Kristoffer L. Nielbo
Is Sentiment Banana-Shaped? Exploring the Geometry and Portability of Sentiment Concept Vectors
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Use cases of sentiment analysis in the humanities often require contextualized, continuous scores. Concept Vector Projections (CVP) offer a recent solution: by modeling sentiment as a direction in embedding space, they produce continuous, multilingual scores that align closely with human judgments. Yet the method's portability across domains and underlying assumptions remain underexplored. We evaluate CVP across genres, historical periods, languages, and affective dimensions, finding that concept vectors trained on one corpus transfer well to others with minimal performance loss. To understand the patterns of generalization, we further examine the linearity assumption underlying CVP. Our findings suggest that while CVP is a portable approach that effectively captures generalizable patterns, its linearity assumption is approximate, pointing to potential for further development.
Event Flow -- How Events Shaped the Flow of the News, 1950-1995
Sep 17, 2021
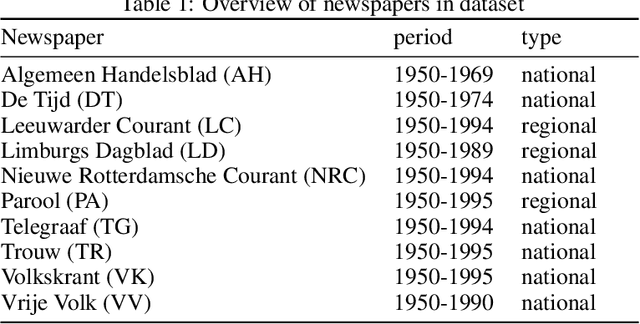


Abstract:This article relies on information-theoretic measures to examine how events impacted the news for the period 1950-1995. Moreover, we present a method for event characterization in (unstructured) textual sources, offering a taxonomy of events based on the different ways they impacted the flow of news information. The results give us a better understanding of the relationship between events and their impact on news sources with varying ideological backgrounds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge