Maayan Gelboim
Accelerated Full Waveform Inversion by Deep Compressed Learning
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:We propose and test a method to reduce the dimensionality of Full Waveform Inversion (FWI) inputs as computational cost mitigation approach. Given modern seismic acquisition systems, the data (as input for FWI) required for an industrial-strength case is in the teraflop level of storage, therefore solving complex subsurface cases or exploring multiple scenarios with FWI become prohibitive. The proposed method utilizes a deep neural network with a binarized sensing layer that learns by compressed learning a succinct but consequential seismic acquisition layout from a large corpus of subsurface models. Thus, given a large seismic data set to invert, the trained network selects a smaller subset of the data, then by using representation learning, an autoencoder computes latent representations of the data, followed by K-means clustering of the latent representations to further select the most relevant data for FWI. Effectively, this approach can be seen as a hierarchical selection. The proposed approach consistently outperforms random data sampling, even when utilizing only 10% of the data for 2D FWI, these results pave the way to accelerating FWI in large scale 3D inversion.
Deep Compressed Learning for 3D Seismic Inversion
Oct 31, 2023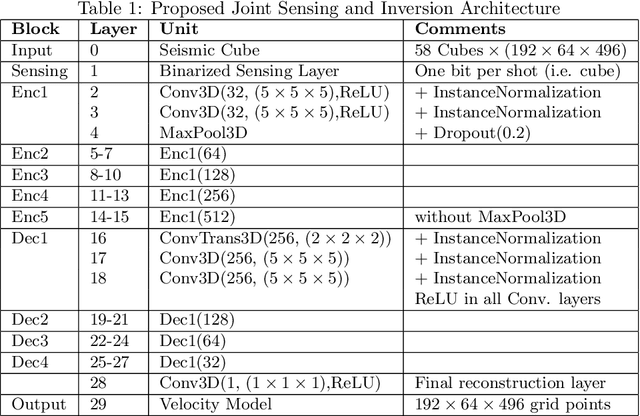
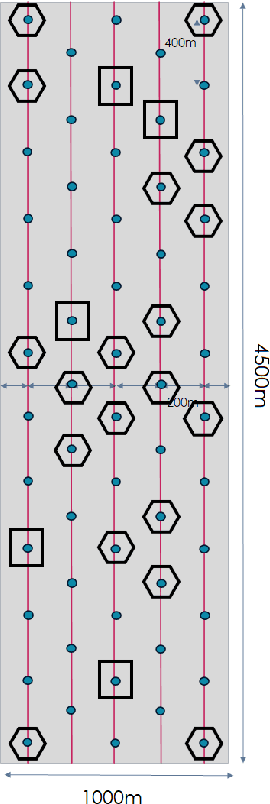
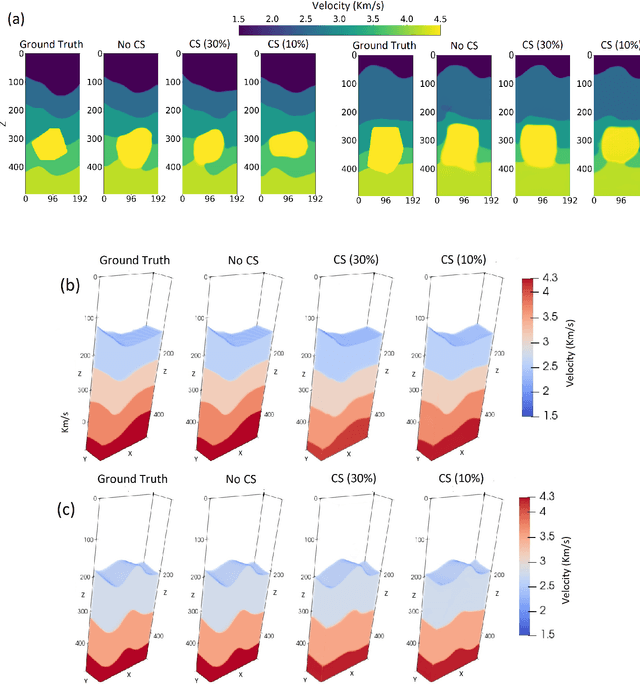
Abstract:We consider the problem of 3D seismic inversion from pre-stack data using a very small number of seismic sources. The proposed solution is based on a combination of compressed-sensing and machine learning frameworks, known as compressed-learning. The solution jointly optimizes a dimensionality reduction operator and a 3D inversion encoder-decoder implemented by a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN). Dimensionality reduction is achieved by learning a sparse binary sensing layer that selects a small subset of the available sources, then the selected data is fed to a DCNN to complete the regression task. The end-to-end learning process provides a reduction by an order-of-magnitude in the number of seismic records used during training, while preserving the 3D reconstruction quality comparable to that obtained by using the entire dataset.
Encoder-Decoder Architecture for 3D Seismic Inversion
Jul 29, 2022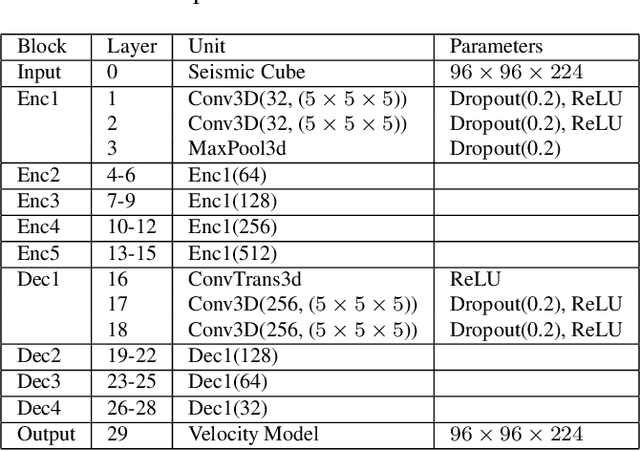
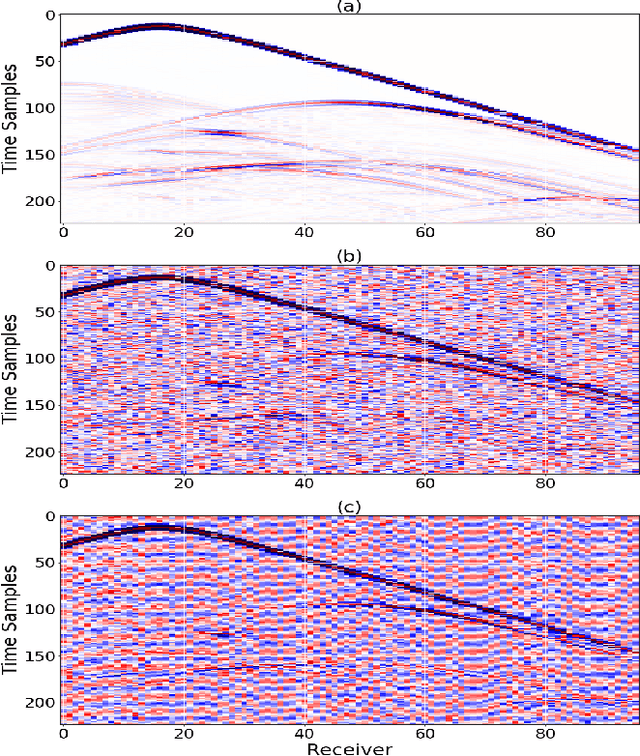
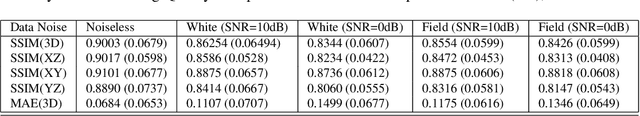
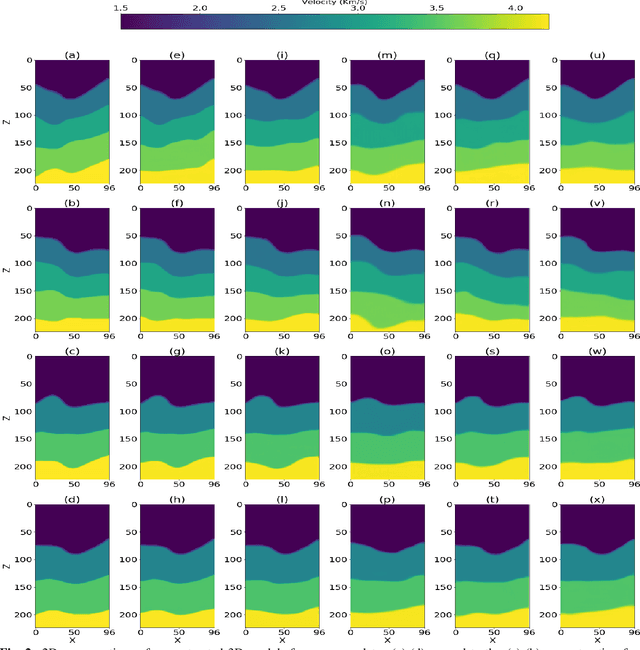
Abstract:Inverting seismic data to build 3D geological structures is a challenging task due to the overwhelming amount of acquired seismic data, and the very-high computational load due to iterative numerical solutions of the wave equation, as required by industry-standard tools such as Full Waveform Inversion (FWI). For example, in an area with surface dimensions of 4.5km $\times$ 4.5km, hundreds of seismic shot-gather cubes are required for 3D model reconstruction, leading to Terabytes of recorded data. This paper presents a deep learning solution for the reconstruction of realistic 3D models in the presence of field noise recorded in seismic surveys. We implement and analyze a convolutional encoder-decoder architecture that efficiently processes the entire collection of hundreds of seismic shot-gather cubes. The proposed solution demonstrates that realistic 3D models can be reconstructed with a structural similarity index measure (SSIM) of 0.8554 (out of 1.0) in the presence of field noise at 10dB signal-to-noise ratio.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge