Mahamudul Hasan
ECORS: An Ensembled Clustering Approach to Eradicate The Local And Global Outlier In Collaborative Filtering Recommender System
Oct 01, 2024



Abstract:Recommender systems are designed to suggest items based on user preferences, helping users navigate the vast amount of information available on the internet. Given the overwhelming content, outlier detection has emerged as a key research area in recommender systems. It involves identifying unusual or suspicious patterns in user behavior. However, existing studies in this field face several challenges, including the limited universality of algorithms, difficulties in selecting users, and a lack of optimization. In this paper, we propose an approach that addresses these challenges by employing various clustering algorithms. Specifically, we utilize a user-user matrix-based clustering technique to detect outliers. By constructing a user-user matrix, we can identify suspicious users in the system. Both local and global outliers are detected to ensure comprehensive analysis. Our experimental results demonstrate that this approach significantly improves the accuracy of outlier detection in recommender systems.
FireLite: Leveraging Transfer Learning for Efficient Fire Detection in Resource-Constrained Environments
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:Fire hazards are extremely dangerous, particularly in sectors such as the transportation industry, where political unrest increases the likelihood of their occurrence. By employing IP cameras to facilitate the setup of fire detection systems on transport vehicles, losses from fire events may be prevented proactively. However, the development of lightweight fire detection models is required due to the computational constraints of the embedded systems within these cameras. We introduce FireLite, a low-parameter convolutional neural network (CNN) designed for quick fire detection in contexts with limited resources, in response to this difficulty. With an accuracy of 98.77\%, our model -- which has just 34,978 trainable parameters achieves remarkable performance numbers. It also shows a validation loss of 8.74 and peaks at 98.77 for precision, recall, and F1-score measures. Because of its precision and efficiency, FireLite is a promising solution for fire detection in resource-constrained environments.
An Efficient Multi-threaded Collaborative Filtering Approach in Recommendation System
Sep 28, 2024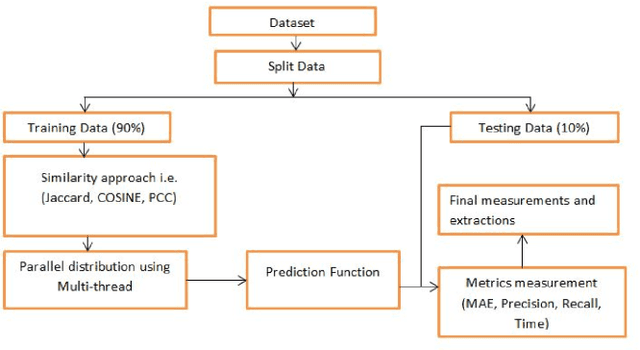
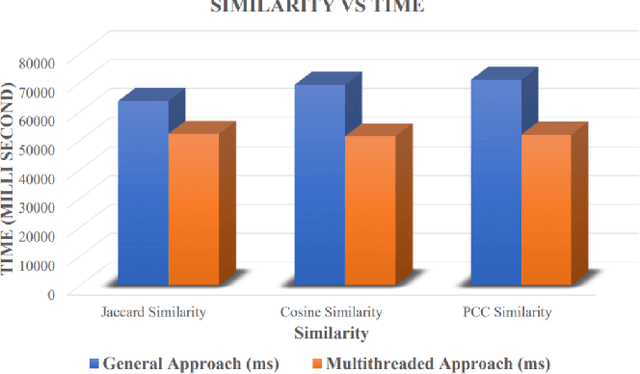
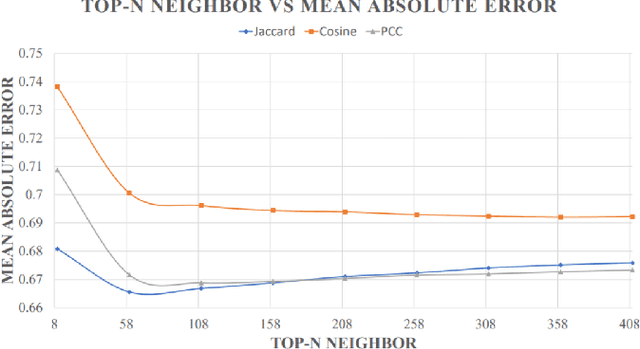
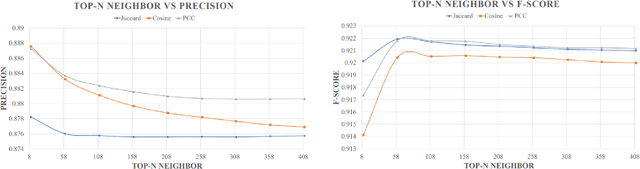
Abstract:Recommender systems are a subset of information filtering systems designed to predict and suggest items that users may find interesting or relevant based on their preferences, behaviors, or interactions. By analyzing user data such as past activities, ratings, and preferences, these systems generate personalized recommendations for products, services, or content, with common applications including online retail, media streaming platforms, and social media. Recommender systems are typically categorized into three types: content-based filtering, which recommends items similar to those the user has shown interest in; collaborative filtering, which analyzes the preferences of similar users; and hybrid methods, which combine both approaches to improve accuracy. These systems enhance user experience by reducing information overload and providing personalized suggestions, thus increasing engagement and satisfaction. However, building a scalable recommendation system capable of handling numerous users efficiently is a significant challenge, particularly when considering both performance consistency and user data security, which are emerging research topics. The primary objective of this research is to address these challenges by reducing the processing time in recommendation systems. A multithreaded similarity approach is employed to achieve this, where users are divided into independent threads that run in parallel. This parallelization significantly reduces computation time compared to traditional methods, resulting in a faster, more efficient, and scalable recommendation system that ensures improved performance without compromising user data security.
Utilizing Collaborative Filtering in a Personalized Research-Paper Recommendation System
Sep 28, 2024



Abstract:Recommendation system is such a platform that helps people to easily find out the things they need within a few seconds. It is implemented based on the preferences of similar users or items. In this digital era, the internet has provided us with huge opportunities to use a lot of open resources for our own needs. But there are too many resources on the internet from which finding the precise one is a difficult job. Recommendation system has made this easier for people. Research-paper recommendation system is a system that is developed for people with common research interests using a collaborative filtering recommender system. In this paper, coauthor, keyword, reference, and common citation similarities are calculated using Jaccard Similarity to find the final similarity and to find the top-n similar users. Based on the test of top-n similar users of the target user research paper recommendations have been made. Finally, the accuracy of our recommendation system has been calculated. An impressive result has been found using our proposed system.
Two-stage Cascaded Classifier for Purchase Prediction
Aug 16, 2015



Abstract:In this paper we describe our machine learning solution for the RecSys Challenge, 2015. We have proposed a time efficient two-stage cascaded classifier for the prediction of buy sessions and purchased items within such sessions. Based on the model, several interesting features found, and formation of our own test bed, we have achieved a reasonable score. Usage of Random Forests helps us to cope with the effect of the multiplicity of good models depending on varying subsets of features in the purchased items prediction and, in its turn, boosting is used as a suitable technique to overcome severe class imbalance of the buy-session prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge