Kriti Singh
Active Learning for Neural Machine Translation
Dec 30, 2022Abstract:The machine translation mechanism translates texts automatically between different natural languages, and Neural Machine Translation (NMT) has gained attention for its rational context analysis and fluent translation accuracy. However, processing low-resource languages that lack relevant training attributes like supervised data is a current challenge for Natural Language Processing (NLP). We incorporated a technique known Active Learning with the NMT toolkit Joey NMT to reach sufficient accuracy and robust predictions of low-resource language translation. With active learning, a semi-supervised machine learning strategy, the training algorithm determines which unlabeled data would be the most beneficial for obtaining labels using selected query techniques. We implemented two model-driven acquisition functions for selecting the samples to be validated. This work uses transformer-based NMT systems; baseline model (BM), fully trained model (FTM) , active learning least confidence based model (ALLCM), and active learning margin sampling based model (ALMSM) when translating English to Hindi. The Bilingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU) metric has been used to evaluate system results. The BLEU scores of BM, FTM, ALLCM and ALMSM systems are 16.26, 22.56 , 24.54, and 24.20, respectively. The findings in this paper demonstrate that active learning techniques helps the model to converge early and improve the overall quality of the translation system.
On-Device User Intent Prediction for Context and Sequence Aware Recommendation
Sep 18, 2019
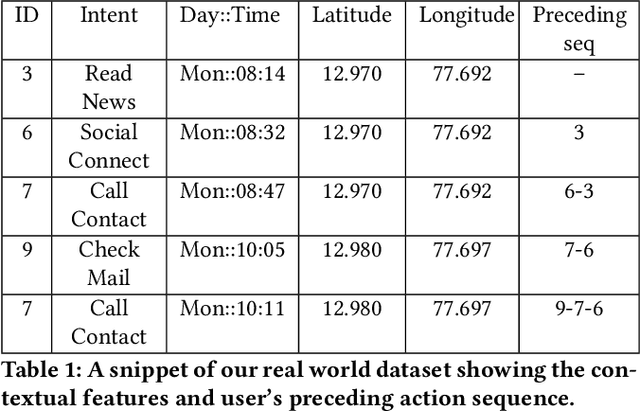
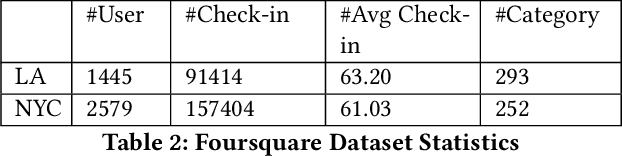
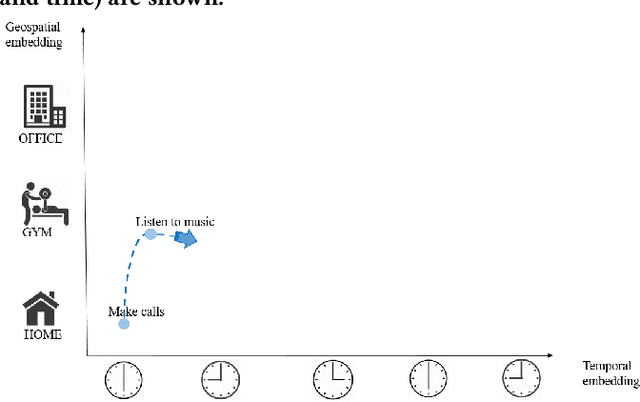
Abstract:The pursuit of improved accuracy in recommender systems has led to the incorporation of user context. Context-aware recommender systems typically handle large amounts of data which must be uploaded and stored on the cloud, putting the user's personal information at risk. While there have been previous studies on privacy-sensitive and context-aware recommender systems, there has not been a full-fledged system deployed in an isolated mobile environment. We propose a secure and efficient on-device mechanism to predict a user's next intention. The knowledge of the user's real-time intention can help recommender systems to provide more relevant recommendations at the right moment. Our proposed algorithm is both context and sequence aware. We embed user intentions as weighted nodes in an n-dimensional vector space where each dimension represents a specific user context factor. Through a neighborhood searching method followed by a sequence matching algorithm, we search for the most relevant node to make the prediction. An evaluation of our methodology was done on a diverse real-world dataset where it was able to address practical scenarios like behavior drifts and sequential patterns efficiently and robustly. Our system also outperformed most of the state-of-the-art methods when evaluated for a similar problem domain on standard datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge