Lena Mondrejevski
Early prediction of the risk of ICU mortality with Deep Federated Learning
Dec 05, 2022Abstract:Intensive Care Units usually carry patients with a serious risk of mortality. Recent research has shown the ability of Machine Learning to indicate the patients' mortality risk and point physicians toward individuals with a heightened need for care. Nevertheless, healthcare data is often subject to privacy regulations and can therefore not be easily shared in order to build Centralized Machine Learning models that use the combined data of multiple hospitals. Federated Learning is a Machine Learning framework designed for data privacy that can be used to circumvent this problem. In this study, we evaluate the ability of deep Federated Learning to predict the risk of Intensive Care Unit mortality at an early stage. We compare the predictive performance of Federated, Centralized, and Local Machine Learning in terms of AUPRC, F1-score, and AUROC. Our results show that Federated Learning performs equally well as the centralized approach and is substantially better than the local approach, thus providing a viable solution for early Intensive Care Unit mortality prediction. In addition, we show that the prediction performance is higher when the patient history window is closer to discharge or death. Finally, we show that using the F1-score as an early stopping metric can stabilize and increase the performance of our approach for the task at hand.
FLICU: A Federated Learning Workflow for Intensive Care Unit Mortality Prediction
May 30, 2022
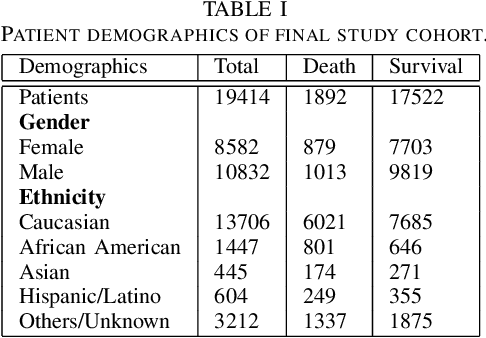
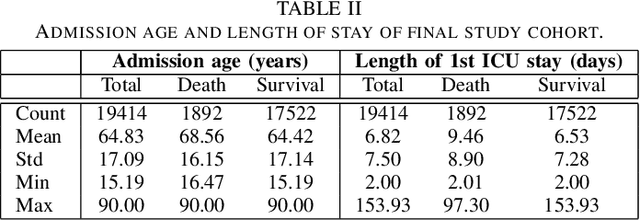
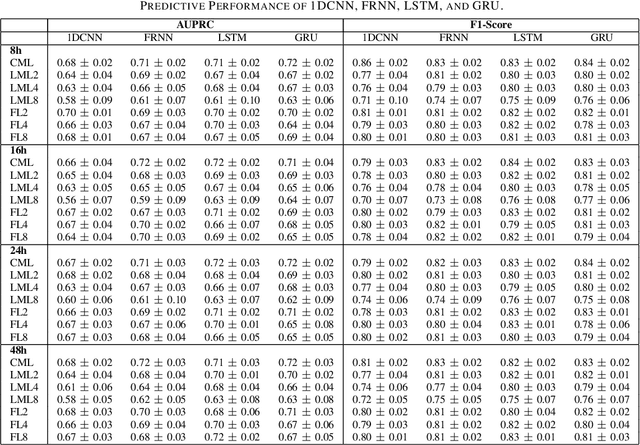
Abstract:Although Machine Learning (ML) can be seen as a promising tool to improve clinical decision-making for supporting the improvement of medication plans, clinical procedures, diagnoses, or medication prescriptions, it remains limited by access to healthcare data. Healthcare data is sensitive, requiring strict privacy practices, and typically stored in data silos, making traditional machine learning challenging. Federated learning can counteract those limitations by training machine learning models over data silos while keeping the sensitive data localized. This study proposes a federated learning workflow for ICU mortality prediction. Hereby, the applicability of federated learning as an alternative to centralized machine learning and local machine learning is investigated by introducing federated learning to the binary classification problem of predicting ICU mortality. We extract multivariate time series data from the MIMIC-III database (lab values and vital signs), and benchmark the predictive performance of four deep sequential classifiers (FRNN, LSTM, GRU, and 1DCNN) varying the patient history window lengths (8h, 16h, 24h, 48h) and the number of FL clients (2, 4, 8). The experiments demonstrate that both centralized machine learning and federated learning are comparable in terms of AUPRC and F1-score. Furthermore, the federated approach shows superior performance over local machine learning. Thus, the federated approach can be seen as a valid and privacy-preserving alternative to centralized machine learning for classifying ICU mortality when sharing sensitive patient data between hospitals is not possible.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge