Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Leila Malihi
Exploring the Properties and Evolution of Neural Network Eigenspaces during Training
Jun 18, 2021Figures and Tables:
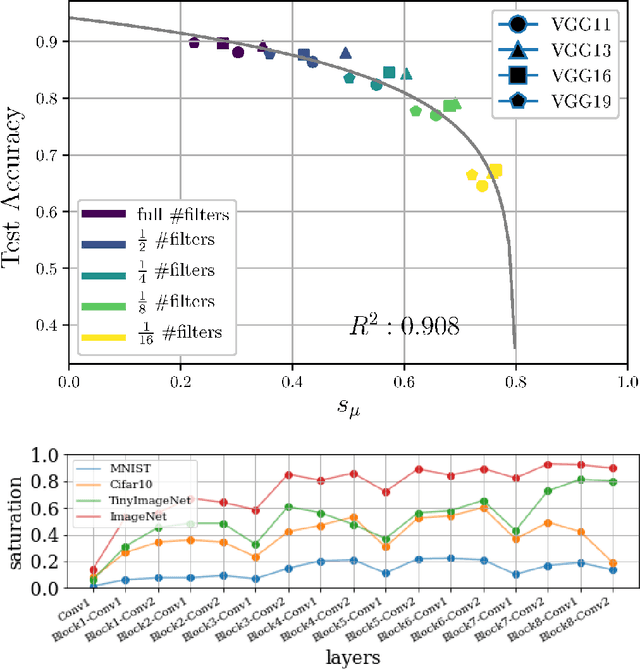
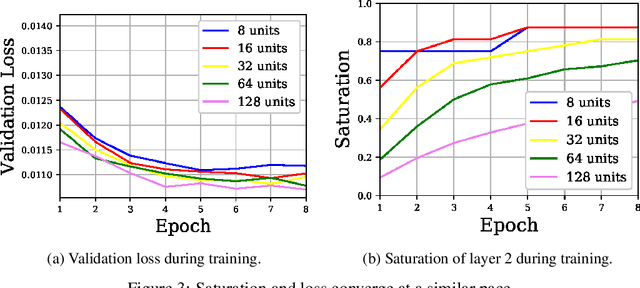
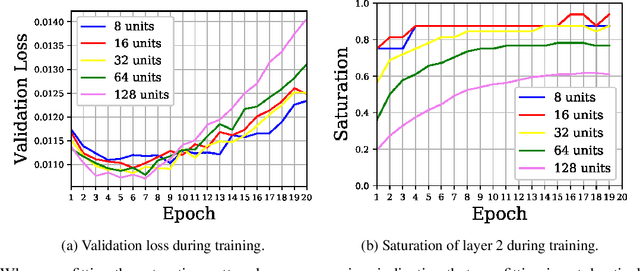




Abstract:In this work we explore the information processing inside neural networks using logistic regression probes \cite{probes} and the saturation metric \cite{featurespace_saturation}. We show that problem difficulty and neural network capacity affect the predictive performance in an antagonistic manner, opening the possibility of detecting over- and under-parameterization of neural networks for a given task. We further show that the observed effects are independent from previously reported pathological patterns like the ``tail pattern'' described in \cite{featurespace_saturation}. Finally we are able to show that saturation patterns converge early during training, allowing for a quicker cycle time during analysis
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge