Kriti Suneja
Plagiarism Detection in Polyphonic Music using Monaural Signal Separation
Feb 27, 2015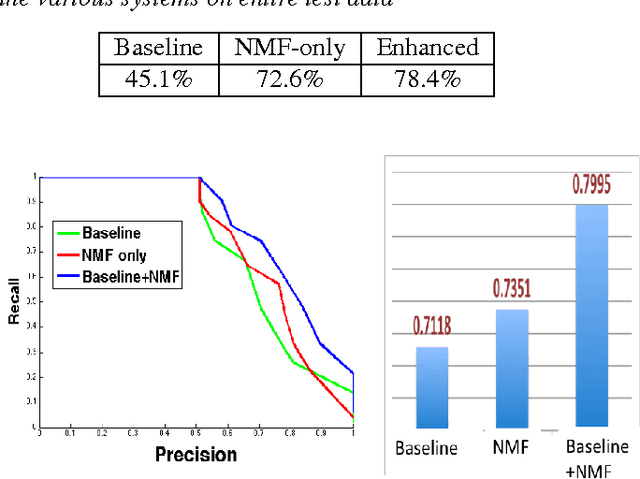
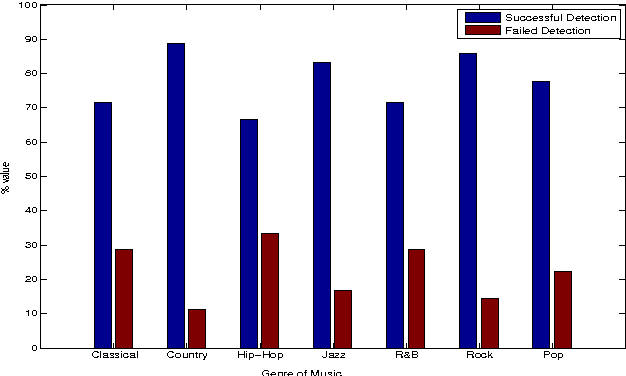
Abstract:Given the large number of new musical tracks released each year, automated approaches to plagiarism detection are essential to help us track potential violations of copyright. Most current approaches to plagiarism detection are based on musical similarity measures, which typically ignore the issue of polyphony in music. We present a novel feature space for audio derived from compositional modelling techniques, commonly used in signal separation, that provides a mechanism to account for polyphony without incurring an inordinate amount of computational overhead. We employ this feature representation in conjunction with traditional audio feature representations in a classification framework which uses an ensemble of distance features to characterize pairs of songs as being plagiarized or not. Our experiments on a database of about 3000 musical track pairs show that the new feature space characterization produces significant improvements over standard baselines.
* Preprint version
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge