Laboni Akter
Ovarian Cancer Prediction from Ovarian Cysts Based on TVUS Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Aug 30, 2021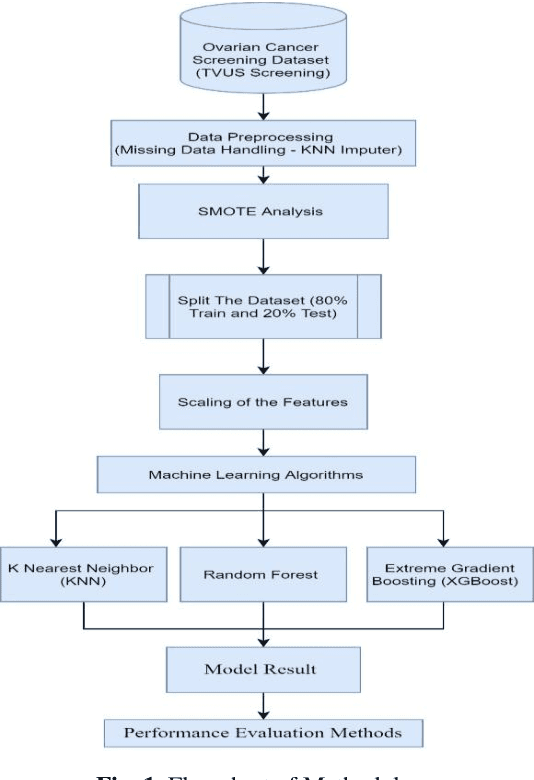
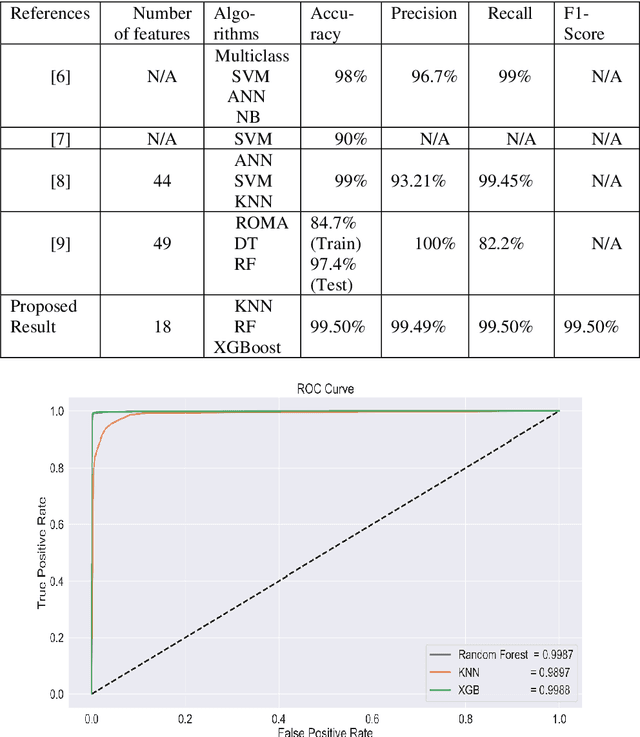
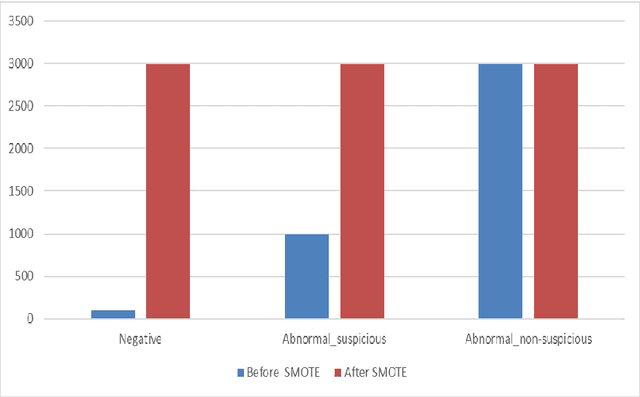
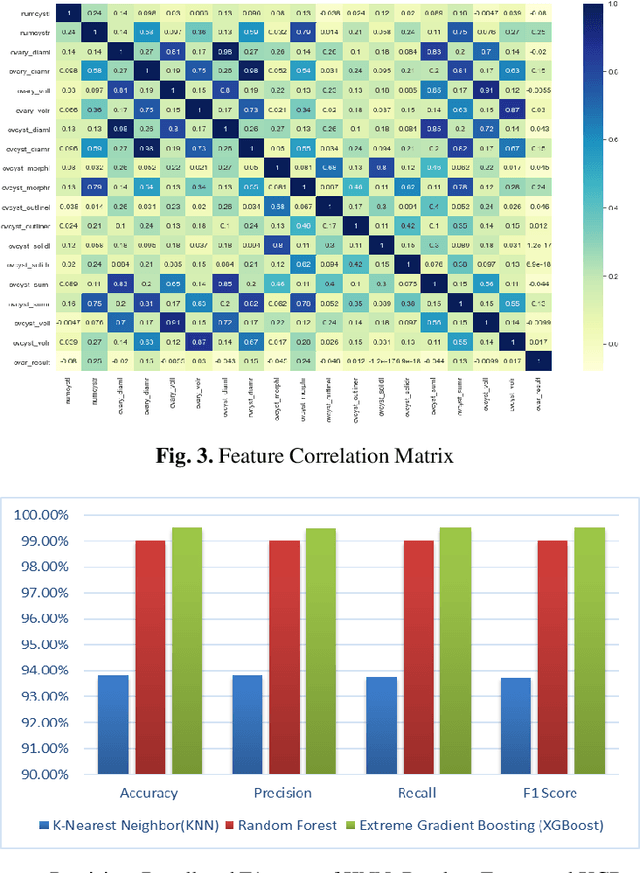
Abstract:Ovarian Cancer (OC) is type of female reproductive malignancy which can be found among young girls and mostly the women in their fertile or reproductive. There are few number of cysts are dangerous and may it cause cancer. So, it is very important to predict and it can be from different types of screening are used for this detection using Transvaginal Ultrasonography (TVUS) screening. In this research, we employed an actual datasets called PLCO with TVUS screening and three machine learning (ML) techniques, respectively Random Forest KNN, and XGBoost within three target variables. We obtained a best performance from this algorithms as far as accuracy, recall, f1 score and precision with the approximations of 99.50%, 99.50%, 99.49% and 99.50% individually. The AUC score of 99.87%, 98.97% and 99.88% are observed in these Random Forest, KNN and XGB algorithms .This approach helps assist physicians and suspects in identifying ovarian risks early on, reducing ovarian malignancy-related complications and deaths.
Development of Risk-Free COVID-19 Screening Algorithm from Routine Blood Test using Ensemble Machine Learning
Aug 12, 2021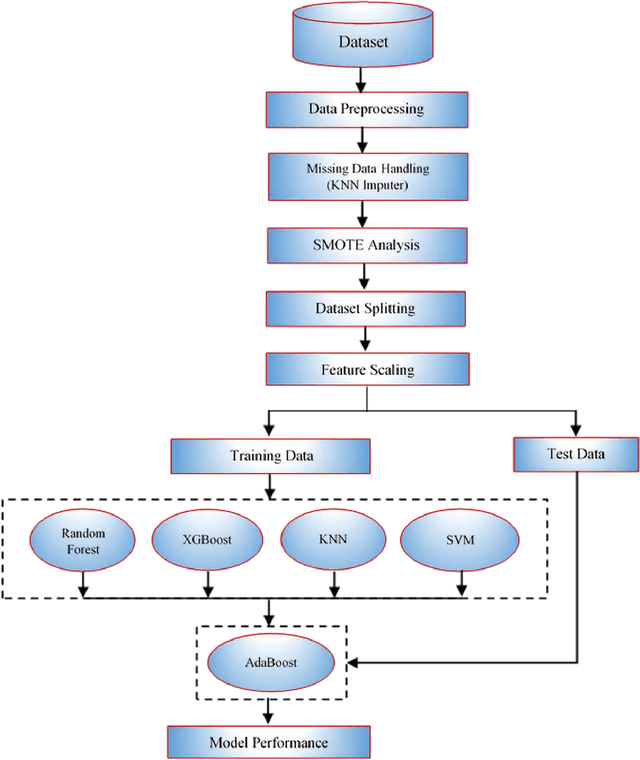
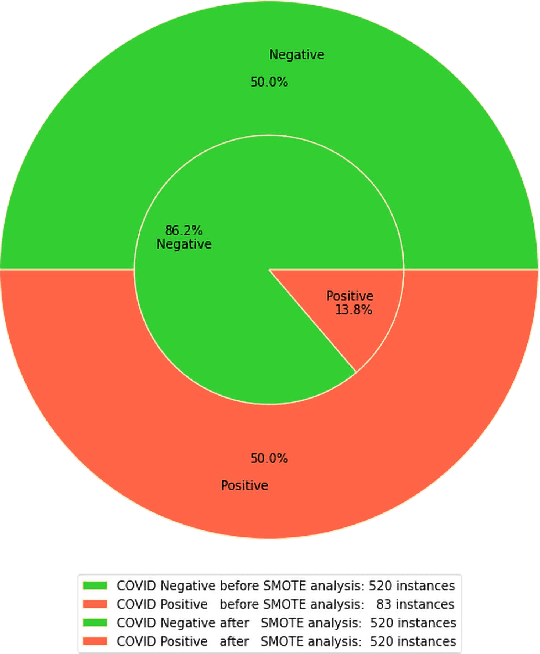
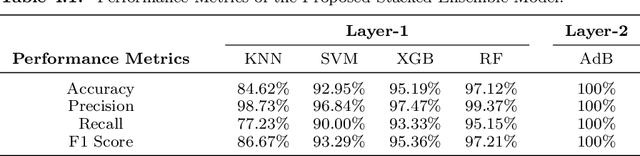
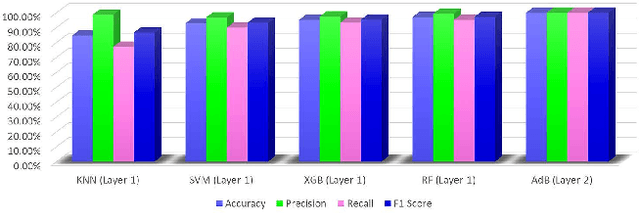
Abstract:The Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RTPCR) test is the silver bullet diagnostic test to discern COVID infection. Rapid antigen detection is a screening test to identify COVID positive patients in little as 15 minutes, but has a lower sensitivity than the PCR tests. Besides having multiple standardized test kits, many people are getting infected & either recovering or dying even before the test due to the shortage and cost of kits, lack of indispensable specialists and labs, time-consuming result compared to bulk population especially in developing and underdeveloped countries. Intrigued by the parametric deviations in immunological & hematological profile of a COVID patient, this research work leveraged the concept of COVID-19 detection by proposing a risk-free and highly accurate Stacked Ensemble Machine Learning model to identify a COVID patient from communally available-widespread-cheap routine blood tests which gives a promising accuracy, precision, recall & F1-score of 100%. Analysis from R-curve also shows the preciseness of the risk-free model to be implemented. The proposed method has the potential for large scale ubiquitous low-cost screening application. This can add an extra layer of protection in keeping the number of infected cases to a minimum and control the pandemic by identifying asymptomatic or pre-symptomatic people early.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge