M. Amine Atoui
Fault Diagnosis across Heterogeneous Domains via Self-Adaptive Temporal-Spatial Attention and Sample Generation
May 16, 2025Abstract:Deep learning methods have shown promising performance in fault diagnosis for multimode process. Most existing studies assume that the collected health state categories from different operating modes are identical. However, in real industrial scenarios, these categories typically exhibit only partial overlap. The incompleteness of the available data and the large distributional differences between the operating modes pose a significant challenge to existing fault diagnosis methods. To address this problem, a novel fault diagnosis model named self-adaptive temporal-spatial attention network (TSA-SAN) is proposed. First, inter-mode mappings are constructed using healthy category data to generate multimode samples. To enrich the diversity of the fault data, interpolation is performed between healthy and fault samples. Subsequently, the fault diagnosis model is trained using real and generated data. The self-adaptive instance normalization is established to suppress irrelevant information while retaining essential statistical features for diagnosis. In addition, a temporal-spatial attention mechanism is constructed to focus on the key features, thus enhancing the generalization ability of the model. The extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed model significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. The code will be available on Github at https://github.com/GuangqiangLi/TSA-SAN.
Attention-Based Multi-Scale Temporal Fusion Network for Uncertain-Mode Fault Diagnosis in Multimode Processes
Apr 07, 2025



Abstract:Fault diagnosis in multimode processes plays a critical role in ensuring the safe operation of industrial systems across multiple modes. It faces a great challenge yet to be addressed - that is, the significant distributional differences among monitoring data from multiple modes make it difficult for the models to extract shared feature representations related to system health conditions. In response to this problem, this paper introduces a novel method called attention-based multi-scale temporal fusion network. The multi-scale depthwise convolution and gated recurrent unit are employed to extract multi-scale contextual local features and long-short-term features. A temporal attention mechanism is designed to focus on critical time points with higher cross-mode shared information, thereby enhancing the accuracy of fault diagnosis. The proposed model is applied to Tennessee Eastman process dataset and three-phase flow facility dataset. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed model achieves superior diagnostic performance and maintains a small model size.
Double Gradient Reversal Network for Single-Source Domain Generalization in Multi-mode Fault Diagnosis
Jul 19, 2024



Abstract:Domain generalization achieves fault diagnosis on unseen modes. In process industrial systems, fault samples are limited, and only single-mode fault data can be obtained. Extracting domain-invariant fault features from single-mode data for unseen mode fault diagnosis poses challenges. Existing methods utilize a generator module to simulate samples of unseen modes. However, multi-mode samples contain complex spatiotemporal information, which brings significant difficulties to accurate sample generation. Therefore, double gradient reversal network (DGRN) is proposed. First, the model is pre-trained to acquire fault knowledge from the single seen mode. Then, pseudo-fault feature generation strategy is designed by Adaptive instance normalization, to simulate fault features of unseen mode. The dual adversarial training strategy is created to enhance the diversity of pseudo-fault features, which models unseen modes with significant distribution differences. Subsequently, domain-invariant feature extraction strategy is constructed by contrastive learning and adversarial learning. This strategy extracts common features of faults and helps multi-mode fault diagnosis. Finally, the experiments were conducted on Tennessee Eastman process and continuous stirred-tank reactor. The experiments demonstrate that DGRN achieves high classification accuracy on unseen modes while maintaining a small model size.
Spatial Clustering Approach for Vessel Path Identification
Mar 09, 2024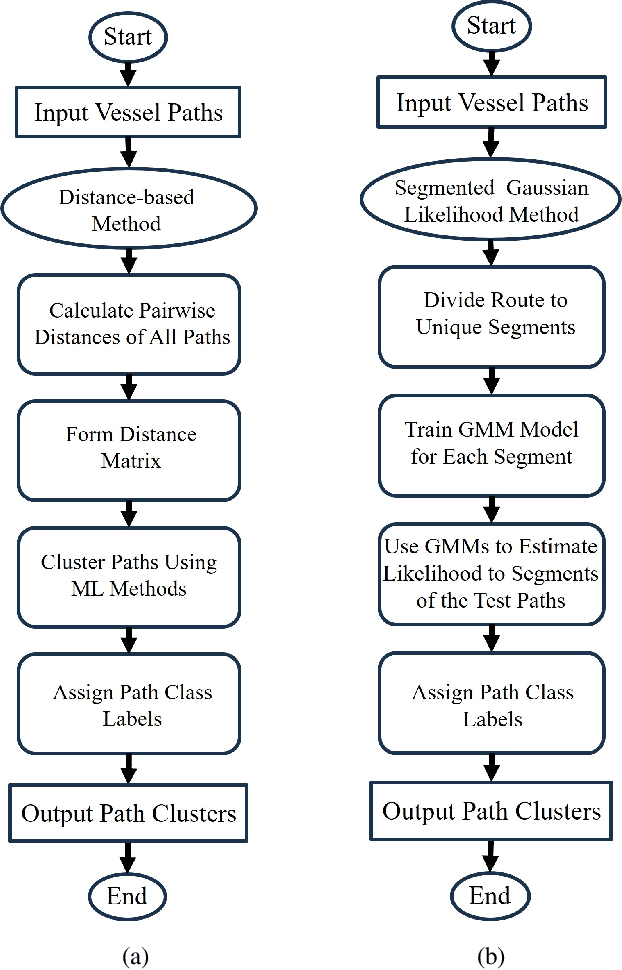
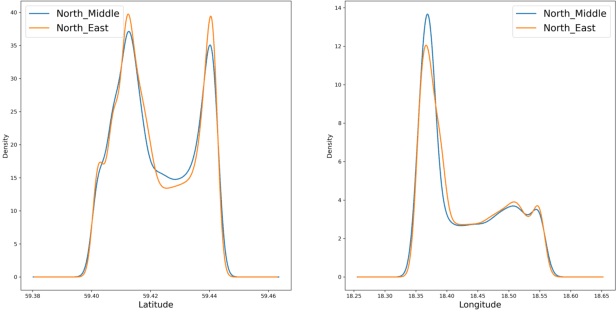
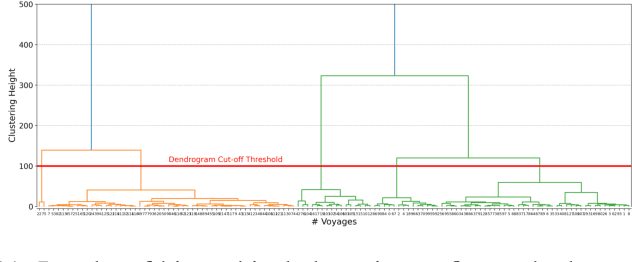
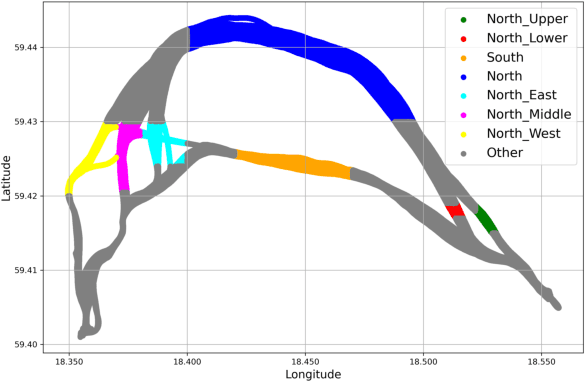
Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of identifying the paths for vessels with operating routes of repetitive paths, partially repetitive paths, and new paths. We propose a spatial clustering approach for labeling the vessel paths by using only position information. We develop a path clustering framework employing two methods: a distance-based path modeling and a likelihood estimation method. The former enhances the accuracy of path clustering through the integration of unsupervised machine learning techniques, while the latter focuses on likelihood-based path modeling and introduces segmentation for a more detailed analysis. The result findings highlight the superior performance and efficiency of the developed approach, as both methods for clustering vessel paths into five classes achieve a perfect F1-score. The approach aims to offer valuable insights for route planning, ultimately contributing to improving safety and efficiency in maritime transportation.
Unknown Health States Recognition With Collective Decision Based Deep Learning Networks In Predictive Maintenance Applications
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:At present, decision making solutions developed based on deep learning (DL) models have received extensive attention in predictive maintenance (PM) applications along with the rapid improvement of computing power. Relying on the superior properties of shared weights and spatial pooling, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) can learn effective representations of health states from industrial data. Many developed CNN-based schemes, such as advanced CNNs that introduce residual learning and multi-scale learning, have shown good performance in health state recognition tasks under the assumption that all the classes are known. However, these schemes have no ability to deal with new abnormal samples that belong to state classes not part of the training set. In this paper, a collective decision framework for different CNNs is proposed. It is based on a One-vs-Rest network (OVRN) to simultaneously achieve classification of known and unknown health states. OVRN learn state-specific discriminative features and enhance the ability to reject new abnormal samples incorporated to different CNNs. According to the validation results on the public dataset of Tennessee Eastman Process (TEP), the proposed CNN-based decision schemes incorporating OVRN have outstanding recognition ability for samples of unknown heath states, while maintaining satisfactory accuracy on known states. The results show that the new DL framework outperforms conventional CNNs, and the one based on residual and multi-scale learning has the best overall performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge