Leon Sterling
Swinburne University of Technology
Adapting a General Purpose Social Robot for Paediatric Rehabilitation through In-situ Design
Mar 08, 2018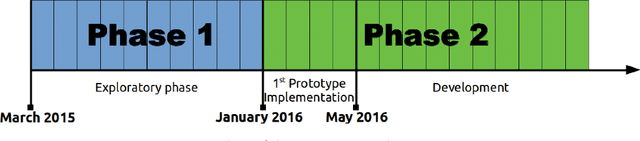
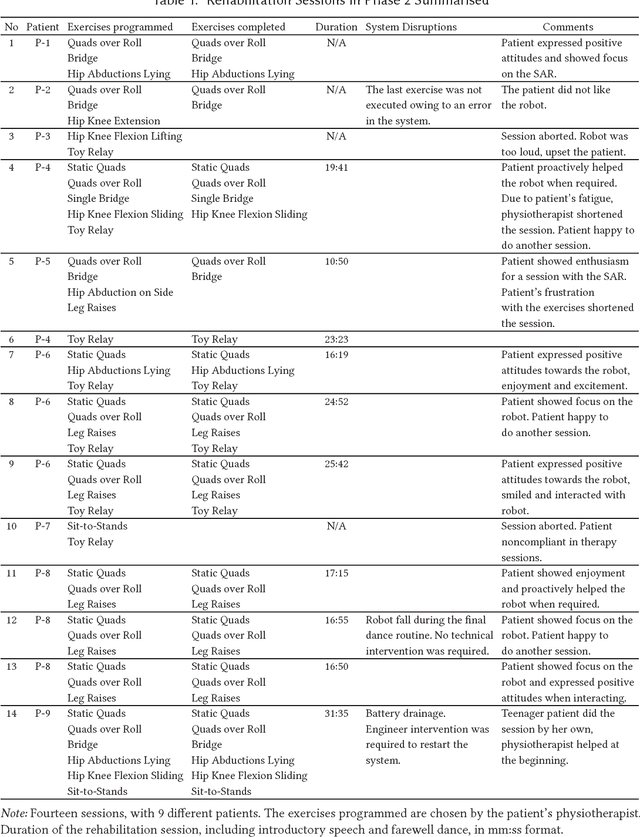
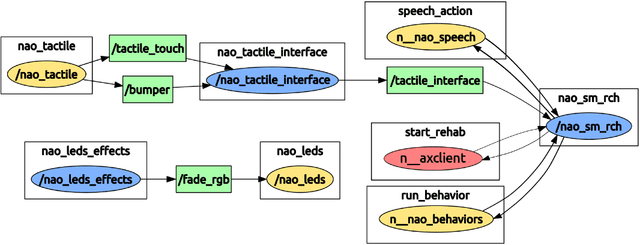
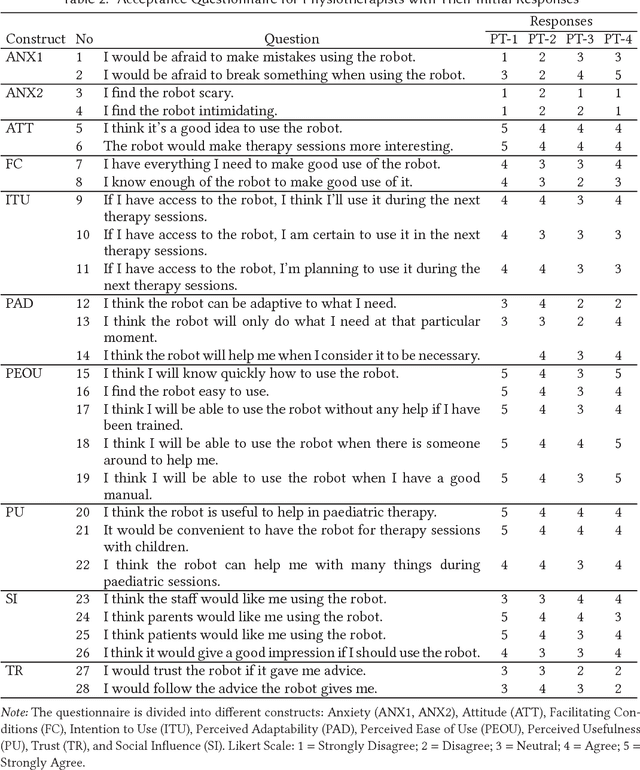
Abstract:Socially Assistive Robots (SARs) offer great promise for improving outcomes in paediatric rehabilitation. However, the design of software and interactive capabilities for SARs must be carefully considered in the context of their intended clinical use. While previous work has explored specific roles and functionalities to support paediatric rehabilitation, few have considered the design of such capabilities in the context of ongoing clinical deployment. In this paper we present a two-phase In-situ design process for SARs in health care, emphasising stakeholder engagement and on-site development. We explore this in the context of developing the humanoid social robot NAO as a socially assistive rehabilitation aid for children with cerebral palsy. We present and evaluate our design process, outcomes achieved, and preliminary results from ongoing clinical testing with 9 patients and 5 therapists over 14 sessions. We argue that our in-situ Design methodology has been central to the rapid and successful deployment of our system.
Logic-Based Specification Languages for Intelligent Software Agents
Nov 20, 2003

Abstract:The research field of Agent-Oriented Software Engineering (AOSE) aims to find abstractions, languages, methodologies and toolkits for modeling, verifying, validating and prototyping complex applications conceptualized as Multiagent Systems (MASs). A very lively research sub-field studies how formal methods can be used for AOSE. This paper presents a detailed survey of six logic-based executable agent specification languages that have been chosen for their potential to be integrated in our ARPEGGIO project, an open framework for specifying and prototyping a MAS. The six languages are ConGoLog, Agent-0, the IMPACT agent programming language, DyLog, Concurrent METATEM and Ehhf. For each executable language, the logic foundations are described and an example of use is shown. A comparison of the six languages and a survey of similar approaches complete the paper, together with considerations of the advantages of using logic-based languages in MAS modeling and prototyping.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge