Lorenzo Corti
ARTIST: ARTificial Intelligence for Simplified Text
Aug 25, 2023
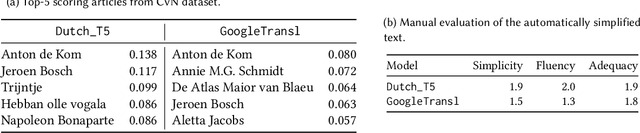
Abstract:Complex text is a major barrier for many citizens when accessing public information and knowledge. While often done manually, Text Simplification is a key Natural Language Processing task that aims for reducing the linguistic complexity of a text while preserving the original meaning. Recent advances in Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) have enabled automatic text simplification both on the lexical and syntactical levels. However, as applications often focus on English, little is understood about the effectiveness of Generative AI techniques on low-resource languages such as Dutch. For this reason, we carry out empirical studies to understand the benefits and limitations of applying generative technologies for text simplification and provide the following outcomes: 1) the design and implementation for a configurable text simplification pipeline that orchestrates state-of-the-art generative text simplification models, domain and reader adaptation, and visualisation modules; 2) insights and lessons learned, showing the strengths of automatic text simplification while exposing the challenges in handling cultural and commonsense knowledge. These outcomes represent a first step in the exploration of Dutch text simplification and shed light on future endeavours both for research and practice.
A.I. Robustness: a Human-Centered Perspective on Technological Challenges and Opportunities
Oct 19, 2022
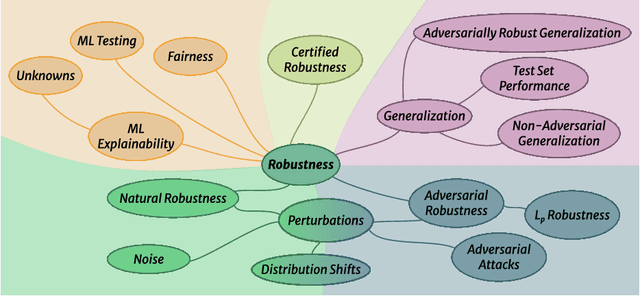
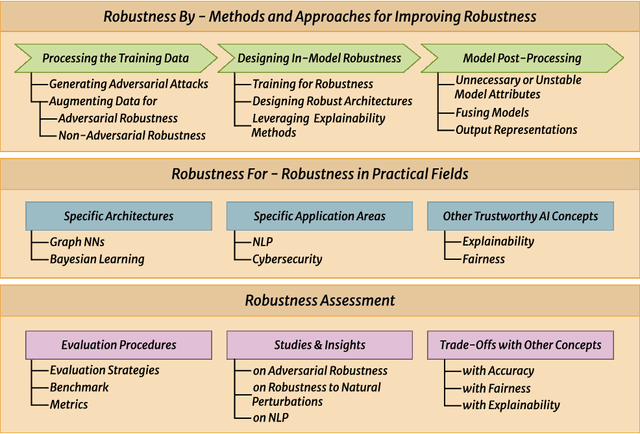
Abstract:Despite the impressive performance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems, their robustness remains elusive and constitutes a key issue that impedes large-scale adoption. Robustness has been studied in many domains of AI, yet with different interpretations across domains and contexts. In this work, we systematically survey the recent progress to provide a reconciled terminology of concepts around AI robustness. We introduce three taxonomies to organize and describe the literature both from a fundamental and applied point of view: 1) robustness by methods and approaches in different phases of the machine learning pipeline; 2) robustness for specific model architectures, tasks, and systems; and in addition, 3) robustness assessment methodologies and insights, particularly the trade-offs with other trustworthiness properties. Finally, we identify and discuss research gaps and opportunities and give an outlook on the field. We highlight the central role of humans in evaluating and enhancing AI robustness, considering the necessary knowledge humans can provide, and discuss the need for better understanding practices and developing supportive tools in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge