Lilin Zhang
Negative Metric Learning for Graphs
May 15, 2025Abstract:Graph contrastive learning (GCL) often suffers from false negatives, which degrades the performance on downstream tasks. The existing methods addressing the false negative issue usually rely on human prior knowledge, still leading GCL to suboptimal results. In this paper, we propose a novel Negative Metric Learning (NML) enhanced GCL (NML-GCL). NML-GCL employs a learnable Negative Metric Network (NMN) to build a negative metric space, in which false negatives can be distinguished better from true negatives based on their distance to anchor node. To overcome the lack of explicit supervision signals for NML, we propose a joint training scheme with bi-level optimization objective, which implicitly utilizes the self-supervision signals to iteratively optimize the encoder and the negative metric network. The solid theoretical analysis and the extensive experiments conducted on widely used benchmarks verify the superiority of the proposed method.
Weakly Supervised Contrastive Adversarial Training for Learning Robust Features from Semi-supervised Data
Mar 14, 2025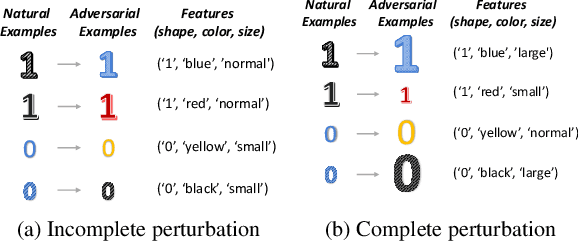
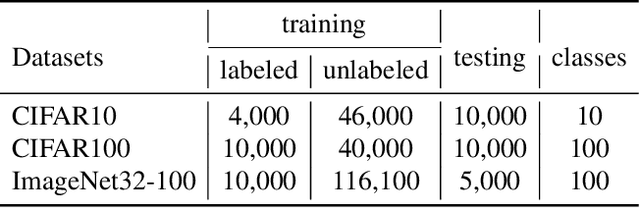
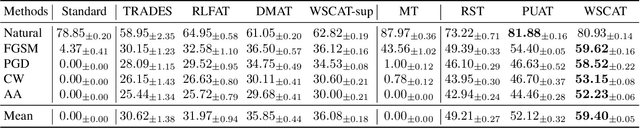
Abstract:Existing adversarial training (AT) methods often suffer from incomplete perturbation, meaning that not all non-robust features are perturbed when generating adversarial examples (AEs). This results in residual correlations between non-robust features and labels, leading to suboptimal learning of robust features. However, achieving complete perturbation, i.e., perturbing as many non-robust features as possible, is challenging due to the difficulty in distinguishing robust and non-robust features and the sparsity of labeled data. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach called Weakly Supervised Contrastive Adversarial Training (WSCAT). WSCAT ensures complete perturbation for improved learning of robust features by disrupting correlations between non-robust features and labels through complete AE generation over partially labeled data, grounded in information theory. Extensive theoretical analysis and comprehensive experiments on widely adopted benchmarks validate the superiority of WSCAT.
Adaptive Fair Representation Learning for Personalized Fairness in Recommendations via Information Alignment
Apr 13, 2024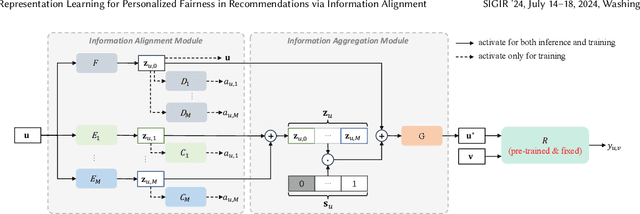
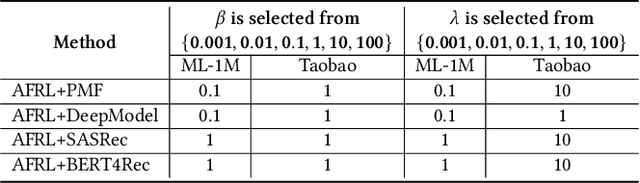
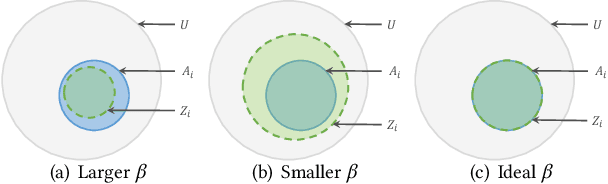
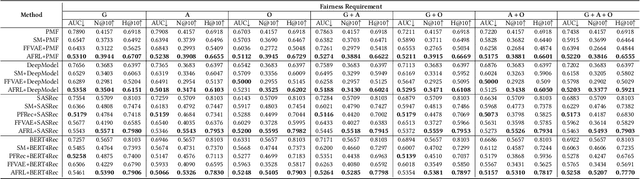
Abstract:Personalized fairness in recommendations has been attracting increasing attention from researchers. The existing works often treat a fairness requirement, represented as a collection of sensitive attributes, as a hyper-parameter, and pursue extreme fairness by completely removing information of sensitive attributes from the learned fair embedding, which suffer from two challenges: huge training cost incurred by the explosion of attribute combinations, and the suboptimal trade-off between fairness and accuracy. In this paper, we propose a novel Adaptive Fair Representation Learning (AFRL) model, which achieves a real personalized fairness due to its advantage of training only one model to adaptively serve different fairness requirements during inference phase. Particularly, AFRL treats fairness requirements as inputs and can learn an attribute-specific embedding for each attribute from the unfair user embedding, which endows AFRL with the adaptability during inference phase to determine the non-sensitive attributes under the guidance of the user's unique fairness requirement. To achieve a better trade-off between fairness and accuracy in recommendations, AFRL conducts a novel Information Alignment to exactly preserve discriminative information of non-sensitive attributes and incorporate a debiased collaborative embedding into the fair embedding to capture attribute-independent collaborative signals, without loss of fairness. Finally, the extensive experiments conducted on real datasets together with the sound theoretical analysis demonstrate the superiority of AFRL.
Contrastive Collaborative Filtering for Cold-Start Item Recommendation
Feb 22, 2023Abstract:The cold-start problem is a long-standing challenge in recommender systems. As a promising solution, content-based generative models usually project a cold-start item's content onto a warm-start item embedding to capture collaborative signals from item content so that collaborative filtering can be applied. However, since the training of the cold-start recommendation models is conducted on warm datasets, the existent methods face the issue that the collaborative embeddings of items will be blurred, which significantly degenerates the performance of cold-start item recommendation. To address this issue, we propose a novel model called Contrastive Collaborative Filtering for Cold-start item Recommendation (CCFCRec), which capitalizes on the co-occurrence collaborative signals in warm training data to alleviate the issue of blurry collaborative embeddings for cold-start item recommendation. In particular, we devise a contrastive collaborative filtering (CF) framework, consisting of a content CF module and a co-occurrence CF module to generate the content-based collaborative embedding and the co-occurrence collaborative embedding for a training item, respectively. During the joint training of the two CF modules, we apply a contrastive learning between the two collaborative embeddings, by which the knowledge about the co-occurrence signals can be indirectly transferred to the content CF module, so that the blurry collaborative embeddings can be rectified implicitly by the memorized co-occurrence collaborative signals during the applying phase. Together with the sound theoretical analysis, the extensive experiments conducted on real datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model. The codes and datasets are available on https://github.com/zzhin/CCFCRec.
Provable Unrestricted Adversarial Training without Compromise with Generalizability
Jan 22, 2023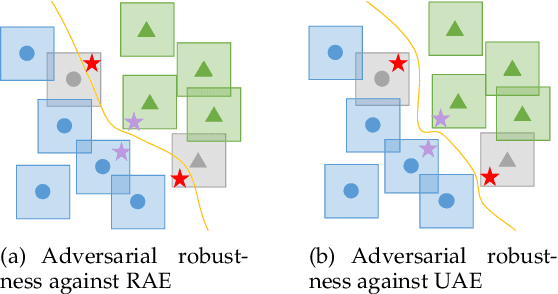
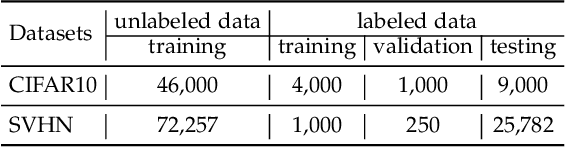
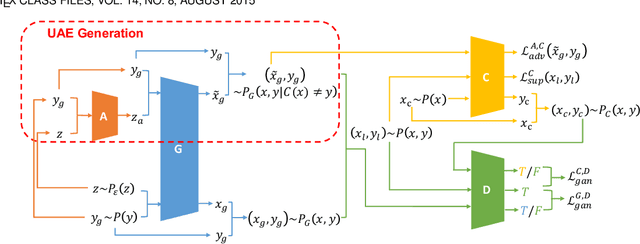
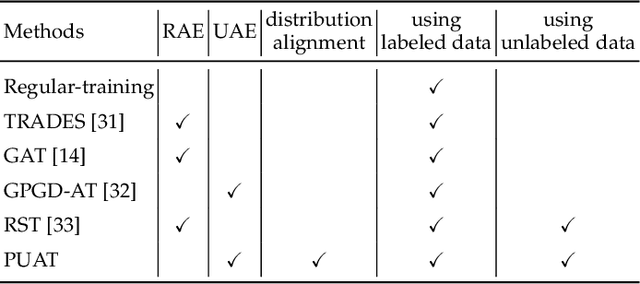
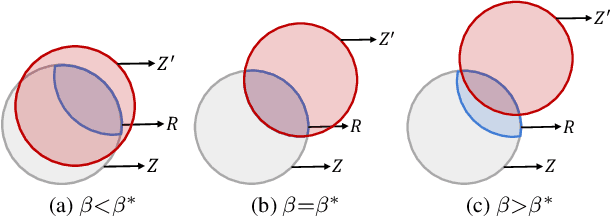
Abstract:Adversarial training (AT) is widely considered as the most promising strategy to defend against adversarial attacks and has drawn increasing interest from researchers. However, the existing AT methods still suffer from two challenges. First, they are unable to handle unrestricted adversarial examples (UAEs), which are built from scratch, as opposed to restricted adversarial examples (RAEs), which are created by adding perturbations bound by an $l_p$ norm to observed examples. Second, the existing AT methods often achieve adversarial robustness at the expense of standard generalizability (i.e., the accuracy on natural examples) because they make a tradeoff between them. To overcome these challenges, we propose a unique viewpoint that understands UAEs as imperceptibly perturbed unobserved examples. Also, we find that the tradeoff results from the separation of the distributions of adversarial examples and natural examples. Based on these ideas, we propose a novel AT approach called Provable Unrestricted Adversarial Training (PUAT), which can provide a target classifier with comprehensive adversarial robustness against both UAE and RAE, and simultaneously improve its standard generalizability. Particularly, PUAT utilizes partially labeled data to achieve effective UAE generation by accurately capturing the natural data distribution through a novel augmented triple-GAN. At the same time, PUAT extends the traditional AT by introducing the supervised loss of the target classifier into the adversarial loss and achieves the alignment between the UAE distribution, the natural data distribution, and the distribution learned by the classifier, with the collaboration of the augmented triple-GAN. Finally, the solid theoretical analysis and extensive experiments conducted on widely-used benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of PUAT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge