analysis) to remove ineffcient features. Then, we apply different classifiers such as k-nearest neighborhood (knn) and minimum distance. We use the public available FERET database to evaluate the performance of proposed method. Simulation results indicate the superior robustness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge