Lewis Birch
Bypassing Prompt Injection and Jailbreak Detection in LLM Guardrails
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) guardrail systems are designed to protect against prompt injection and jailbreak attacks. However, they remain vulnerable to evasion techniques. We demonstrate two approaches for bypassing LLM prompt injection and jailbreak detection systems via traditional character injection methods and algorithmic Adversarial Machine Learning (AML) evasion techniques. Through testing against six prominent protection systems, including Microsoft's Azure Prompt Shield and Meta's Prompt Guard, we show that both methods can be used to evade detection while maintaining adversarial utility achieving in some instances up to 100% evasion success. Furthermore, we demonstrate that adversaries can enhance Attack Success Rates (ASR) against black-box targets by leveraging word importance ranking computed by offline white-box models. Our findings reveal vulnerabilities within current LLM protection mechanisms and highlight the need for more robust guardrail systems.
Compilation as a Defense: Enhancing DL Model Attack Robustness via Tensor Optimization
Sep 20, 2023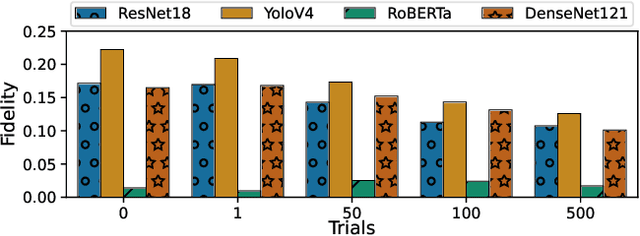
Abstract:Adversarial Machine Learning (AML) is a rapidly growing field of security research, with an often overlooked area being model attacks through side-channels. Previous works show such attacks to be serious threats, though little progress has been made on efficient remediation strategies that avoid costly model re-engineering. This work demonstrates a new defense against AML side-channel attacks using model compilation techniques, namely tensor optimization. We show relative model attack effectiveness decreases of up to 43% using tensor optimization, discuss the implications, and direction of future work.
Model Leeching: An Extraction Attack Targeting LLMs
Sep 19, 2023Abstract:Model Leeching is a novel extraction attack targeting Large Language Models (LLMs), capable of distilling task-specific knowledge from a target LLM into a reduced parameter model. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our attack by extracting task capability from ChatGPT-3.5-Turbo, achieving 73% Exact Match (EM) similarity, and SQuAD EM and F1 accuracy scores of 75% and 87%, respectively for only $50 in API cost. We further demonstrate the feasibility of adversarial attack transferability from an extracted model extracted via Model Leeching to perform ML attack staging against a target LLM, resulting in an 11% increase to attack success rate when applied to ChatGPT-3.5-Turbo.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge