M. Şafak Bilici
Transformers as Neural Augmentors: Class Conditional Sentence Generation via Variational Bayes
May 19, 2022



Abstract:Data augmentation methods for Natural Language Processing tasks are explored in recent years, however they are limited and it is hard to capture the diversity on sentence level. Besides, it is not always possible to perform data augmentation on supervised tasks. To address those problems, we propose a neural data augmentation method, which is a combination of Conditional Variational Autoencoder and encoder-decoder Transformer model. While encoding and decoding the input sentence, our model captures the syntactic and semantic representation of the input language with its class condition. Following the developments in the past years on pre-trained language models, we train and evaluate our models on several benchmarks to strengthen the downstream tasks. We compare our method with 3 different augmentation techniques. The presented results show that, our model increases the performance of current models compared to other data augmentation techniques with a small amount of computation power.
Exploring The Limits Of Data Augmentation For Retinal Vessel Segmentation
May 30, 2021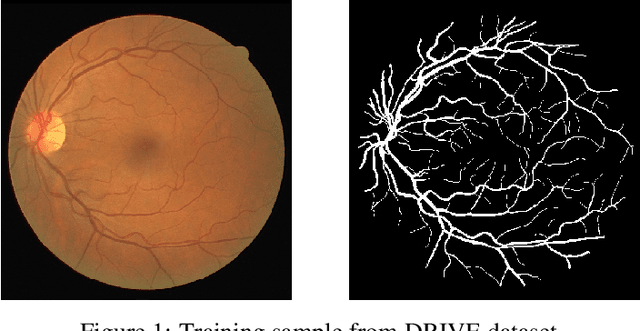
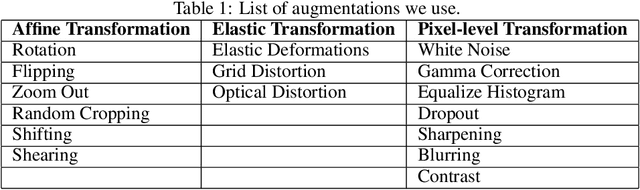
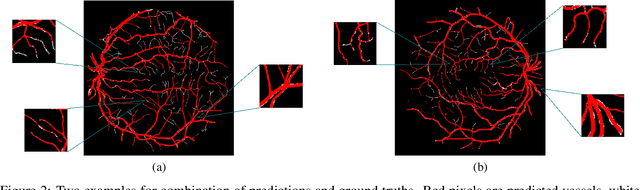
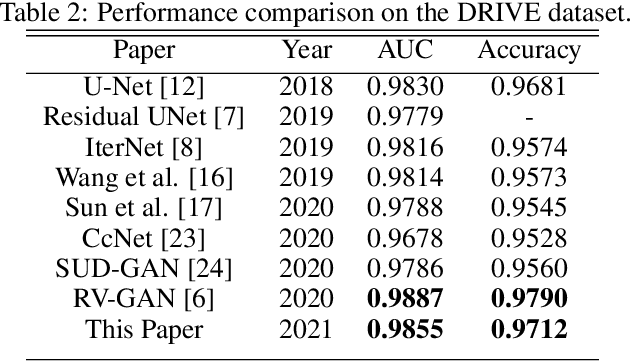
Abstract:Retinal Vessel Segmentation is important for the diagnosis of various diseases. The research on retinal vessel segmentation focuses mainly on the improvement of the segmentation model which is usually based on U-Net architecture. In our study, we use the U-Net architecture and we rely on heavy data augmentation in order to achieve better performance. The success of the data augmentation relies on successfully addressing the problem of input images. By analyzing input images and performing the augmentation accordingly we show that the performance of the U-Net model can be increased dramatically. Results are reported using the most widely used retina dataset, DRIVE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge