Laura R. Marusich
Using AI Uncertainty Quantification to Improve Human Decision-Making
Sep 19, 2023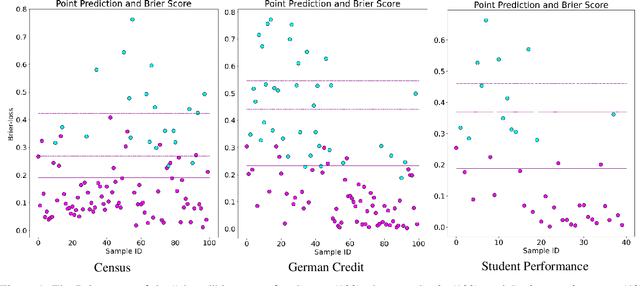
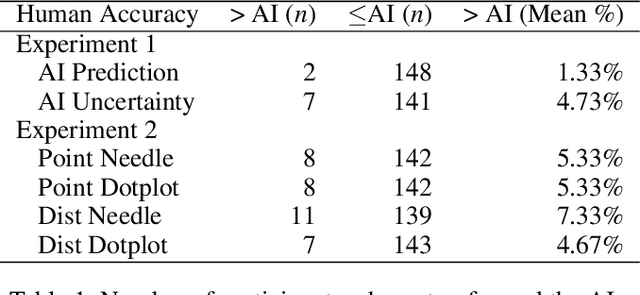
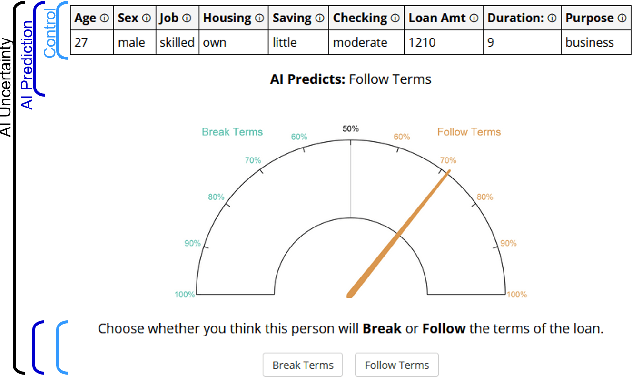
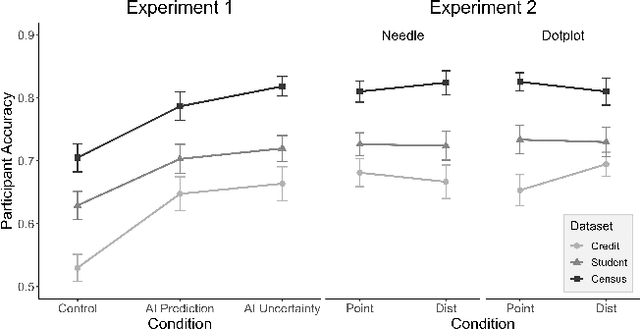
Abstract:AI Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) has the potential to improve human decision-making beyond AI predictions alone by providing additional useful probabilistic information to users. The majority of past research on AI and human decision-making has concentrated on model explainability and interpretability. We implemented instance-based UQ for three real datasets. To achieve this, we trained different AI models for classification for each dataset, and used random samples generated around the neighborhood of the given instance to create confidence intervals for UQ. The computed UQ was calibrated using a strictly proper scoring rule as a form of quality assurance for UQ. We then conducted two preregistered online behavioral experiments that compared objective human decision-making performance under different AI information conditions, including UQ. In Experiment 1, we compared decision-making for no AI (control), AI prediction alone, and AI prediction with a visualization of UQ. We found UQ significantly improved decision-making beyond the other two conditions. In Experiment 2, we focused on comparing different representations of UQ information: Point vs. distribution of uncertainty and visualization type (needle vs. dotplot). We did not find meaningful differences in decision-making performance among these different representations of UQ. Overall, our results indicate that human decision-making can be improved by providing UQ information along with AI predictions, and that this benefit generalizes across a variety of representations of UQ.
Does Explainable Artificial Intelligence Improve Human Decision-Making?
Jun 19, 2020



Abstract:Explainable AI provides insight into the "why" for model predictions, offering potential for users to better understand and trust a model, and to recognize and correct AI predictions that are incorrect. Prior research on human and explainable AI interactions has focused on measures such as interpretability, trust, and usability of the explanation. Whether explainable AI can improve actual human decision-making and the ability to identify the problems with the underlying model are open questions. Using real datasets, we compare and evaluate objective human decision accuracy without AI (control), with an AI prediction (no explanation), and AI prediction with explanation. We find providing any kind of AI prediction tends to improve user decision accuracy, but no conclusive evidence that explainable AI has a meaningful impact. Moreover, we observed the strongest predictor for human decision accuracy was AI accuracy and that users were somewhat able to detect when the AI was correct versus incorrect, but this was not significantly affected by including an explanation. Our results indicate that, at least in some situations, the "why" information provided in explainable AI may not enhance user decision-making, and further research may be needed to understand how to integrate explainable AI into real systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge