Leif Bergerhoff
Learning Antenna Pointing Correction in Operations: Efficient Calibration of a Black Box
May 24, 2024Abstract:We propose an efficient offline pointing calibration method for operational antenna systems which does not require any downtime. Our approach minimizes the calibration effort and exploits technical signal information which is typically used for monitoring and control purposes in ground station operations. Using a standard antenna interface and data from an operational satellite contact, we come up with a robust strategy for training data set generation. On top of this, we learn the parameters of a suitable coordinate transform by means of linear regression. In our experiments, we show the usefulness of the method in a real-world setup.
Seeing the World through an Antenna's Eye: Reception Quality Visualization Using Incomplete Technical Signal Information
May 24, 2024Abstract:We come up with a novel application for image analysis methods in the context of direction dependent signal characteristics. For this purpose, we describe an inpainting approach adding benefit to technical signal information which are typically only used for monitoring and control purposes in ground station operations. Recalling the theoretical properties of the employed inpainting technique and appropriate modeling allow us to demonstrate the usefulness of our approach for satellite data reception quality assessment. In our application, we show the advantages of inpainting products over raw data as well as the rich potential of the visualization of technical signal information.
Stable Backward Diffusion Models that Minimise Convex Energies
Mar 08, 2019
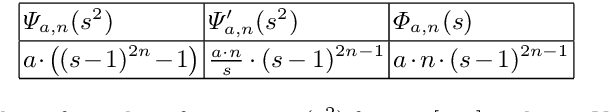
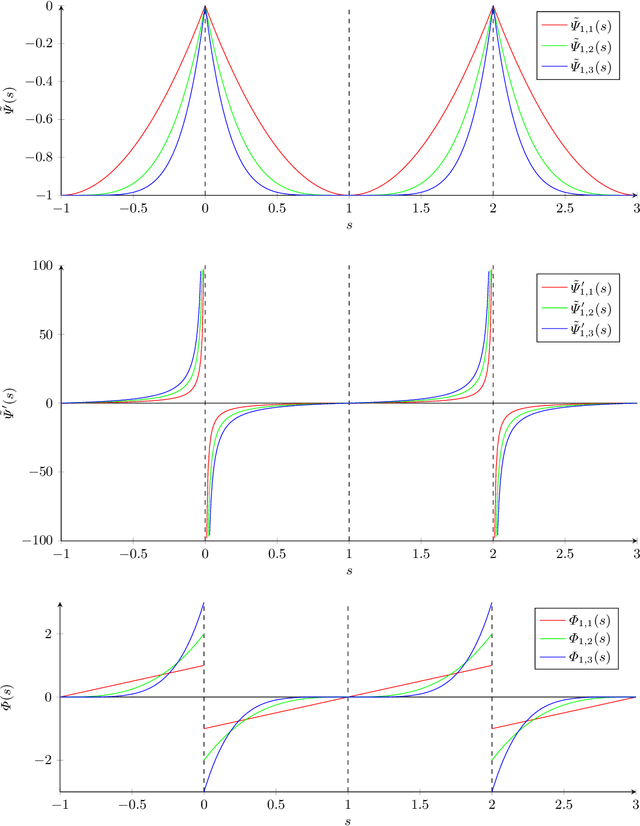
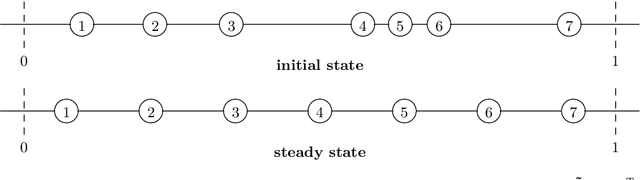
Abstract:Backward diffusion processes appear naturally in image enhancement and deblurring applications. However, the inverse problem of backward diffusion is known to be ill-posed and straightforward numerical algorithms are unstable. So far, existing stabilisation strategies in the literature require sophisticated numerics to solve the underlying initial value problem. Therefore, it is desirable to establish a backward diffusion model which implements a smart stabilisation approach that can be used in combination with a simple numerical scheme. We derive a class of space-discrete one-dimensional backward diffusion as gradient descent of energies where we gain stability by imposing range constraints. Interestingly, these energies are even convex. Furthermore, we establish a comprehensive theory for the time-continuous evolution and we show that stability carries over to a simple explicit time discretisation of our model. Finally, we confirm the stability and usefulness of our technique in experiments in which we enhance the contrast of digital greyscale and colour images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge