Lama Hassan
Future Artificial Intelligence tools and perspectives in medicine
Jun 04, 2022Abstract:Purpose of review: Artificial intelligence (AI) has become popular in medical applications, specifically as a clinical support tool for computer-aided diagnosis. These tools are typically employed on medical data (i.e., image, molecular data, clinical variables, etc.) and used the statistical and machine learning methods to measure the model performance. In this review, we summarized and discussed the most recent radiomic pipeline used for clinical analysis. Recent findings:Currently, limited management of cancers benefits from artificial intelligence, mostly related to a computer-aided diagnosis that avoids a biopsy analysis that presents additional risks and costs. Most AI tools are based on imaging features, known as radiomic analysis that can be refined into predictive models in non-invasively acquired imaging data. This review explores the progress of AI-based radiomic tools for clinical applications with a brief description of necessary technical steps. Explaining new radiomic approaches based on deep learning techniques will explain how the new radiomic models (deep radiomic analysis) can benefit from deep convolutional neural networks and be applied on limited data sets. Summary: To consider the radiomic algorithms, further investigations are recommended to involve deep learning in radiomic models with additional validation steps on various cancer types.
Deep Radiomic Analysis for Predicting Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Computerized Tomography and X-ray Images
Jun 04, 2022



Abstract:This paper proposes to encode the distribution of features learned from a convolutional neural network using a Gaussian Mixture Model. These parametric features, called GMM-CNN, are derived from chest computed tomography and X-ray scans of patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. We use the proposed GMM-CNN features as input to a robust classifier based on random forests to differentiate between COVID-19 and other pneumonia cases. Our experiments assess the advantage of GMM-CNN features compared to standard CNN classification on test images. Using a random forest classifier (80\% samples for training; 20\% samples for testing), GMM-CNN features encoded with two mixture components provided a significantly better performance than standard CNN classification (p\,$<$\,0.05). Specifically, our method achieved an accuracy in the range of 96.00\,--\,96.70\% and an area under the ROC curve in the range of 99.29\,--\,99.45\%, with the best performance obtained by combining GMM-CNN features from both computed tomography and X-ray images. Our results suggest that the proposed GMM-CNN features could improve the prediction of COVID-19 in chest computed tomography and X-ray scans.
Modeling of Textures to Predict Immune Cell Status and Survival of Brain Tumour Patients
Jun 04, 2022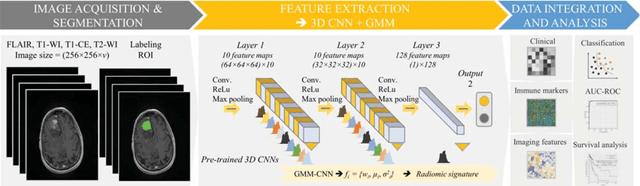
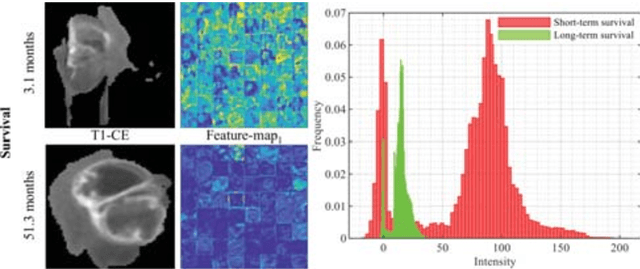
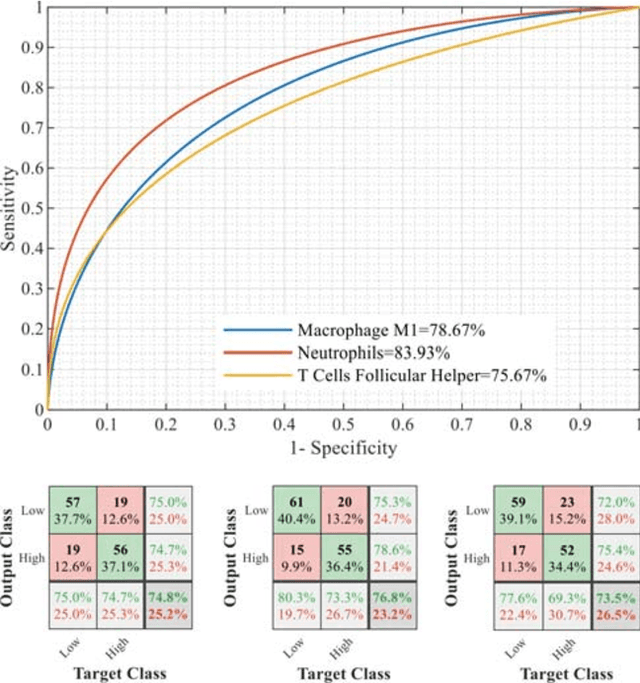
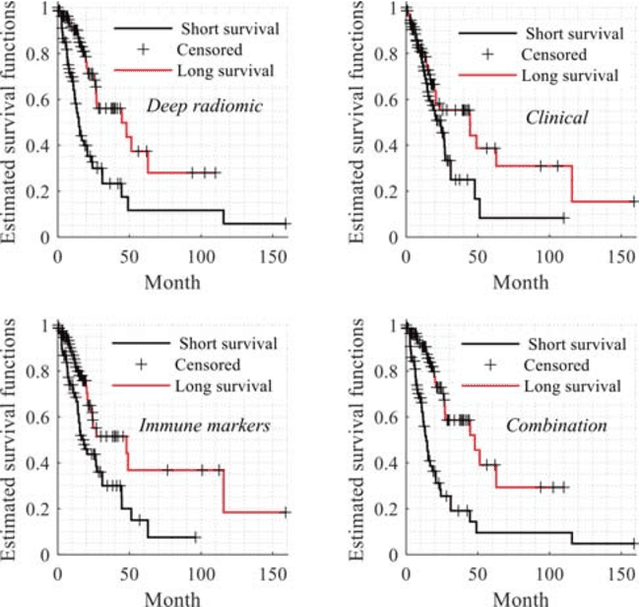
Abstract:Radiomics has shown a capability for different types of cancers such as glioma to predict the clinical outcome. It can have a non-invasive means of evaluating the immunotherapy response prior to treatment. However, the use of deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs)-based radiomics requires large training image sets. To avoid this problem, we investigate a new imaging features that model distribution with a Gaussian mixture model (GMM) of learned 3D CNN features. Using these deep radiomic features (DRFs), we aim to predict the immune marker status (low versus high) and overall survival for glioma patients. We extract the DRFs by aggregating the activation maps of a pre-trained 3D-CNN within labeled tumor regions of MRI scans that corresponded immune markers of 151 patients. Our experiments are performed to assess the relationship between the proposed DRFs, three immune cell markers (Macrophage M1, Neutrophils and T Cells Follicular Helper), and measure their association with overall survival. Using the random forest (RF) model, DRFs was able to predict the immune marker status with area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 78.67, 83.93 and 75.67\% for Macrophage M1, Neutrophils and T Cells Follicular Helper, respectively. Combined the immune markers with DRFs and clinical variables, Kaplan-Meier estimator and Log-rank test achieved the most significant difference between predicted groups of patients (short-term versus long-term survival) with p\,=\,4.31$\times$10$^{-7}$ compared to p\,=\,0.03 for Immune cell markers, p\,=\,0.07 for clinical variables , and p\,=\,1.45$\times$10$^{-5}$ for DRFs. Our findings indicate that the proposed features (DRFs) used in RF models may significantly consider prognosticating patients with brain tumour prior to surgery through regularly acquired imaging data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge