Magnus Tournoy
The Neuron as a Direct Data-Driven Controller
Jan 03, 2024Abstract:In the quest to model neuronal function amidst gaps in physiological data, a promising strategy is to develop a normative theory that interprets neuronal physiology as optimizing a computational objective. This study extends the current normative models, which primarily optimize prediction, by conceptualizing neurons as optimal feedback controllers. We posit that neurons, especially those beyond early sensory areas, act as controllers, steering their environment towards a specific desired state through their output. This environment comprises both synaptically interlinked neurons and external motor sensory feedback loops, enabling neurons to evaluate the effectiveness of their control via synaptic feedback. Utilizing the novel Direct Data-Driven Control (DD-DC) framework, we model neurons as biologically feasible controllers which implicitly identify loop dynamics, infer latent states and optimize control. Our DD-DC neuron model explains various neurophysiological phenomena: the shift from potentiation to depression in Spike-Timing-Dependent Plasticity (STDP) with its asymmetry, the duration and adaptive nature of feedforward and feedback neuronal filters, the imprecision in spike generation under constant stimulation, and the characteristic operational variability and noise in the brain. Our model presents a significant departure from the traditional, feedforward, instant-response McCulloch-Pitts-Rosenblatt neuron, offering a novel and biologically-informed fundamental unit for constructing neural networks.
A Step Towards Uncovering The Structure of Multistable Neural Networks
Oct 06, 2022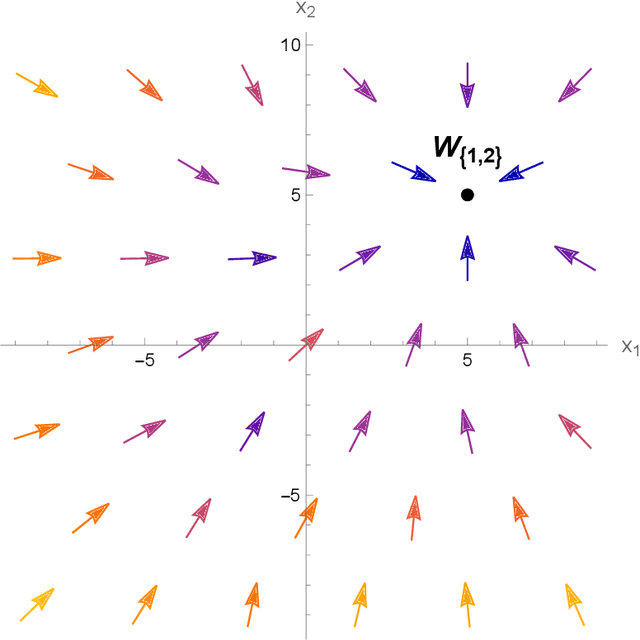
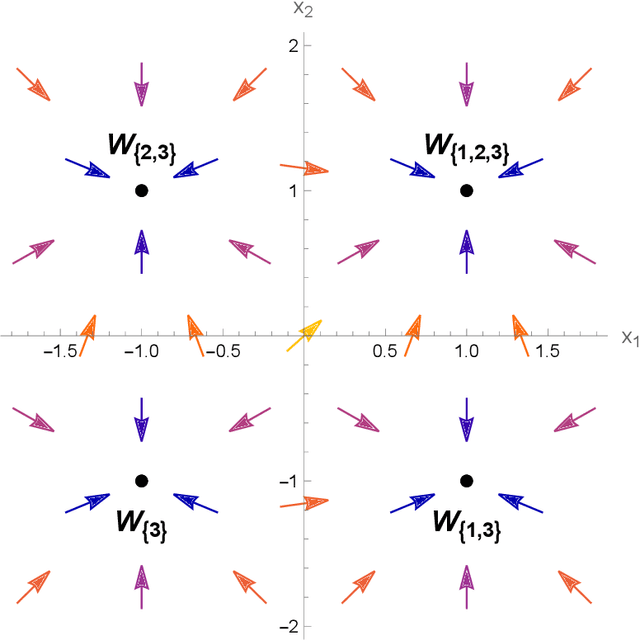
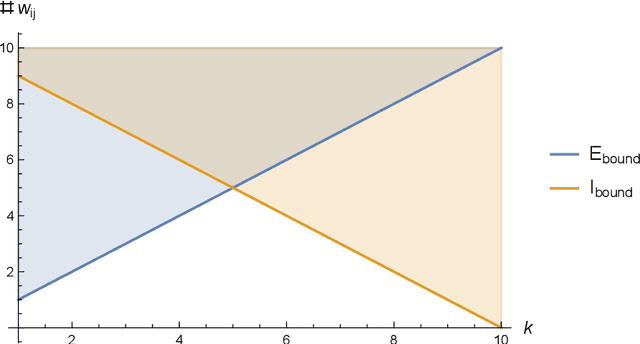
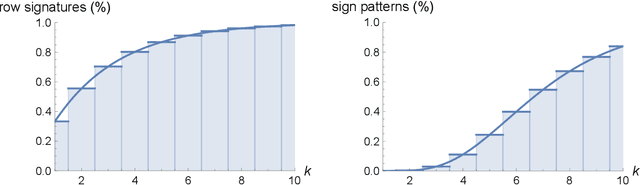
Abstract:We study the structure of multistable recurrent neural networks. The activation function is simplified by a nonsmooth Heaviside step function. This nonlinearity partitions the phase space into regions with different, yet linear dynamics. We derive how multistability is encoded within the network architecture. Stable states are identified by their semipositivity constraints on the synaptic weight matrix. The restrictions can be separated by their effects on the signs or the strengths of the connections. Exact results on network topology, sign stability, weight matrix factorization, pattern completion and pattern coupling are derived and proven. These may lay the foundation of more complex recurrent neural networks and neurocomputing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge