Li Huo
The changing rule of human bone density with aging based on a novel definition and mensuration of bone density with computed tomography
Aug 05, 2023
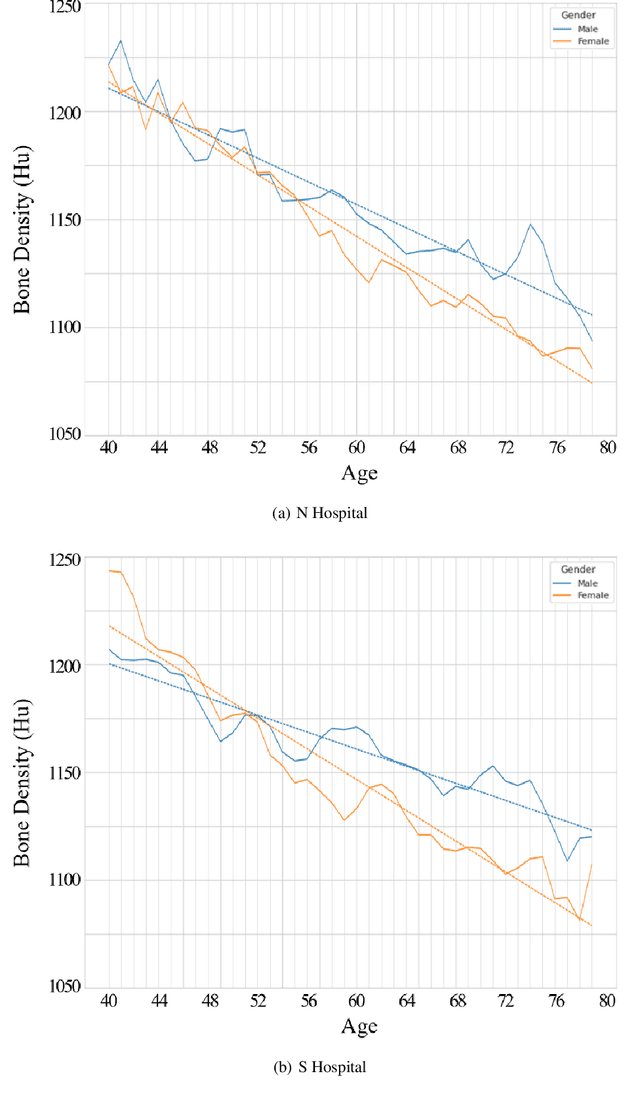
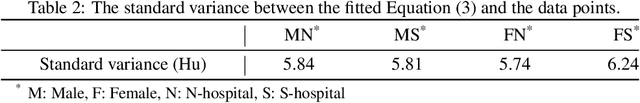
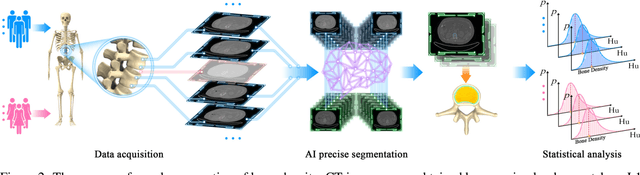
Abstract:Osteoporosis and fragility fractures have emerged as major public health concerns in an aging population. However, measuring age-related changes in bone density using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry has limited personalized risk assessment due to susceptibility to interference from various factors. In this study, we propose an innovative statistical model of bone pixel distribution in fine-segmented computed tomography (CT) images, along with a novel approach to measuring bone density based on CT values of bone pixels. Our findings indicate that bone density exhibits a linear decline with age during adulthood between the ages of 39 and 80, with the rate of decline being approximately 1.6 times faster in women than in men. This contradicts the widely accepted notion that bone density starts declining in women at menopause and in men at around 50 years of age. The linearity of age-related changes provides further insights into the dynamics of the aging human body. Consequently, our findings suggest that the definition of osteoporosis by the World Health Organization should be revised to the standard deviation of age-based bone density. Furthermore, these results open up new avenues for research in bone health care and clinical investigation of osteoporosis.
Adversarial Attack Driven Data Augmentation for Accurate And Robust Medical Image Segmentation
May 25, 2021



Abstract:Segmentation is considered to be a very crucial task in medical image analysis. This task has been easier since deep learning models have taken over with its high performing behavior. However, deep learning models dependency on large data proves it to be an obstacle in medical image analysis because of insufficient data samples. Several data augmentation techniques have been used to mitigate this problem. We propose a new augmentation method by introducing adversarial learning attack techniques, specifically Fast Gradient Sign Method (FGSM). Furthermore, We have also introduced the concept of Inverse FGSM (InvFGSM), which works in the opposite manner of FGSM for the data augmentation. This two approaches worked together to improve the segmentation accuracy, as well as helped the model to gain robustness against adversarial attacks. The overall analysis of experiments indicates a novel use of adversarial machine learning along with robustness enhancement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge