Libo Zi
Incremental Learning for End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition
May 11, 2020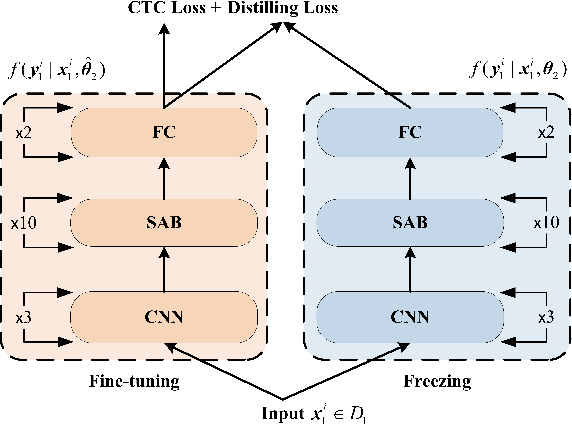
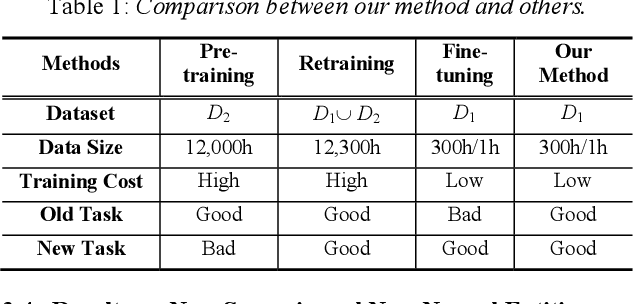
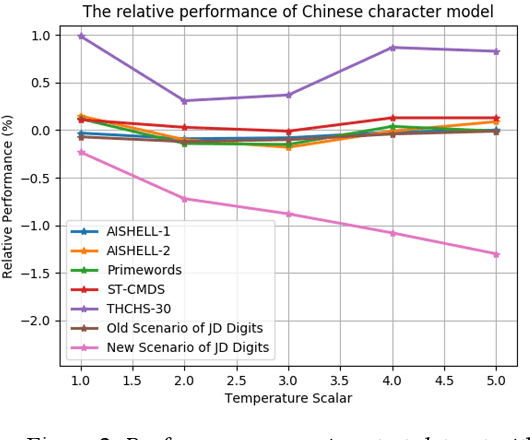
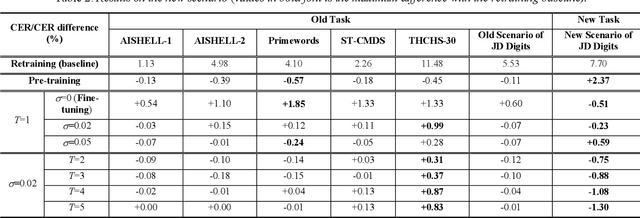
Abstract:We propose an incremental learning for end-to-end Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) to extend the model's capacity on a new task while retaining the performance on existing ones. The proposed method is effective without accessing to the old dataset to address the issues of high training cost and old dataset unavailability. To achieve this, knowledge distillation is applied as a guidance to retain the recognition ability from the previous model, which is then combined with the new ASR task for model optimization. With an ASR model pre-trained on 12,000h Mandarin speech, we test our proposed method on 300h new scenario task and 1h new named entities task. Experiments show that our method yields 3.25% and 0.88% absolute Character Error Rate (CER) reduction on the new scenario, when compared with the pre-trained model and the full-data retraining baseline, respectively. It even yields a surprising 0.37% absolute CER reduction on the new scenario than the fine-tuning. For the new named entities task, our method significantly improves the accuracy compared with the pre-trained model, i.e. 16.95% absolute CER reduction. For both of the new task adaptions, the new models still maintain a same accuracy with the baseline on the old tasks.
Research on Modeling Units of Transformer Transducer for Mandarin Speech Recognition
Apr 26, 2020



Abstract:Modeling unit and model architecture are two key factors of Recurrent Neural Network Transducer (RNN-T) in end-to-end speech recognition. To improve the performance of RNN-T for Mandarin speech recognition task, a novel transformer transducer with the combination architecture of self-attention transformer and RNN is proposed. And then the choice of different modeling units for transformer transducer is explored. In addition, we present a new mix-bandwidth training method to obtain a general model that is able to accurately recognize Mandarin speech with different sampling rates simultaneously. All of our experiments are conducted on about 12,000 hours of Mandarin speech with sampling rate in 8kHz and 16kHz. Experimental results show that Mandarin transformer transducer using syllable with tone achieves the best performance. It yields an average of 14.4% and 44.1% relative Word Error Rate (WER) reduction when compared with the models using syllable initial/final with tone and Chinese character, respectively. Also, it outperforms the model based on syllable initial/final with tone with an average of 13.5% relative Character Error Rate (CER) reduction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge