Mahmoud Abdelsalam
ReGAIN: Retrieval-Grounded AI Framework for Network Traffic Analysis
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Modern networks generate vast, heterogeneous traffic that must be continuously analyzed for security and performance. Traditional network traffic analysis systems, whether rule-based or machine learning-driven, often suffer from high false positives and lack interpretability, limiting analyst trust. In this paper, we present ReGAIN, a multi-stage framework that combines traffic summarization, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning for transparent and accurate network traffic analysis. ReGAIN creates natural-language summaries from network traffic, embeds them into a multi-collection vector database, and utilizes a hierarchical retrieval pipeline to ground LLM responses with evidence citations. The pipeline features metadata-based filtering, MMR sampling, a two-stage cross-encoder reranking mechanism, and an abstention mechanism to reduce hallucinations and ensure grounded reasoning. Evaluated on ICMP ping flood and TCP SYN flood traces from the real-world traffic dataset, it demonstrates robust performance, achieving accuracy between 95.95% and 98.82% across different attack types and evaluation benchmarks. These results are validated against two complementary sources: dataset ground truth and human expert assessments. ReGAIN also outperforms rule-based, classical ML, and deep learning baselines while providing unique explainability through trustworthy, verifiable responses.
FedP3E: Privacy-Preserving Prototype Exchange for Non-IID IoT Malware Detection in Cross-Silo Federated Learning
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:As IoT ecosystems continue to expand across critical sectors, they have become prominent targets for increasingly sophisticated and large-scale malware attacks. The evolving threat landscape, combined with the sensitive nature of IoT-generated data, demands detection frameworks that are both privacy-preserving and resilient to data heterogeneity. Federated Learning (FL) offers a promising solution by enabling decentralized model training without exposing raw data. However, standard FL algorithms such as FedAvg and FedProx often fall short in real-world deployments characterized by class imbalance and non-IID data distributions -- particularly in the presence of rare or disjoint malware classes. To address these challenges, we propose FedP3E (Privacy-Preserving Prototype Exchange), a novel FL framework that supports indirect cross-client representation sharing while maintaining data privacy. Each client constructs class-wise prototypes using Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs), perturbs them with Gaussian noise, and transmits only these compact summaries to the server. The aggregated prototypes are then distributed back to clients and integrated into local training, supported by SMOTE-based augmentation to enhance representation of minority malware classes. Rather than relying solely on parameter averaging, our prototype-driven mechanism enables clients to enrich their local models with complementary structural patterns observed across the federation -- without exchanging raw data or gradients. This targeted strategy reduces the adverse impact of statistical heterogeneity with minimal communication overhead. We evaluate FedP3E on the N-BaIoT dataset under realistic cross-silo scenarios with varying degrees of data imbalance.
TT-LoRA MoE: Unifying Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning and Sparse Mixture-of-Experts
Apr 29, 2025



Abstract:We propose Tensor-Trained Low-Rank Adaptation Mixture of Experts (TT-LoRA MoE), a novel computational framework integrating Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) with sparse MoE routing to address scalability challenges in large model deployments. Unlike traditional MoE approaches, which face substantial computational overhead as expert counts grow, TT-LoRA MoE decomposes training into two distinct, optimized stages. First, we independently train lightweight, tensorized low-rank adapters (TT-LoRA experts), each specialized for specific tasks. Subsequently, these expert adapters remain frozen, eliminating inter-task interference and catastrophic forgetting in multi-task setting. A sparse MoE router, trained separately, dynamically leverages base model representations to select exactly one specialized adapter per input at inference time, automating expert selection without explicit task specification. Comprehensive experiments confirm our architecture retains the memory efficiency of low-rank adapters, seamlessly scales to large expert pools, and achieves robust task-level optimization. This structured decoupling significantly enhances computational efficiency and flexibility: uses only 2% of LoRA, 0.3% of Adapters and 0.03% of AdapterFusion parameters and outperforms AdapterFusion by 4 value in multi-tasking, enabling practical and scalable multi-task inference deployments.
Deep Learning Based XIoT Malware Analysis: A Comprehensive Survey, Taxonomy, and Research Challenges
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:The Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the fastest-growing computing industries. By the end of 2027, more than 29 billion devices are expected to be connected. These smart devices can communicate with each other with and without human intervention. This rapid growth has led to the emergence of new types of malware. However, traditional malware detection methods, such as signature-based and heuristic-based techniques, are becoming increasingly ineffective against these new types of malware. Therefore, it has become indispensable to find practical solutions for detecting IoT malware. Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) approaches have proven effective in dealing with these new IoT malware variants, exhibiting high detection rates. In this paper, we bridge the gap in research between the IoT malware analysis and the wide adoption of deep learning in tackling the problems in this domain. As such, we provide a comprehensive review on deep learning based malware analysis across various categories of the IoT domain (i.e. Extended Internet of Things (XIoT)), including Industrial IoT (IIoT), Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), Internet of Vehicles (IoV), and Internet of Battlefield Things (IoBT).
Machine Learning in Access Control: A Taxonomy and Survey
Jul 04, 2022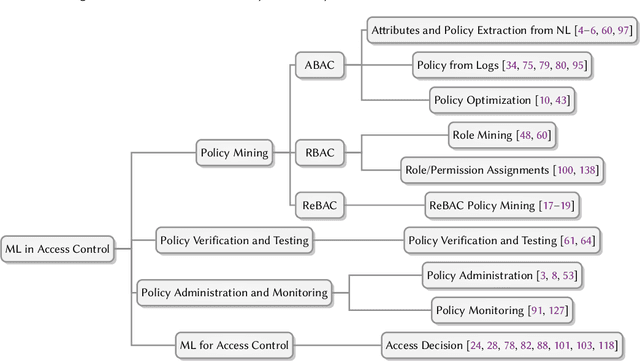
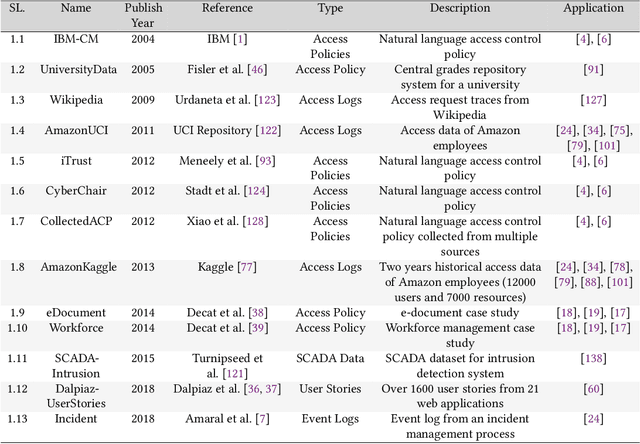

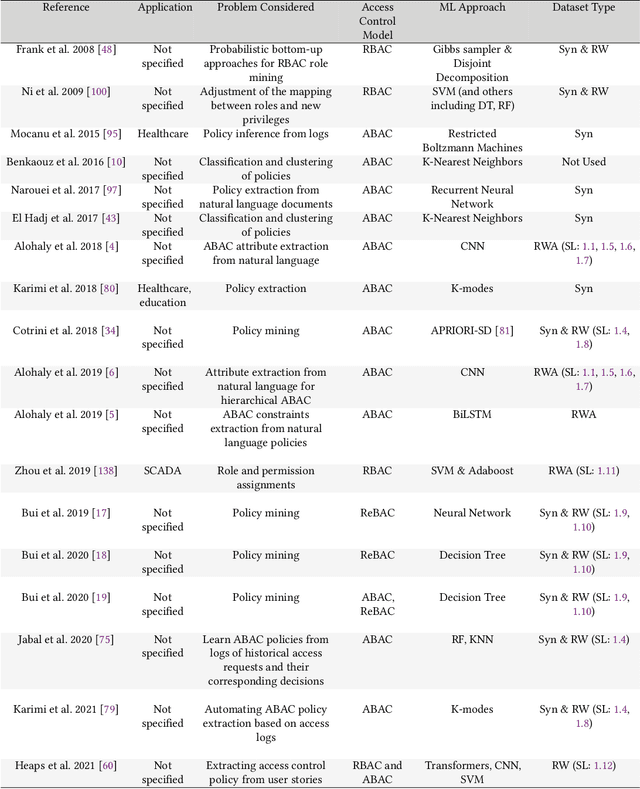
Abstract:An increasing body of work has recognized the importance of exploiting machine learning (ML) advancements to address the need for efficient automation in extracting access control attributes, policy mining, policy verification, access decisions, etc. In this work, we survey and summarize various ML approaches to solve different access control problems. We propose a novel taxonomy of the ML model's application in the access control domain. We highlight current limitations and open challenges such as lack of public real-world datasets, administration of ML-based access control systems, understanding a black-box ML model's decision, etc., and enumerate future research directions.
Analyzing Machine Learning Approaches for Online Malware Detection in Cloud
May 19, 2021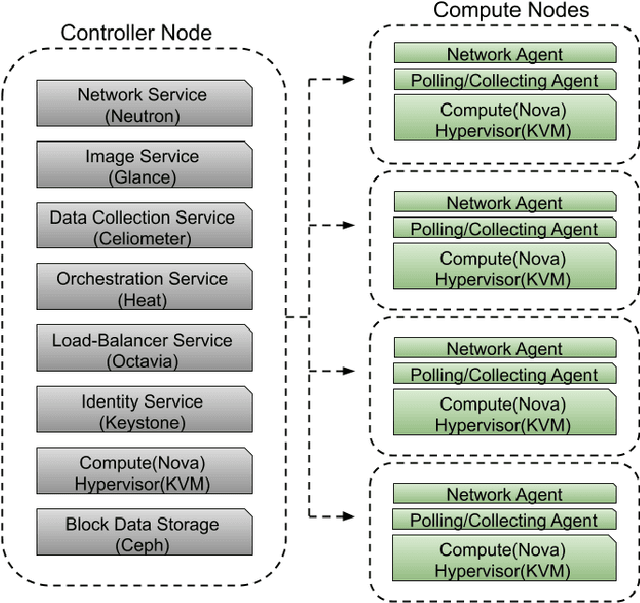



Abstract:The variety of services and functionality offered by various cloud service providers (CSP) have exploded lately. Utilizing such services has created numerous opportunities for enterprises infrastructure to become cloud-based and, in turn, assisted the enterprises to easily and flexibly offer services to their customers. The practice of renting out access to servers to clients for computing and storage purposes is known as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). The popularity of IaaS has led to serious and critical concerns with respect to the cyber security and privacy. In particular, malware is often leveraged by malicious entities against cloud services to compromise sensitive data or to obstruct their functionality. In response to this growing menace, malware detection for cloud environments has become a widely researched topic with numerous methods being proposed and deployed. In this paper, we present online malware detection based on process level performance metrics, and analyze the effectiveness of different baseline machine learning models including, Support Vector Classifier (SVC), Random Forest Classifier (RFC), KNearest Neighbor (KNN), Gradient Boosted Classifier (GBC), Gaussian Naive Bayes (GNB) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). Our analysis conclude that neural network models can most accurately detect the impact malware have on the process level features of virtual machines in the cloud, and therefore are best suited to detect them. Our models were trained, validated, and tested by using a dataset of 40,680 malicious and benign samples. The dataset was complied by running different families of malware (collected from VirusTotal) in a live cloud environment and collecting the process level features.
Enabling and Enforcing Social Distancing Measures using Smart City and ITS Infrastructures: A COVID-19 Use Case
Apr 13, 2020

Abstract:Internet of Things is a revolutionary domain that has the caliber to impact our lives and bring significant changes to the world. Several IoT applications have been envisioned to facilitate data driven and smart application for the user. Smart City and Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) offer a futuristic vision of smart, secure and safe experience to the end user, and at the same time efficiently manage the sparse resources and optimize the efficiency of city operations. However, outbreaks and pandemics like COVID-19 have revealed limitations of the existing deployments, therefore, architecture, applications and technology systems need to be developed for swift and timely enforcement of guidelines, rules and government orders to contain such future outbreaks. This work outlines novel architecture, potential use-cases and some future directions in developing such applications using Smart City and ITS.
Analyzing CNN Based Behavioural Malware Detection Techniques on Cloud IaaS
Feb 15, 2020



Abstract:Cloud Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is vulnerable to malware due to its exposure to external adversaries, making it a lucrative attack vector for malicious actors. A datacenter infected with malware can cause data loss and/or major disruptions to service for its users. This paper analyzes and compares various Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for online detection of malware in cloud IaaS. The detection is performed based on behavioural data using process level performance metrics including cpu usage, memory usage, disk usage etc. We have used the state of the art DenseNets and ResNets in effectively detecting malware in online cloud system. CNN are designed to extract features from data gathered from a live malware running on a real cloud environment. Experiments are performed on OpenStack (a cloud IaaS software) testbed designed to replicate a typical 3-tier web architecture. Comparative analysis is performed for different metrics for different CNN models used in this research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge