Louis-Marie Traonouez
Towards a Multi-Agent Simulation of Cyber-attackers and Cyber-defenders Battles
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:As cyber-attacks show to be more and more complex and coordinated, cyber-defenders strategy through multi-agent approaches could be key to tackle against cyber-attacks as close as entry points in a networked system. This paper presents a Markovian modeling and implementation through a simulator of fighting cyber-attacker agents and cyber-defender agents deployed on host network nodes. It aims to provide an experimental framework to implement realistically based coordinated cyber-attack scenarios while assessing cyber-defenders dynamic organizations. We abstracted network nodes by sets of properties including agents' ones. Actions applied by agents model how the network reacts depending in a given state and what properties are to change. Collective choice of the actions brings the whole environment closer or farther from respective cyber-attackers and cyber-defenders goals. Using the simulator, we implemented a realistically inspired scenario with several behavior implementation approaches for cyber-defenders and cyber-attackers.
A MARL-based Approach for Easing MAS Organization Engineering
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) have been successfully applied in industry for their ability to address complex, distributed problems, especially in IoT-based systems. Their efficiency in achieving given objectives and meeting design requirements is strongly dependent on the MAS organization during the engineering process of an application-specific MAS. To design a MAS that can achieve given goals, available methods rely on the designer's knowledge of the deployment environment. However, high complexity and low readability in some deployment environments make the application of these methods to be costly or raise safety concerns. In order to ease the MAS organization design regarding those concerns, we introduce an original Assisted MAS Organization Engineering Approach (AOMEA). AOMEA relies on combining a Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) process with an organizational model to suggest relevant organizational specifications to help in MAS engineering.
Streamlining Resilient Kubernetes Autoscaling with Multi-Agent Systems via an Automated Online Design Framework
May 26, 2025Abstract:In cloud-native systems, Kubernetes clusters with interdependent services often face challenges to their operational resilience due to poor workload management issues such as resource blocking, bottlenecks, or continuous pod crashes. These vulnerabilities are further amplified in adversarial scenarios, such as Distributed Denial-of-Service attacks (DDoS). Conventional Horizontal Pod Autoscaling (HPA) approaches struggle to address such dynamic conditions, while reinforcement learning-based methods, though more adaptable, typically optimize single goals like latency or resource usage, neglecting broader failure scenarios. We propose decomposing the overarching goal of maintaining operational resilience into failure-specific sub-goals delegated to collaborative agents, collectively forming an HPA Multi-Agent System (MAS). We introduce an automated, four-phase online framework for HPA MAS design: 1) modeling a digital twin built from cluster traces; 2) training agents in simulation using roles and missions tailored to failure contexts; 3) analyzing agent behaviors for explainability; and 4) transferring learned policies to the real cluster. Experimental results demonstrate that the generated HPA MASs outperform three state-of-the-art HPA systems in sustaining operational resilience under various adversarial conditions in a proposed complex cluster.
An Organizationally-Oriented Approach to Enhancing Explainability and Control in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Mar 30, 2025



Abstract:Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning can lead to the development of collaborative agent behaviors that show similarities with organizational concepts. Pushing forward this perspective, we introduce a novel framework that explicitly incorporates organizational roles and goals from the $\mathcal{M}OISE^+$ model into the MARL process, guiding agents to satisfy corresponding organizational constraints. By structuring training with roles and goals, we aim to enhance both the explainability and control of agent behaviors at the organizational level, whereas much of the literature primarily focuses on individual agents. Additionally, our framework includes a post-training analysis method to infer implicit roles and goals, offering insights into emergent agent behaviors. This framework has been applied across various MARL environments and algorithms, demonstrating coherence between predefined organizational specifications and those inferred from trained agents.
Scalable Verification of Markov Decision Processes
Sep 17, 2014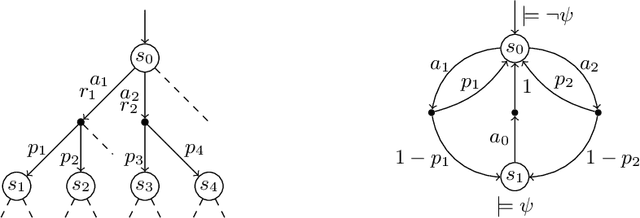
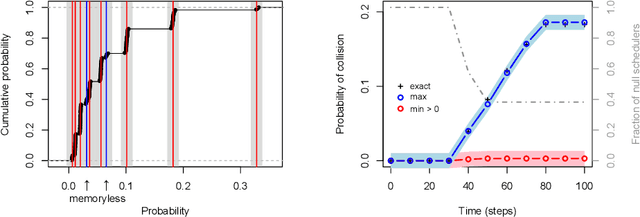
Abstract:Markov decision processes (MDP) are useful to model concurrent process optimisation problems, but verifying them with numerical methods is often intractable. Existing approximative approaches do not scale well and are limited to memoryless schedulers. Here we present the basis of scalable verification for MDPSs, using an O(1) memory representation of history-dependent schedulers. We thus facilitate scalable learning techniques and the use of massively parallel verification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge