Luca Verginer
Understanding Online Migration Decisions Following the Banning of Radical Communities
Dec 09, 2022Abstract:The proliferation of radical online communities and their violent offshoots has sparked great societal concern. However, the current practice of banning such communities from mainstream platforms has unintended consequences: (I) the further radicalization of their members in fringe platforms where they migrate; and (ii) the spillover of harmful content from fringe back onto mainstream platforms. Here, in a large observational study on two banned subreddits, r/The\_Donald and r/fatpeoplehate, we examine how factors associated with the RECRO radicalization framework relate to users' migration decisions. Specifically, we quantify how these factors affect users' decisions to post on fringe platforms and, for those who do, whether they continue posting on the mainstream platform. Our results show that individual-level factors, those relating to the behavior of users, are associated with the decision to post on the fringe platform. Whereas social-level factors, users' connection with the radical community, only affect the propensity to be coactive on both platforms. Overall, our findings pave the way for evidence-based moderation policies, as the decisions to migrate and remain coactive amplify unintended consequences of community bans.
Spillover of Antisocial Behavior from Fringe Platforms: The Unintended Consequences of Community Banning
Sep 20, 2022
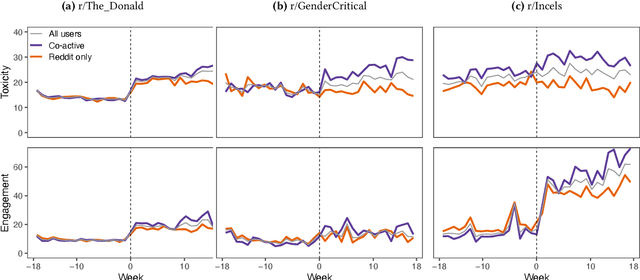

Abstract:Online platforms face pressure to keep their communities civil and respectful. Thus, the bannings of problematic online communities from mainstream platforms like Reddit and Facebook are often met with enthusiastic public reactions. However, this policy can lead users to migrate to alternative fringe platforms with lower moderation standards and where antisocial behaviors like trolling and harassment are widely accepted. As users of these communities often remain \ca across mainstream and fringe platforms, antisocial behaviors may spill over onto the mainstream platform. We study this possible spillover by analyzing around $70,000$ users from three banned communities that migrated to fringe platforms: r/The\_Donald, r/GenderCritical, and r/Incels. Using a difference-in-differences design, we contrast \ca users with matched counterparts to estimate the causal effect of fringe platform participation on users' antisocial behavior on Reddit. Our results show that participating in the fringe communities increases users' toxicity on Reddit (as measured by Perspective API) and involvement with subreddits similar to the banned community -- which often also breach platform norms. The effect intensifies with time and exposure to the fringe platform. In short, we find evidence for a spillover of antisocial behavior from fringe platforms onto Reddit via co-participation.
When standard network measures fail to rank journals: A theoretical and empirical analysis
Jun 29, 2021



Abstract:Journal rankings are widely used and are often based on citation data in combination with a network perspective. We argue that some of these network-based rankings can produce misleading results. From a theoretical point of view, we show that the standard network modelling approach of citation data at the journal level (i.e., the projection of paper citations onto journals) introduces fictitious relations among journals. To overcome this problem, we propose a citation path perspective, and empirically show that rankings based on the network and the citation path perspective are very different. Based on our theoretical and empirical analysis, we highlight the limitations of standard network metrics, and propose a method to overcome these limitations and compute journal rankings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge